SRC/route_common.c File Reference
#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <assert.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "vpr_utils.h"#include "globals.h"#include "mst.h"#include "route_export.h"#include "route_common.h"#include "route_tree_timing.h"#include "route_timing.h"#include "route_breadth_first.h"#include "route_directed_search.h"#include "place_and_route.h"#include "rr_graph.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | NCHUNK 200 |
Functions | |
| static void | free_trace_data (struct s_trace *tptr) |
| static void | load_route_bb (int bb_factor) |
| static struct s_trace * | alloc_trace_data (void) |
| static void | add_to_heap (struct s_heap *hptr) |
| static struct s_heap * | alloc_heap_data (void) |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | alloc_linked_f_pointer (void) |
| static t_ivec ** | alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally (t_subblock_data subblock_data) |
| static void | adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost (int inode, int add_or_sub, float pres_fac) |
| void | save_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | restore_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | get_serial_num (void) |
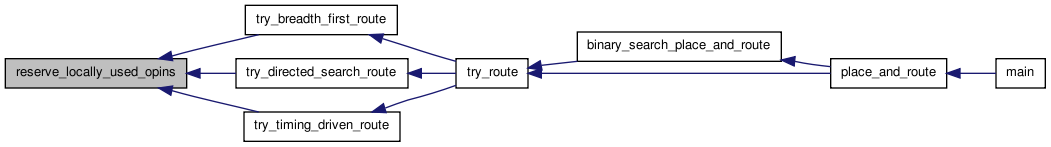
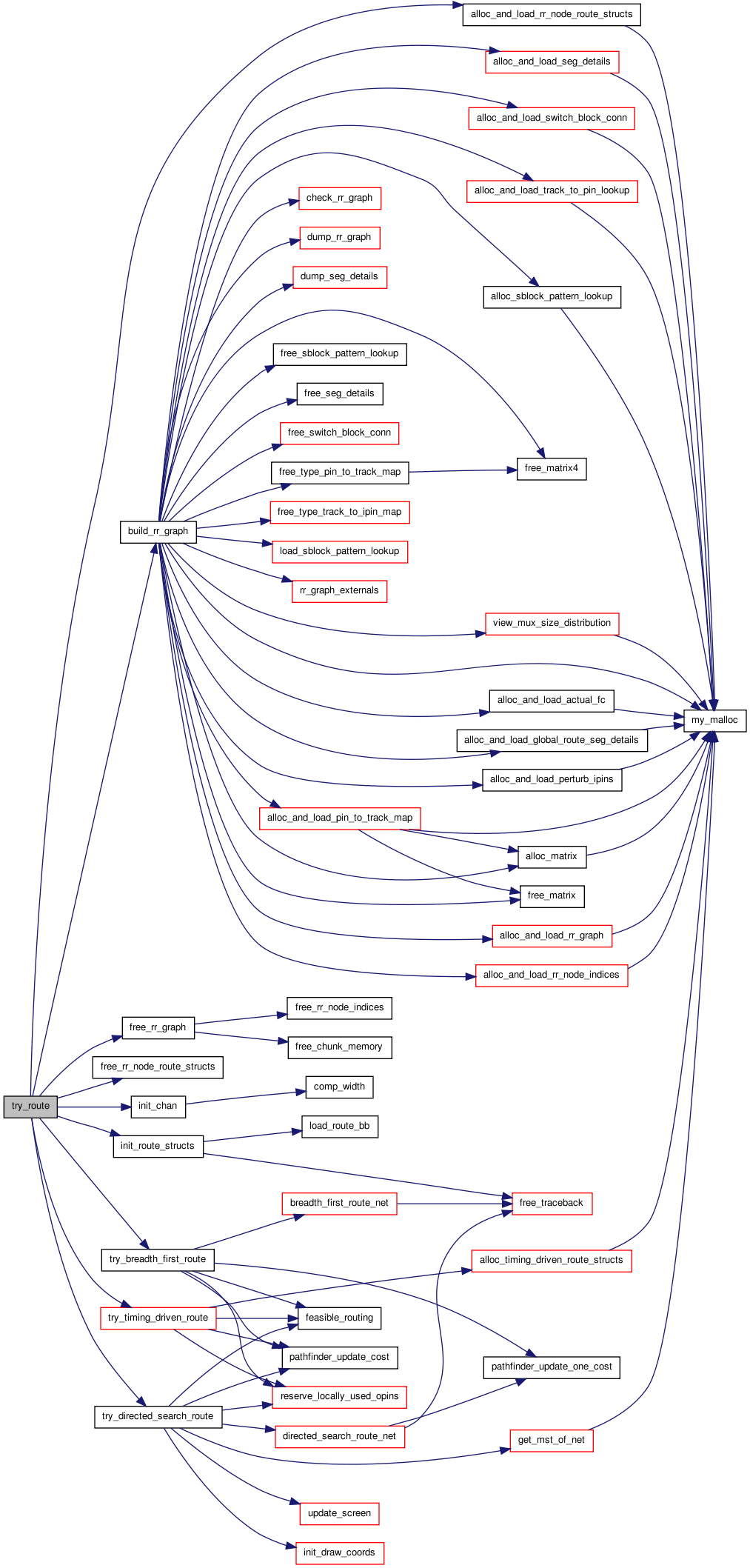
| boolean | try_route (int width_fac, struct s_router_opts router_opts, struct s_det_routing_arch det_routing_arch, t_segment_inf *segment_inf, t_timing_inf timing_inf, float **net_slack, float **net_delay, t_chan_width_dist chan_width_dist, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally, t_mst_edge **mst, boolean *Fc_clipped) |
| boolean | feasible_routing (void) |
| void | pathfinder_update_one_cost (struct s_trace *route_segment_start, int add_or_sub, float pres_fac) |
| void | pathfinder_update_cost (float pres_fac, float acc_fac) |
| void | init_route_structs (int bb_factor) |
| struct s_trace * | update_traceback (struct s_heap *hptr, int inet) |
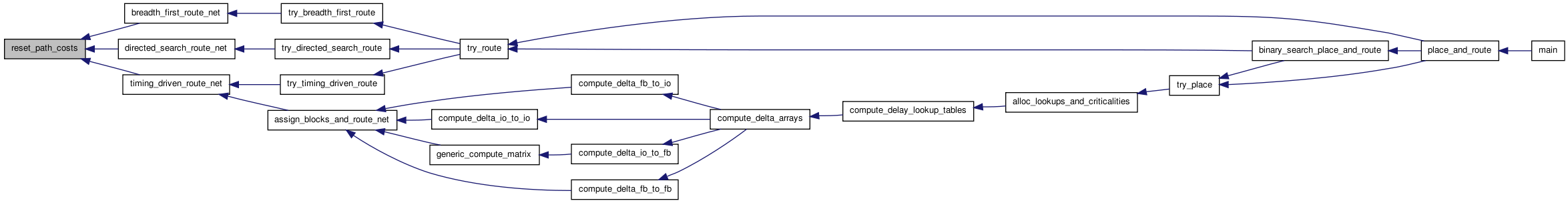
| void | reset_path_costs (void) |
| float | get_rr_cong_cost (int inode) |
| void | mark_ends (int inet) |
| void | node_to_heap (int inode, float cost, int prev_node, int prev_edge, float backward_path_cost, float R_upstream) |
| void | free_traceback (int inet) |
| t_ivec ** | alloc_route_structs (t_subblock_data subblock_data) |
| struct s_trace ** | alloc_saved_routing (t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec ***saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr) |
| void | free_trace_structs (void) |
| void | free_route_structs (t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | free_saved_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs (void) |
| void | free_rr_node_route_structs (void) |
| void | add_to_mod_list (float *fptr) |
| boolean | is_empty_heap (void) |
| struct s_heap * | get_heap_head (void) |
| void | empty_heap (void) |
| void | free_heap_data (struct s_heap *hptr) |
| void | invalidate_heap_entries (int sink_node, int ipin_node) |
| void | print_route (char *route_file) |
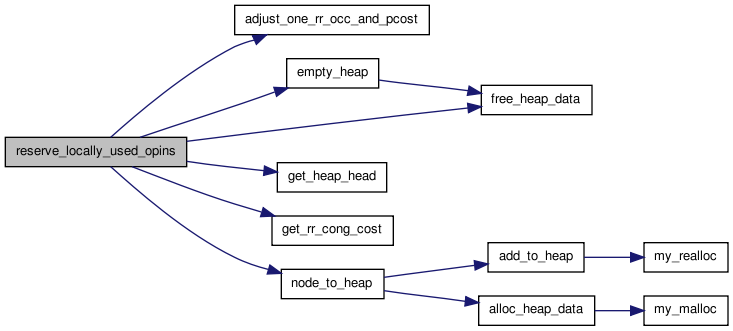
| void | reserve_locally_used_opins (float pres_fac, boolean rip_up_local_opins, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally) |
Variables | |
| t_rr_node_route_inf * | rr_node_route_inf = NULL |
| struct s_bb * | route_bb = NULL |
| static struct s_heap ** | heap |
| static int | heap_size |
| static int | heap_tail |
| static struct s_heap * | heap_free_head = NULL |
| static struct s_trace * | trace_free_head = NULL |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | rr_modified_head = NULL |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | linked_f_pointer_free_head = NULL |
Define Documentation
| #define NCHUNK 200 |
Definition at line 1138 of file route_common.c.
Function Documentation
| static void add_to_heap | ( | struct s_heap * | hptr | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 1038 of file route_common.c.
01039 { 01040 01041 /* Adds an item to the heap, expanding the heap if necessary. */ 01042 01043 int ito, ifrom; 01044 struct s_heap *temp_ptr; 01045 01046 if(heap_tail > heap_size) 01047 { /* Heap is full */ 01048 heap_size *= 2; 01049 heap = my_realloc((void *)(heap + 1), heap_size * 01050 sizeof(struct s_heap *)); 01051 heap--; /* heap goes from [1..heap_size] */ 01052 } 01053 01054 heap[heap_tail] = hptr; 01055 ifrom = heap_tail; 01056 ito = ifrom / 2; 01057 heap_tail++; 01058 01059 while((ito >= 1) && (heap[ifrom]->cost < heap[ito]->cost)) 01060 { 01061 temp_ptr = heap[ito]; 01062 heap[ito] = heap[ifrom]; 01063 heap[ifrom] = temp_ptr; 01064 ifrom = ito; 01065 ito = ifrom / 2; 01066 } 01067 }
| void add_to_mod_list | ( | float * | fptr | ) |
Definition at line 1018 of file route_common.c.
01019 { 01020 01021 /* This routine adds the floating point pointer (fptr) into a * 01022 * linked list that indicates all the pathcosts that have been * 01023 * modified thus far. */ 01024 01025 struct s_linked_f_pointer *mod_ptr; 01026 01027 mod_ptr = alloc_linked_f_pointer(); 01028 01029 /* Add this element to the start of the modified list. */ 01030 01031 mod_ptr->next = rr_modified_head; 01032 mod_ptr->fptr = fptr; 01033 rr_modified_head = mod_ptr; 01034 }

| static void adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost | ( | int | inode, | |
| int | add_or_sub, | |||
| float | pres_fac | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 1499 of file route_common.c.
01502 { 01503 01504 /* Increments or decrements (depending on add_or_sub) the occupancy of * 01505 * one rr_node, and adjusts the present cost of that node appropriately. */ 01506 01507 int occ, capacity; 01508 01509 occ = rr_node[inode].occ + add_or_sub; 01510 capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity; 01511 rr_node[inode].occ = occ; 01512 01513 if(occ < capacity) 01514 { 01515 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.; 01516 } 01517 else 01518 { 01519 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) * 01520 pres_fac; 01521 } 01522 }
| static t_ivec ** alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally | ( | t_subblock_data | subblock_data | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 781 of file route_common.c.
00782 { 00783 00784 /* Allocates and loads the data needed to make the router reserve some FB * 00785 * output pins for connections made locally within a FB (if the netlist * 00786 * specifies that this is necessary). */ 00787 00788 t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally; 00789 int *num_subblocks_per_block; 00790 t_subblock **subblock_inf; 00791 int iblk, isub, clb_pin, opin, iclass, num_local_opins; 00792 int class_low, class_high; 00793 t_type_ptr type; 00794 00795 fb_opins_used_locally = 00796 (t_ivec **) my_malloc(num_blocks * sizeof(t_ivec *)); 00797 num_subblocks_per_block = subblock_data.num_subblocks_per_block; 00798 subblock_inf = subblock_data.subblock_inf; 00799 00800 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 00801 { 00802 type = block[iblk].type; 00803 get_class_range_for_block(iblk, &class_low, &class_high); 00804 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk] = 00805 (t_ivec *) my_malloc(type->num_class * sizeof(t_ivec)); 00806 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 00807 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem = 0; 00808 00809 for(isub = 0; isub < num_subblocks_per_block[iblk]; isub++) 00810 { 00811 for(opin = 0; 00812 opin < block[iblk].type->max_subblock_outputs; opin++) 00813 { 00814 clb_pin = subblock_inf[iblk][isub].outputs[opin]; 00815 00816 /* Subblock output used only locally, but must connect to a FB OPIN? */ 00817 if(clb_pin != OPEN 00818 && block[iblk].nets[clb_pin] == OPEN) 00819 { 00820 iclass = type->pin_class[clb_pin]; 00821 /* Check to make sure class is in same range as that assigned to block */ 00822 assert(iclass >= class_low 00823 && iclass <= class_high); 00824 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 00825 nelem++; 00826 } 00827 } 00828 } 00829 00830 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 00831 { 00832 num_local_opins = 00833 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 00834 00835 if(num_local_opins == 0) 00836 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list = NULL; 00837 else 00838 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list = 00839 (int *)my_malloc(num_local_opins * sizeof(int)); 00840 } 00841 } 00842 00843 return (fb_opins_used_locally); 00844 }

| void alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 909 of file route_common.c.
00910 { 00911 00912 /* Allocates some extra information about each rr_node that is used only * 00913 * during routing. */ 00914 00915 int inode; 00916 00917 if(rr_node_route_inf != NULL) 00918 { 00919 printf("Error in alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs: \n" 00920 "old rr_node_route_inf array exists.\n"); 00921 exit(1); 00922 } 00923 00924 rr_node_route_inf = my_malloc(num_rr_nodes * sizeof(t_rr_node_route_inf)); 00925 00926 for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++) 00927 { 00928 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = NO_PREVIOUS; 00929 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge = NO_PREVIOUS; 00930 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.; 00931 rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost = 1.; 00932 rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = HUGE_FLOAT; 00933 rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag = 0; 00934 } 00935 }


| static struct s_heap * alloc_heap_data | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
Definition at line 1142 of file route_common.c.
01143 { 01144 01145 int i; 01146 struct s_heap *temp_ptr; 01147 01148 if(heap_free_head == NULL) 01149 { /* No elements on the free list */ 01150 heap_free_head = (struct s_heap *)my_malloc(NCHUNK * 01151 sizeof(struct 01152 s_heap)); 01153 01154 /* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer * 01155 * somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory * 01156 * for post-routing stages, look into it. */ 01157 01158 for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++) 01159 (heap_free_head + i)->u.next = heap_free_head + i + 1; 01160 (heap_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->u.next = NULL; 01161 } 01162 01163 temp_ptr = heap_free_head; 01164 heap_free_head = heap_free_head->u.next; 01165 #ifdef DEBUG 01166 num_heap_allocated++; 01167 #endif 01168 return (temp_ptr); 01169 }

| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * alloc_linked_f_pointer | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
Definition at line 1249 of file route_common.c.
01250 { 01251 01252 /* This routine returns a linked list element with a float pointer as * 01253 * the node data. */ 01254 01255 int i; 01256 struct s_linked_f_pointer *temp_ptr; 01257 01258 if(linked_f_pointer_free_head == NULL) 01259 { 01260 /* No elements on the free list */ 01261 linked_f_pointer_free_head = (struct s_linked_f_pointer *) 01262 my_malloc(NCHUNK * sizeof(struct s_linked_f_pointer)); 01263 01264 /* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer * 01265 * somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory * 01266 * for post-routing stages, look into it. */ 01267 01268 for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++) 01269 { 01270 (linked_f_pointer_free_head + i)->next = 01271 linked_f_pointer_free_head + i + 1; 01272 } 01273 (linked_f_pointer_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->next = NULL; 01274 } 01275 01276 temp_ptr = linked_f_pointer_free_head; 01277 linked_f_pointer_free_head = linked_f_pointer_free_head->next; 01278 01279 #ifdef DEBUG 01280 num_linked_f_pointer_allocated++; 01281 #endif 01282 01283 return (temp_ptr); 01284 }

| t_ivec** alloc_route_structs | ( | t_subblock_data | subblock_data | ) |
Definition at line 703 of file route_common.c.
00704 { 00705 00706 /* Allocates the data structures needed for routing. */ 00707 00708 t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally; 00709 00710 trace_head = (struct s_trace **)my_calloc(num_nets, 00711 sizeof(struct s_trace *)); 00712 trace_tail = (struct s_trace **)my_malloc(num_nets * 00713 sizeof(struct s_trace *)); 00714 00715 heap_size = nx * ny; 00716 heap = (struct s_heap **)my_malloc(heap_size * sizeof(struct s_heap *)); 00717 heap--; /* heap stores from [1..heap_size] */ 00718 heap_tail = 1; 00719 00720 route_bb = (struct s_bb *)my_malloc(num_nets * sizeof(struct s_bb)); 00721 00722 fb_opins_used_locally = 00723 alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally(subblock_data); 00724 00725 return (fb_opins_used_locally); 00726 }

| struct s_trace** alloc_saved_routing | ( | t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally, | |
| t_ivec *** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr | |||
| ) | [read] |
Definition at line 730 of file route_common.c.
00732 { 00733 00734 /* Allocates data structures into which the key routing data can be saved, * 00735 * allowing the routing to be recovered later (e.g. after a another routing * 00736 * is attempted). */ 00737 00738 struct s_trace **best_routing; 00739 t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally; 00740 int iblk, iclass, num_local_opins; 00741 t_type_ptr type; 00742 00743 best_routing = (struct s_trace **)my_calloc(num_nets, 00744 sizeof(struct s_trace *)); 00745 00746 saved_clb_opins_used_locally = 00747 (t_ivec **) my_malloc(num_blocks * sizeof(t_ivec *)); 00748 00749 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 00750 { 00751 type = block[iblk].type; 00752 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk] = 00753 (t_ivec *) my_malloc(type->num_class * sizeof(t_ivec)); 00754 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 00755 { 00756 num_local_opins = 00757 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 00758 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem = 00759 num_local_opins; 00760 00761 if(num_local_opins == 0) 00762 { 00763 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list = 00764 NULL; 00765 } 00766 else 00767 { 00768 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list = 00769 (int *)my_malloc(num_local_opins * 00770 sizeof(int)); 00771 } 00772 } 00773 } 00774 00775 *saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr = saved_clb_opins_used_locally; 00776 return (best_routing); 00777 }

| static struct s_trace * alloc_trace_data | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
Definition at line 1205 of file route_common.c.
01206 { 01207 01208 int i; 01209 struct s_trace *temp_ptr; 01210 01211 if(trace_free_head == NULL) 01212 { /* No elements on the free list */ 01213 trace_free_head = (struct s_trace *)my_malloc(NCHUNK * 01214 sizeof(struct 01215 s_trace)); 01216 01217 /* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer * 01218 * somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory * 01219 * for post-routing stages, look into it. */ 01220 01221 for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++) 01222 (trace_free_head + i)->next = trace_free_head + i + 1; 01223 (trace_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->next = NULL; 01224 } 01225 temp_ptr = trace_free_head; 01226 trace_free_head = trace_free_head->next; 01227 #ifdef DEBUG 01228 num_trace_allocated++; 01229 #endif 01230 return (temp_ptr); 01231 }

| void empty_heap | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1127 of file route_common.c.
01128 { 01129 01130 int i; 01131 01132 for(i = 1; i < heap_tail; i++) 01133 free_heap_data(heap[i]); 01134 01135 heap_tail = 1; 01136 }

| boolean feasible_routing | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 337 of file route_common.c.
00338 { 00339 00340 /* This routine checks to see if this is a resource-feasible routing. * 00341 * That is, are all rr_node capacity limitations respected? It assumes * 00342 * that the occupancy arrays are up to date when it is called. */ 00343 00344 int inode; 00345 00346 for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++) 00347 if(rr_node[inode].occ > rr_node[inode].capacity) 00348 return (FALSE); 00349 00350 return (TRUE); 00351 }
| void free_heap_data | ( | struct s_heap * | hptr | ) |
Definition at line 1173 of file route_common.c.
01174 { 01175 01176 hptr->u.next = heap_free_head; 01177 heap_free_head = hptr; 01178 #ifdef DEBUG 01179 num_heap_allocated--; 01180 #endif 01181 }
| void free_route_structs | ( | t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally | ) |
Definition at line 864 of file route_common.c.
00865 { 00866 00867 /* Frees the temporary storage needed only during the routing. The * 00868 * final routing result is not freed. */ 00869 int i; 00870 00871 free(heap + 1); 00872 free(route_bb); 00873 00874 heap = NULL; /* Defensive coding: crash hard if I use these. */ 00875 route_bb = NULL; 00876 00877 for(i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++) 00878 { 00879 free_ivec_vector(fb_opins_used_locally[i], 0, 00880 block[i].type->num_class - 1); 00881 } 00882 free(fb_opins_used_locally); 00883 00884 /* NB: Should use my chunk_malloc for tptr, hptr, and mod_ptr structures. * 00885 * I could free everything except the tptrs at the end then. */ 00886 00887 }

| void free_rr_node_route_structs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 939 of file route_common.c.
00940 { 00941 00942 /* Frees the extra information about each rr_node that is needed only * 00943 * during routing. */ 00944 00945 free(rr_node_route_inf); 00946 rr_node_route_inf = NULL; /* Mark as free */ 00947 }

Definition at line 891 of file route_common.c.
00893 { 00894 00895 /* Frees the data structures needed to save a routing. */ 00896 int i; 00897 00898 free(best_routing); 00899 for(i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++) 00900 { 00901 free_ivec_vector(saved_clb_opins_used_locally[i], 0, 00902 block[i].type->num_class - 1); 00903 } 00904 free(saved_clb_opins_used_locally); 00905 }

| static void free_trace_data | ( | struct s_trace * | tptr | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 1235 of file route_common.c.
01236 { 01237 01238 /* Puts the traceback structure pointed to by tptr on the free list. */ 01239 01240 tptr->next = trace_free_head; 01241 trace_free_head = tptr; 01242 #ifdef DEBUG 01243 num_trace_allocated--; 01244 #endif 01245 }
| void free_trace_structs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 847 of file route_common.c.
00848 { 00849 /*the trace lists are only freed after use by the timing-driven placer */ 00850 /*Do not free them after use by the router, since stats, and draw */ 00851 /*routines use the trace values */ 00852 int i; 00853 00854 for(i = 0; i < num_nets; i++) 00855 free_traceback(i); 00856 00857 free(trace_head); 00858 free(trace_tail); 00859 trace_head = NULL; 00860 trace_tail = NULL; 00861 }


| void free_traceback | ( | int | inet | ) |
Definition at line 680 of file route_common.c.
00681 { 00682 00683 /* Puts the entire traceback (old routing) for this net on the free list * 00684 * and sets the trace_head pointers etc. for the net to NULL. */ 00685 00686 struct s_trace *tptr, *tempptr; 00687 00688 tptr = trace_head[inet]; 00689 00690 while(tptr != NULL) 00691 { 00692 tempptr = tptr->next; 00693 free_trace_data(tptr); 00694 tptr = tempptr; 00695 } 00696 00697 trace_head[inet] = NULL; 00698 trace_tail[inet] = NULL; 00699 }

| struct s_heap* get_heap_head | ( | void | ) | [read] |
Definition at line 1077 of file route_common.c.
01078 { 01079 01080 /* Returns a pointer to the smallest element on the heap, or NULL if the * 01081 * heap is empty. Invalid (index == OPEN) entries on the heap are never * 01082 * returned -- they are just skipped over. */ 01083 01084 int ito, ifrom; 01085 struct s_heap *heap_head, *temp_ptr; 01086 01087 do 01088 { 01089 if(heap_tail == 1) 01090 { /* Empty heap. */ 01091 printf("Empty heap occurred in get_heap_head.\n"); 01092 printf 01093 ("Some blocks are impossible to connect in this architecture.\n"); 01094 return (NULL); 01095 } 01096 01097 heap_head = heap[1]; /* Smallest element. */ 01098 01099 /* Now fix up the heap */ 01100 01101 heap_tail--; 01102 heap[1] = heap[heap_tail]; 01103 ifrom = 1; 01104 ito = 2 * ifrom; 01105 01106 while(ito < heap_tail) 01107 { 01108 if(heap[ito + 1]->cost < heap[ito]->cost) 01109 ito++; 01110 if(heap[ito]->cost > heap[ifrom]->cost) 01111 break; 01112 temp_ptr = heap[ito]; 01113 heap[ito] = heap[ifrom]; 01114 heap[ifrom] = temp_ptr; 01115 ifrom = ito; 01116 ito = 2 * ifrom; 01117 } 01118 01119 } 01120 while(heap_head->index == OPEN); /* Get another one if invalid entry. */ 01121 01122 return (heap_head); 01123 }
| float get_rr_cong_cost | ( | int | inode | ) |
Definition at line 611 of file route_common.c.
00612 { 00613 00614 /* Returns the *congestion* cost of using this rr_node. */ 00615 00616 short cost_index; 00617 float cost; 00618 00619 cost_index = rr_node[inode].cost_index; 00620 cost = rr_indexed_data[cost_index].base_cost * 00621 rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost * 00622 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost; 00623 return (cost); 00624 }
| void get_serial_num | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 210 of file route_common.c.
00211 { 00212 00213 /* This routine finds a "magic cookie" for the routing and prints it. * 00214 * Use this number as a routing serial number to ensure that programming * 00215 * changes do not break the router. */ 00216 00217 int inet, serial_num, inode; 00218 struct s_trace *tptr; 00219 00220 serial_num = 0; 00221 00222 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00223 { 00224 00225 /* Global nets will have null trace_heads (never routed) so they * 00226 * are not included in the serial number calculation. */ 00227 00228 tptr = trace_head[inet]; 00229 while(tptr != NULL) 00230 { 00231 inode = tptr->index; 00232 serial_num += 00233 (inet + 1) * (rr_node[inode].xlow * (nx + 1) - 00234 rr_node[inode].yhigh); 00235 00236 serial_num -= rr_node[inode].ptc_num * (inet + 1) * 10; 00237 00238 serial_num -= rr_node[inode].type * (inet + 1) * 100; 00239 serial_num %= 2000000000; /* Prevent overflow */ 00240 tptr = tptr->next; 00241 } 00242 } 00243 printf("Serial number (magic cookie) for the routing is: %d\n", 00244 serial_num); 00245 }

| void init_route_structs | ( | int | bb_factor | ) |
Definition at line 451 of file route_common.c.
00452 { 00453 00454 /* Call this before you route any nets. It frees any old traceback and * 00455 * sets the list of rr_nodes touched to empty. */ 00456 00457 int i; 00458 00459 for(i = 0; i < num_nets; i++) 00460 free_traceback(i); 00461 00462 load_route_bb(bb_factor); 00463 00464 /* Check that things that should have been emptied after the last routing * 00465 * really were. */ 00466 00467 if(rr_modified_head != NULL) 00468 { 00469 printf 00470 ("Error in init_route_structs. List of modified rr nodes is \n" 00471 "not empty.\n"); 00472 exit(1); 00473 } 00474 00475 if(heap_tail != 1) 00476 { 00477 printf("Error in init_route_structs. Heap is not empty.\n"); 00478 exit(1); 00479 } 00480 }


| void invalidate_heap_entries | ( | int | sink_node, | |
| int | ipin_node | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 1185 of file route_common.c.
01187 { 01188 01189 /* Marks all the heap entries consisting of sink_node, where it was reached * 01190 * via ipin_node, as invalid (OPEN). Used only by the breadth_first router * 01191 * and even then only in rare circumstances. */ 01192 01193 int i; 01194 01195 for(i = 1; i < heap_tail; i++) 01196 { 01197 if(heap[i]->index == sink_node 01198 && heap[i]->u.prev_node == ipin_node) 01199 heap[i]->index = OPEN; /* Invalid. */ 01200 } 01201 }

| boolean is_empty_heap | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1071 of file route_common.c.
01072 { 01073 return (heap_tail == 1); 01074 }

| static void load_route_bb | ( | int | bb_factor | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 951 of file route_common.c.
00952 { 00953 00954 /* This routine loads the bounding box arrays used to limit the space * 00955 * searched by the maze router when routing each net. The search is * 00956 * limited to channels contained with the net bounding box expanded * 00957 * by bb_factor channels on each side. For example, if bb_factor is * 00958 * 0, the maze router must route each net within its bounding box. * 00959 * If bb_factor = nx, the maze router will search every channel in * 00960 * the FPGA if necessary. The bounding boxes returned by this routine * 00961 * are different from the ones used by the placer in that they are * 00962 * clipped to lie within (0,0) and (nx+1,ny+1) rather than (1,1) and * 00963 * (nx,ny). */ 00964 00965 int k, xmax, ymax, xmin, ymin, x, y, inet; 00966 00967 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00968 { 00969 x = block[net[inet].node_block[0]].x; 00970 y = block[net[inet].node_block[0]].y; 00971 00972 xmin = x; 00973 ymin = y; 00974 xmax = x; 00975 ymax = y; 00976 00977 for(k = 1; k <= net[inet].num_sinks; k++) 00978 { 00979 x = block[net[inet].node_block[k]].x; 00980 y = block[net[inet].node_block[k]].y; 00981 00982 if(x < xmin) 00983 { 00984 xmin = x; 00985 } 00986 else if(x > xmax) 00987 { 00988 xmax = x; 00989 } 00990 00991 if(y < ymin) 00992 { 00993 ymin = y; 00994 } 00995 else if(y > ymax) 00996 { 00997 ymax = y; 00998 } 00999 } 01000 01001 /* Want the channels on all 4 sides to be usuable, even if bb_factor = 0. */ 01002 01003 xmin -= 1; 01004 ymin -= 1; 01005 01006 /* Expand the net bounding box by bb_factor, then clip to the physical * 01007 * chip area. */ 01008 01009 route_bb[inet].xmin = max(xmin - bb_factor, 0); 01010 route_bb[inet].xmax = min(xmax + bb_factor, nx + 1); 01011 route_bb[inet].ymin = max(ymin - bb_factor, 0); 01012 route_bb[inet].ymax = min(ymax + bb_factor, ny + 1); 01013 } 01014 }

| void mark_ends | ( | int | inet | ) |
Definition at line 628 of file route_common.c.
00629 { 00630 00631 /* Mark all the SINKs of this net as targets by setting their target flags * 00632 * to the number of times the net must connect to each SINK. Note that * 00633 * this number can occassionally be greater than 1 -- think of connecting * 00634 * the same net to two inputs of an and-gate (and-gate inputs are logically * 00635 * equivalent, so both will connect to the same SINK). */ 00636 00637 int ipin, inode; 00638 00639 for(ipin = 1; ipin <= net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) 00640 { 00641 inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][ipin]; 00642 rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag++; 00643 } 00644 }
| void node_to_heap | ( | int | inode, | |
| float | cost, | |||
| int | prev_node, | |||
| int | prev_edge, | |||
| float | backward_path_cost, | |||
| float | R_upstream | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 648 of file route_common.c.
00654 { 00655 00656 /* Puts an rr_node on the heap, if the new cost given is lower than the * 00657 * current path_cost to this channel segment. The index of its predecessor * 00658 * is stored to make traceback easy. The index of the edge used to get * 00659 * from its predecessor to it is also stored to make timing analysis, etc. * 00660 * easy. The backward_path_cost and R_upstream values are used only by the * 00661 * timing-driven router -- the breadth-first router ignores them. */ 00662 00663 struct s_heap *hptr; 00664 00665 if(cost >= rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost) 00666 return; 00667 00668 hptr = alloc_heap_data(); 00669 hptr->index = inode; 00670 hptr->cost = cost; 00671 hptr->u.prev_node = prev_node; 00672 hptr->prev_edge = prev_edge; 00673 hptr->backward_path_cost = backward_path_cost; 00674 hptr->R_upstream = R_upstream; 00675 add_to_heap(hptr); 00676 }

| void pathfinder_update_cost | ( | float | pres_fac, | |
| float | acc_fac | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 412 of file route_common.c.
00414 { 00415 00416 /* This routine recomputes the pres_cost and acc_cost of each routing * 00417 * resource for the pathfinder algorithm after all nets have been routed. * 00418 * It updates the accumulated cost to by adding in the number of extra * 00419 * signals sharing a resource right now (i.e. after each complete iteration) * 00420 * times acc_fac. It also updates pres_cost, since pres_fac may have * 00421 * changed. THIS ROUTINE ASSUMES THE OCCUPANCY VALUES IN RR_NODE ARE UP TO * 00422 * DATE. */ 00423 00424 int inode, occ, capacity; 00425 00426 for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++) 00427 { 00428 occ = rr_node[inode].occ; 00429 capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity; 00430 00431 if(occ > capacity) 00432 { 00433 rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost += 00434 (occ - capacity) * acc_fac; 00435 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 00436 1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) * pres_fac; 00437 } 00438 00439 /* If occ == capacity, we don't need to increase acc_cost, but a change * 00440 * in pres_fac could have made it necessary to recompute the cost anyway. */ 00441 00442 else if(occ == capacity) 00443 { 00444 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1. + pres_fac; 00445 } 00446 } 00447 }
| void pathfinder_update_one_cost | ( | struct s_trace * | route_segment_start, | |
| int | add_or_sub, | |||
| float | pres_fac | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 355 of file route_common.c.
00358 { 00359 00360 /* This routine updates the occupancy and pres_cost of the rr_nodes that are * 00361 * affected by the portion of the routing of one net that starts at * 00362 * route_segment_start. If route_segment_start is trace_head[inet], the * 00363 * cost of all the nodes in the routing of net inet are updated. If * 00364 * add_or_sub is -1 the net (or net portion) is ripped up, if it is 1 the * 00365 * net is added to the routing. The size of pres_fac determines how severly * 00366 * oversubscribed rr_nodes are penalized. */ 00367 00368 struct s_trace *tptr; 00369 int inode, occ, capacity; 00370 00371 tptr = route_segment_start; 00372 if(tptr == NULL) /* No routing yet. */ 00373 return; 00374 00375 for(;;) 00376 { 00377 inode = tptr->index; 00378 00379 occ = rr_node[inode].occ + add_or_sub; 00380 capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity; 00381 00382 rr_node[inode].occ = occ; 00383 00384 /* pres_cost is Pn in the Pathfinder paper. I set my pres_cost according to * 00385 * the overuse that would result from having ONE MORE net use this routing * 00386 * node. */ 00387 00388 if(occ < capacity) 00389 { 00390 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.; 00391 } 00392 else 00393 { 00394 rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 00395 1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) * pres_fac; 00396 } 00397 00398 if(rr_node[inode].type == SINK) 00399 { 00400 tptr = tptr->next; /* Skip next segment. */ 00401 if(tptr == NULL) 00402 break; 00403 } 00404 00405 tptr = tptr->next; 00406 00407 } /* End while loop -- did an entire traceback. */ 00408 }
| void print_route | ( | char * | route_file | ) |
Definition at line 1288 of file route_common.c.
01289 { 01290 01291 /* Prints out the routing to file route_file. */ 01292 01293 int inet, inode, ipin, bnum, ilow, jlow, node_block_pin, iclass; 01294 t_rr_type rr_type; 01295 struct s_trace *tptr; 01296 char *name_type[] = 01297 { "SOURCE", "SINK", "IPIN", "OPIN", "CHANX", "CHANY" }; 01298 FILE *fp; 01299 01300 fp = my_fopen(route_file, "w"); 01301 01302 fprintf(fp, "Array size: %d x %d logic blocks.\n", nx, ny); 01303 fprintf(fp, "\nRouting:"); 01304 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 01305 { 01306 if(net[inet].is_global == FALSE) 01307 { 01308 fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s)\n\n", inet, net[inet].name); 01309 tptr = trace_head[inet]; 01310 01311 while(tptr != NULL) 01312 { 01313 inode = tptr->index; 01314 rr_type = rr_node[inode].type; 01315 ilow = rr_node[inode].xlow; 01316 jlow = rr_node[inode].ylow; 01317 01318 fprintf(fp, "%6s (%d,%d) ", name_type[rr_type], 01319 ilow, jlow); 01320 01321 if((ilow != rr_node[inode].xhigh) || (jlow != 01322 rr_node 01323 [inode]. 01324 yhigh)) 01325 fprintf(fp, "to (%d,%d) ", 01326 rr_node[inode].xhigh, 01327 rr_node[inode].yhigh); 01328 01329 switch (rr_type) 01330 { 01331 01332 case IPIN: 01333 case OPIN: 01334 if(grid[ilow][jlow].type == IO_TYPE) 01335 { 01336 fprintf(fp, " Pad: "); 01337 } 01338 else 01339 { /* IO Pad. */ 01340 fprintf(fp, " Pin: "); 01341 } 01342 break; 01343 01344 case CHANX: 01345 case CHANY: 01346 fprintf(fp, " Track: "); 01347 break; 01348 01349 case SOURCE: 01350 case SINK: 01351 if(grid[ilow][jlow].type == IO_TYPE) 01352 { 01353 fprintf(fp, " Pad: "); 01354 } 01355 else 01356 { /* IO Pad. */ 01357 fprintf(fp, " Class: "); 01358 } 01359 break; 01360 01361 default: 01362 printf 01363 ("Error in print_route: Unexpected traceback element " 01364 "type: %d (%s).\n", rr_type, 01365 name_type[rr_type]); 01366 exit(1); 01367 break; 01368 } 01369 01370 fprintf(fp, "%d ", rr_node[inode].ptc_num); 01371 01372 /* Uncomment line below if you're debugging and want to see the switch types * 01373 * used in the routing. */ 01374 /* fprintf (fp, "Switch: %d", tptr->iswitch); */ 01375 01376 fprintf(fp, "\n"); 01377 01378 tptr = tptr->next; 01379 } 01380 } 01381 01382 else 01383 { /* Global net. Never routed. */ 01384 fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s): global net connecting:\n\n", 01385 inet, net[inet].name); 01386 01387 for(ipin = 0; ipin <= net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) 01388 { 01389 bnum = net[inet].node_block[ipin]; 01390 01391 node_block_pin = net[inet].node_block_pin[ipin]; 01392 iclass = 01393 block[bnum].type->pin_class[node_block_pin]; 01394 01395 fprintf(fp, 01396 "Block %s (#%d) at (%d, %d), Pin class %d.\n", 01397 block[bnum].name, bnum, block[bnum].x, 01398 block[bnum].y, iclass); 01399 } 01400 } 01401 } 01402 01403 fclose(fp); 01404 01405 #ifdef CREATE_ECHO_FILES 01406 fp = my_fopen("mem.echo", "w"); 01407 fprintf(fp, "\nNum_heap_allocated: %d Num_trace_allocated: %d\n", 01408 num_heap_allocated, num_trace_allocated); 01409 fprintf(fp, "Num_linked_f_pointer_allocated: %d\n", 01410 num_linked_f_pointer_allocated); 01411 fclose(fp); 01412 #endif /* CREATE_ECHO_FILES */ 01413 01414 }


| void reserve_locally_used_opins | ( | float | pres_fac, | |
| boolean | rip_up_local_opins, | |||
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 1418 of file route_common.c.
01421 { 01422 01423 /* If some subblock outputs are hooked directly to FB outputs, then * 01424 * some FB outputs are occupied if their associated subblock is used * 01425 * locally, even though the inter-FB netlist does not say those outputs * 01426 * have to connect to anything. This is important when you have * 01427 * logically equivalent outputs. Code below makes sure any FB outputs * 01428 * that are used by being directly hooked to subblocks get properly * 01429 * reserved. */ 01430 01431 int iblk, num_local_opin, inode, from_node, iconn, num_edges, to_node; 01432 int iclass, ipin; 01433 float cost; 01434 struct s_heap *heap_head_ptr; 01435 t_type_ptr type; 01436 01437 if(rip_up_local_opins) 01438 { 01439 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 01440 { 01441 type = block[iblk].type; 01442 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 01443 { 01444 num_local_opin = 01445 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 01446 /* Always 0 for pads and for RECEIVER (IPIN) classes */ 01447 for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opin; ipin++) 01448 { 01449 inode = 01450 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 01451 list[ipin]; 01452 adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost(inode, -1, 01453 pres_fac); 01454 } 01455 } 01456 } 01457 } 01458 01459 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 01460 { 01461 type = block[iblk].type; 01462 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 01463 { 01464 num_local_opin = 01465 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 01466 /* Always 0 for pads and for RECEIVER (IPIN) classes */ 01467 01468 if(num_local_opin != 0) 01469 { /* Have to reserve (use) some OPINs */ 01470 from_node = rr_blk_source[iblk][iclass]; 01471 num_edges = rr_node[from_node].num_edges; 01472 for(iconn = 0; iconn < num_edges; iconn++) 01473 { 01474 to_node = rr_node[from_node].edges[iconn]; 01475 cost = get_rr_cong_cost(to_node); 01476 node_to_heap(to_node, cost, OPEN, OPEN, 01477 0., 0.); 01478 } 01479 01480 for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opin; ipin++) 01481 { 01482 heap_head_ptr = get_heap_head(); 01483 inode = heap_head_ptr->index; 01484 adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost(inode, 1, 01485 pres_fac); 01486 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 01487 list[ipin] = inode; 01488 free_heap_data(heap_head_ptr); 01489 } 01490 01491 empty_heap(); 01492 } 01493 } 01494 } 01495 }
| void reset_path_costs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 564 of file route_common.c.
00565 { 00566 00567 /* The routine sets the path_cost to HUGE_FLOAT for all channel segments * 00568 * touched by previous routing phases. */ 00569 00570 struct s_linked_f_pointer *mod_ptr; 00571 00572 #ifdef DEBUG 00573 int num_mod_ptrs; 00574 #endif 00575 00576 /* The traversal method below is slightly painful to make it faster. */ 00577 00578 if(rr_modified_head != NULL) 00579 { 00580 mod_ptr = rr_modified_head; 00581 00582 #ifdef DEBUG 00583 num_mod_ptrs = 1; 00584 #endif 00585 00586 while(mod_ptr->next != NULL) 00587 { 00588 *(mod_ptr->fptr) = HUGE_FLOAT; 00589 mod_ptr = mod_ptr->next; 00590 #ifdef DEBUG 00591 num_mod_ptrs++; 00592 #endif 00593 } 00594 *(mod_ptr->fptr) = HUGE_FLOAT; /* Do last one. */ 00595 00596 /* Reset the modified list and put all the elements back in the free * 00597 * list. */ 00598 00599 mod_ptr->next = linked_f_pointer_free_head; 00600 linked_f_pointer_free_head = rr_modified_head; 00601 rr_modified_head = NULL; 00602 00603 #ifdef DEBUG 00604 num_linked_f_pointer_allocated -= num_mod_ptrs; 00605 #endif 00606 } 00607 }
| void restore_routing | ( | struct s_trace ** | best_routing, | |
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally, | |||
| t_ivec ** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 162 of file route_common.c.
00165 { 00166 00167 /* Deallocates any current routing in trace_head, and replaces it with * 00168 * the routing in best_routing. Best_routing is set to NULL to show that * 00169 * it no longer points to a valid routing. NOTE: trace_tail is not * 00170 * restored -- it is set to all NULLs since it is only used in * 00171 * update_traceback. If you need trace_tail restored, modify this * 00172 * routine. Also restores the locally used opin data. */ 00173 00174 int inet, iblk, ipin, iclass, num_local_opins; 00175 t_type_ptr type; 00176 00177 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00178 { 00179 00180 /* Free any current routing. */ 00181 free_traceback(inet); 00182 00183 /* Set the current routing to the saved one. */ 00184 trace_head[inet] = best_routing[inet]; 00185 best_routing[inet] = NULL; /* No stored routing. */ 00186 } 00187 00188 /* Save which OPINs are locally used. */ 00189 00190 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 00191 { 00192 type = block[iblk].type; 00193 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 00194 { 00195 num_local_opins = 00196 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 00197 for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opins; ipin++) 00198 { 00199 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list[ipin] = 00200 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 00201 list[ipin]; 00202 } 00203 } 00204 00205 } 00206 }


| void save_routing | ( | struct s_trace ** | best_routing, | |
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally, | |||
| t_ivec ** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 101 of file route_common.c.
00104 { 00105 00106 /* This routing frees any routing currently held in best routing, * 00107 * then copies over the current routing (held in trace_head), and * 00108 * finally sets trace_head and trace_tail to all NULLs so that the * 00109 * connection to the saved routing is broken. This is necessary so * 00110 * that the next iteration of the router does not free the saved * 00111 * routing elements. Also saves any data about locally used clb_opins, * 00112 * since this is also part of the routing. */ 00113 00114 int inet, iblk, iclass, ipin, num_local_opins; 00115 struct s_trace *tptr, *tempptr; 00116 t_type_ptr type; 00117 00118 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00119 { 00120 00121 /* Free any previously saved routing. It is no longer best. */ 00122 tptr = best_routing[inet]; 00123 while(tptr != NULL) 00124 { 00125 tempptr = tptr->next; 00126 free_trace_data(tptr); 00127 tptr = tempptr; 00128 } 00129 00130 /* Save a pointer to the current routing in best_routing. */ 00131 best_routing[inet] = trace_head[inet]; 00132 00133 /* Set the current (working) routing to NULL so the current trace * 00134 * elements won't be reused by the memory allocator. */ 00135 00136 trace_head[inet] = NULL; 00137 trace_tail[inet] = NULL; 00138 } 00139 00140 /* Save which OPINs are locally used. */ 00141 00142 for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++) 00143 { 00144 type = block[iblk].type; 00145 for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++) 00146 { 00147 num_local_opins = 00148 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem; 00149 for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opins; ipin++) 00150 { 00151 saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 00152 list[ipin] = 00153 fb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass]. 00154 list[ipin]; 00155 } 00156 } 00157 } 00158 }


| boolean try_route | ( | int | width_fac, | |
| struct s_router_opts | router_opts, | |||
| struct s_det_routing_arch | det_routing_arch, | |||
| t_segment_inf * | segment_inf, | |||
| t_timing_inf | timing_inf, | |||
| float ** | net_slack, | |||
| float ** | net_delay, | |||
| t_chan_width_dist | chan_width_dist, | |||
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally, | |||
| t_mst_edge ** | mst, | |||
| boolean * | Fc_clipped | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 249 of file route_common.c.
00260 { 00261 00262 /* Attempts a routing via an iterated maze router algorithm. Width_fac * 00263 * specifies the relative width of the channels, while the members of * 00264 * router_opts determine the value of the costs assigned to routing * 00265 * resource node, etc. det_routing_arch describes the detailed routing * 00266 * architecture (connection and switch boxes) of the FPGA; it is used * 00267 * only if a DETAILED routing has been selected. */ 00268 00269 int tmp; 00270 boolean success; 00271 t_graph_type graph_type; 00272 00273 if(router_opts.route_type == GLOBAL) { 00274 graph_type = GRAPH_GLOBAL; 00275 } else { 00276 graph_type = (det_routing_arch.directionality == 00277 BI_DIRECTIONAL ? GRAPH_BIDIR : GRAPH_UNIDIR); 00278 } 00279 00280 /* Set the channel widths */ 00281 00282 init_chan(width_fac, chan_width_dist); 00283 00284 /* Free any old routing graph, if one exists. */ 00285 00286 free_rr_graph(); 00287 00288 /* Set up the routing resource graph defined by this FPGA architecture. */ 00289 00290 build_rr_graph(graph_type, 00291 num_types, type_descriptors, nx, ny, grid, 00292 chan_width_x[0], NULL, 00293 det_routing_arch.switch_block_type, det_routing_arch.Fs, 00294 det_routing_arch.num_segment, det_routing_arch.num_switch, segment_inf, 00295 det_routing_arch.global_route_switch, 00296 det_routing_arch.delayless_switch, timing_inf, 00297 det_routing_arch.wire_to_ipin_switch, 00298 router_opts.base_cost_type, &tmp); 00299 00300 /* Allocate and load some additional rr_graph information needed only by * 00301 * the router. */ 00302 00303 alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs(); 00304 00305 init_route_structs(router_opts.bb_factor); 00306 00307 if(router_opts.router_algorithm == BREADTH_FIRST) 00308 { 00309 printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: BREADTH_FIRST.\n"); 00310 success = 00311 try_breadth_first_route(router_opts, fb_opins_used_locally, 00312 width_fac); 00313 } 00314 else if(router_opts.router_algorithm == TIMING_DRIVEN) 00315 { /* TIMING_DRIVEN route */ 00316 printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: TIMING_DRIVEN.\n"); 00317 assert(router_opts.route_type != GLOBAL); 00318 success = 00319 try_timing_driven_route(router_opts, net_slack, net_delay, 00320 fb_opins_used_locally); 00321 } 00322 else 00323 { /* Directed Search Routability Driven */ 00324 printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: DIRECTED_SEARCH.\n"); 00325 success = 00326 try_directed_search_route(router_opts, fb_opins_used_locally, 00327 width_fac, mst); 00328 } 00329 00330 free_rr_node_route_structs(); 00331 00332 return (success); 00333 }

Definition at line 484 of file route_common.c.
00486 { 00487 00488 /* This routine adds the most recently finished wire segment to the * 00489 * traceback linked list. The first connection starts with the net SOURCE * 00490 * and begins at the structure pointed to by trace_head[inet]. Each * 00491 * connection ends with a SINK. After each SINK, the next connection * 00492 * begins (if the net has more than 2 pins). The first element after the * 00493 * SINK gives the routing node on a previous piece of the routing, which is * 00494 * the link from the existing net to this new piece of the net. * 00495 * In each traceback I start at the end of a path and trace back through * 00496 * its predecessors to the beginning. I have stored information on the * 00497 * predecesser of each node to make traceback easy -- this sacrificies some * 00498 * memory for easier code maintenance. This routine returns a pointer to * 00499 * the first "new" node in the traceback (node not previously in trace). */ 00500 00501 struct s_trace *tptr, *prevptr, *temptail, *ret_ptr; 00502 int inode; 00503 short iedge; 00504 00505 #ifdef DEBUG 00506 t_rr_type rr_type; 00507 #endif 00508 00509 inode = hptr->index; 00510 00511 #ifdef DEBUG 00512 rr_type = rr_node[inode].type; 00513 if(rr_type != SINK) 00514 { 00515 printf("Error in update_traceback. Expected type = SINK (%d).\n", 00516 SINK); 00517 printf("Got type = %d while tracing back net %d.\n", rr_type, 00518 inet); 00519 exit(1); 00520 } 00521 #endif 00522 00523 tptr = alloc_trace_data(); /* SINK on the end of the connection */ 00524 tptr->index = inode; 00525 tptr->iswitch = OPEN; 00526 tptr->next = NULL; 00527 temptail = tptr; /* This will become the new tail at the end */ 00528 /* of the routine. */ 00529 00530 /* Now do it's predecessor. */ 00531 00532 inode = hptr->u.prev_node; 00533 iedge = hptr->prev_edge; 00534 00535 while(inode != NO_PREVIOUS) 00536 { 00537 prevptr = alloc_trace_data(); 00538 prevptr->index = inode; 00539 prevptr->iswitch = rr_node[inode].switches[iedge]; 00540 prevptr->next = tptr; 00541 tptr = prevptr; 00542 00543 iedge = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge; 00544 inode = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node; 00545 } 00546 00547 if(trace_tail[inet] != NULL) 00548 { 00549 trace_tail[inet]->next = tptr; /* Traceback ends with tptr */ 00550 ret_ptr = tptr->next; /* First new segment. */ 00551 } 00552 else 00553 { /* This was the first "chunk" of the net's routing */ 00554 trace_head[inet] = tptr; 00555 ret_ptr = tptr; /* Whole traceback is new. */ 00556 } 00557 00558 trace_tail[inet] = temptail; 00559 return (ret_ptr); 00560 }

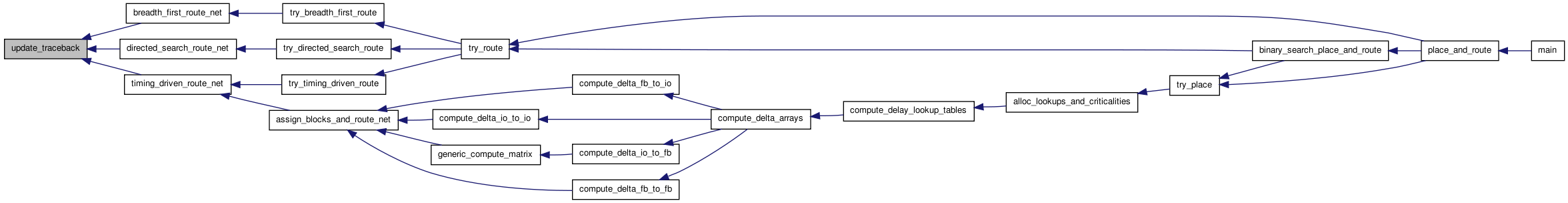
Variable Documentation
Definition at line 29 of file route_common.c.
struct s_heap* heap_free_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 34 of file route_common.c.
int heap_size [static] |
Definition at line 30 of file route_common.c.
int heap_tail [static] |
Definition at line 31 of file route_common.c.
struct s_linked_f_pointer* linked_f_pointer_free_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 46 of file route_common.c.
Definition at line 22 of file route_common.c.
struct s_linked_f_pointer* rr_modified_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 45 of file route_common.c.
| t_rr_node_route_inf* rr_node_route_inf = NULL |
Definition at line 20 of file route_common.c.
struct s_trace* trace_free_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 37 of file route_common.c.
 1.6.1
1.6.1