SRC/route_breadth_first.c File Reference
#include <stdio.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "globals.h"#include "mst.h"#include "route_export.h"#include "route_common.h"#include "route_breadth_first.h"
Include dependency graph for route_breadth_first.c:
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| static boolean | breadth_first_route_net (int inet, float bend_cost) |
| static void | breadth_first_expand_trace_segment (struct s_trace *start_ptr, int remaining_connections_to_sink) |
| static void | breadth_first_expand_neighbours (int inode, float pcost, int inet, float bend_cost) |
| static void | breadth_first_add_source_to_heap (int inet) |
| boolean | try_breadth_first_route (struct s_router_opts router_opts, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally, int width_fac) |
Function Documentation
| static void breadth_first_add_source_to_heap | ( | int | inet | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 338 of file route_breadth_first.c.
00339 { 00340 00341 /* Adds the SOURCE of this net to the heap. Used to start a net's routing. */ 00342 00343 int inode; 00344 float cost; 00345 00346 inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][0]; /* SOURCE */ 00347 cost = get_rr_cong_cost(inode); 00348 00349 node_to_heap(inode, cost, NO_PREVIOUS, NO_PREVIOUS, OPEN, OPEN); 00350 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| static void breadth_first_expand_neighbours | ( | int | inode, | |
| float | pcost, | |||
| int | inet, | |||
| float | bend_cost | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 296 of file route_breadth_first.c.
00300 { 00301 00302 /* Puts all the rr_nodes adjacent to inode on the heap. rr_nodes outside * 00303 * the expanded bounding box specified in route_bb are not added to the * 00304 * heap. pcost is the path_cost to get to inode. */ 00305 00306 int iconn, to_node, num_edges; 00307 t_rr_type from_type, to_type; 00308 float tot_cost; 00309 00310 num_edges = rr_node[inode].num_edges; 00311 for(iconn = 0; iconn < num_edges; iconn++) 00312 { 00313 to_node = rr_node[inode].edges[iconn]; 00314 00315 if(rr_node[to_node].xhigh < route_bb[inet].xmin || 00316 rr_node[to_node].xlow > route_bb[inet].xmax || 00317 rr_node[to_node].yhigh < route_bb[inet].ymin || 00318 rr_node[to_node].ylow > route_bb[inet].ymax) 00319 continue; /* Node is outside (expanded) bounding box. */ 00320 00321 tot_cost = pcost + get_rr_cong_cost(to_node); 00322 00323 if(bend_cost != 0.) 00324 { 00325 from_type = rr_node[inode].type; 00326 to_type = rr_node[to_node].type; 00327 if((from_type == CHANX && to_type == CHANY) || 00328 (from_type == CHANY && to_type == CHANX)) 00329 tot_cost += bend_cost; 00330 } 00331 00332 node_to_heap(to_node, tot_cost, inode, iconn, OPEN, OPEN); 00333 } 00334 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| static void breadth_first_expand_trace_segment | ( | struct s_trace * | start_ptr, | |
| int | remaining_connections_to_sink | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 205 of file route_breadth_first.c.
00207 { 00208 00209 /* Adds all the rr_nodes in the traceback segment starting at tptr (and * 00210 * continuing to the end of the traceback) to the heap with a cost of zero. * 00211 * This allows expansion to begin from the existing wiring. The * 00212 * remaining_connections_to_sink value is 0 if the route segment ending * 00213 * at this location is the last one to connect to the SINK ending the route * 00214 * segment. This is the usual case. If it is not the last connection this * 00215 * net must make to this SINK, I have a hack to ensure the next connection * 00216 * to this SINK goes through a different IPIN. Without this hack, the * 00217 * router would always put all the connections from this net to this SINK * 00218 * through the same IPIN. With LUTs or cluster-based logic blocks, you * 00219 * should never have a net connecting to two logically-equivalent pins on * 00220 * the same logic block, so the hack will never execute. If your logic * 00221 * block is an and-gate, however, nets might connect to two and-inputs on * 00222 * the same logic block, and since the and-inputs are logically-equivalent, * 00223 * this means two connections to the same SINK. */ 00224 00225 struct s_trace *tptr, *next_ptr; 00226 int inode, sink_node, last_ipin_node; 00227 00228 tptr = start_ptr; 00229 00230 if(remaining_connections_to_sink == 0) 00231 { /* Usual case. */ 00232 while(tptr != NULL) 00233 { 00234 node_to_heap(tptr->index, 0., NO_PREVIOUS, NO_PREVIOUS, 00235 OPEN, OPEN); 00236 tptr = tptr->next; 00237 } 00238 } 00239 00240 else 00241 { /* This case never executes for most logic blocks. */ 00242 00243 /* Weird case. Lots of hacks. The cleanest way to do this would be to empty * 00244 * the heap, update the congestion due to the partially-completed route, put * 00245 * the whole route so far (excluding IPINs and SINKs) on the heap with cost * 00246 * 0., and expand till you hit the next SINK. That would be slow, so I * 00247 * do some hacks to enable incremental wavefront expansion instead. */ 00248 00249 if(tptr == NULL) 00250 return; /* No route yet */ 00251 00252 next_ptr = tptr->next; 00253 last_ipin_node = OPEN; /* Stops compiler from complaining. */ 00254 00255 /* Can't put last SINK on heap with NO_PREVIOUS, etc, since that won't let * 00256 * us reach it again. Instead, leave the last traceback element (SINK) off * 00257 * the heap. */ 00258 00259 while(next_ptr != NULL) 00260 { 00261 inode = tptr->index; 00262 node_to_heap(inode, 0., NO_PREVIOUS, NO_PREVIOUS, OPEN, 00263 OPEN); 00264 00265 if(rr_node[inode].type == IPIN) 00266 last_ipin_node = inode; 00267 00268 tptr = next_ptr; 00269 next_ptr = tptr->next; 00270 } 00271 00272 /* This will stop the IPIN node used to get to this SINK from being * 00273 * reexpanded for the remainder of this net's routing. This will make us * 00274 * hook up more IPINs to this SINK (which is what we want). If IPIN * 00275 * doglegs are allowed in the graph, we won't be able to use this IPIN to * 00276 * do a dogleg, since it won't be re-expanded. Shouldn't be a big problem. */ 00277 00278 rr_node_route_inf[last_ipin_node].path_cost = -HUGE_FLOAT; 00279 00280 /* Also need to mark the SINK as having high cost, so another connection can * 00281 * be made to it. */ 00282 00283 sink_node = tptr->index; 00284 rr_node_route_inf[sink_node].path_cost = HUGE_FLOAT; 00285 00286 /* Finally, I need to remove any pending connections to this SINK via the * 00287 * IPIN I just used (since they would result in congestion). Scan through * 00288 * the heap to do this. */ 00289 00290 invalidate_heap_entries(sink_node, last_ipin_node); 00291 } 00292 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| static boolean breadth_first_route_net | ( | int | inet, | |
| float | bend_cost | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 116 of file route_breadth_first.c.
00118 { 00119 00120 /* Uses a maze routing (Dijkstra's) algorithm to route a net. The net * 00121 * begins at the net output, and expands outward until it hits a target * 00122 * pin. The algorithm is then restarted with the entire first wire segment * 00123 * included as part of the source this time. For an n-pin net, the maze * 00124 * router is invoked n-1 times to complete all the connections. Inet is * 00125 * the index of the net to be routed. Bends are penalized by bend_cost * 00126 * (which is typically zero for detailed routing and nonzero only for global * 00127 * routing), since global routes with lots of bends are tougher to detailed * 00128 * route (using a detailed router like SEGA). * 00129 * If this routine finds that a net *cannot* be connected (due to a complete * 00130 * lack of potential paths, rather than congestion), it returns FALSE, as * 00131 * routing is impossible on this architecture. Otherwise it returns TRUE. */ 00132 00133 int i, inode, prev_node, remaining_connections_to_sink; 00134 float pcost, new_pcost; 00135 struct s_heap *current; 00136 struct s_trace *tptr; 00137 00138 free_traceback(inet); 00139 breadth_first_add_source_to_heap(inet); 00140 mark_ends(inet); 00141 00142 tptr = NULL; 00143 remaining_connections_to_sink = 0; 00144 00145 for(i = 1; i <= net[inet].num_sinks; i++) 00146 { /* Need n-1 wires to connect n pins */ 00147 breadth_first_expand_trace_segment(tptr, 00148 remaining_connections_to_sink); 00149 current = get_heap_head(); 00150 00151 if(current == NULL) 00152 { /* Infeasible routing. No possible path for net. */ 00153 reset_path_costs(); /* Clean up before leaving. */ 00154 return (FALSE); 00155 } 00156 00157 inode = current->index; 00158 00159 while(rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag == 0) 00160 { 00161 pcost = rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost; 00162 new_pcost = current->cost; 00163 if(pcost > new_pcost) 00164 { /* New path is lowest cost. */ 00165 rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = new_pcost; 00166 prev_node = current->u.prev_node; 00167 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = prev_node; 00168 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge = 00169 current->prev_edge; 00170 00171 if(pcost > 0.99 * HUGE_FLOAT) /* First time touched. */ 00172 add_to_mod_list(&rr_node_route_inf[inode]. 00173 path_cost); 00174 00175 breadth_first_expand_neighbours(inode, new_pcost, 00176 inet, bend_cost); 00177 } 00178 00179 free_heap_data(current); 00180 current = get_heap_head(); 00181 00182 if(current == NULL) 00183 { /* Impossible routing. No path for net. */ 00184 reset_path_costs(); 00185 return (FALSE); 00186 } 00187 00188 inode = current->index; 00189 } 00190 00191 rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag--; /* Connected to this SINK. */ 00192 remaining_connections_to_sink = 00193 rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag; 00194 tptr = update_traceback(current, inet); 00195 free_heap_data(current); 00196 } 00197 00198 empty_heap(); 00199 reset_path_costs(); 00200 return (TRUE); 00201 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
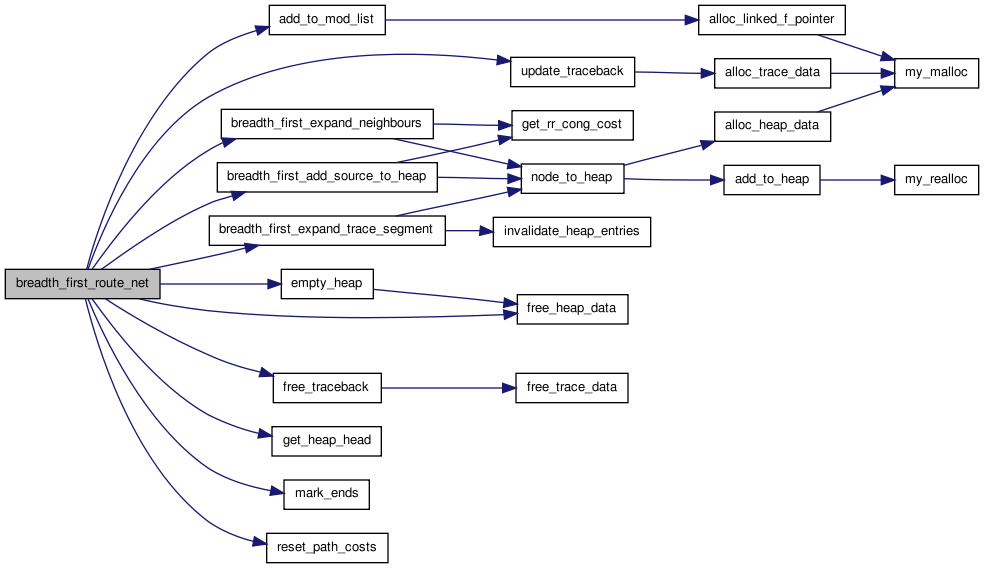
Here is the caller graph for this function:

| boolean try_breadth_first_route | ( | struct s_router_opts | router_opts, | |
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally, | |||
| int | width_fac | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 31 of file route_breadth_first.c.
00034 { 00035 00036 /* Iterated maze router ala Pathfinder Negotiated Congestion algorithm, * 00037 * (FPGA 95 p. 111). Returns TRUE if it can route this FPGA, FALSE if * 00038 * it can't. */ 00039 00040 float pres_fac; 00041 boolean success, is_routable, rip_up_local_opins; 00042 int itry, inet; 00043 00044 /* Usually the first iteration uses a very small (or 0) pres_fac to find * 00045 * the shortest path and get a congestion map. For fast compiles, I set * 00046 * pres_fac high even for the first iteration. */ 00047 00048 pres_fac = router_opts.first_iter_pres_fac; 00049 00050 for(itry = 1; itry <= router_opts.max_router_iterations; itry++) 00051 { 00052 00053 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00054 { 00055 if(net[inet].is_global == FALSE) 00056 { /* Skip global nets. */ 00057 00058 pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], -1, 00059 pres_fac); 00060 00061 is_routable = 00062 breadth_first_route_net(inet, 00063 router_opts. 00064 bend_cost); 00065 00066 /* Impossible to route? (disconnected rr_graph) */ 00067 00068 if(!is_routable) 00069 { 00070 printf("Routing failed.\n"); 00071 return (FALSE); 00072 } 00073 00074 pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], 1, 00075 pres_fac); 00076 00077 } 00078 } 00079 00080 /* Make sure any FB OPINs used up by subblocks being hooked directly * 00081 * to them are reserved for that purpose. */ 00082 00083 if(itry == 1) 00084 rip_up_local_opins = FALSE; 00085 else 00086 rip_up_local_opins = TRUE; 00087 00088 reserve_locally_used_opins(pres_fac, rip_up_local_opins, 00089 fb_opins_used_locally); 00090 00091 success = feasible_routing(); 00092 if(success) 00093 { 00094 printf 00095 ("Successfully routed after %d routing iterations.\n", 00096 itry); 00097 return (TRUE); 00098 } 00099 00100 if(itry == 1) 00101 pres_fac = router_opts.initial_pres_fac; 00102 else 00103 pres_fac *= router_opts.pres_fac_mult; 00104 00105 pres_fac = min (pres_fac, HUGE_FLOAT / 1e5); 00106 00107 pathfinder_update_cost(pres_fac, router_opts.acc_fac); 00108 } 00109 00110 printf("Routing failed.\n"); 00111 return (FALSE); 00112 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
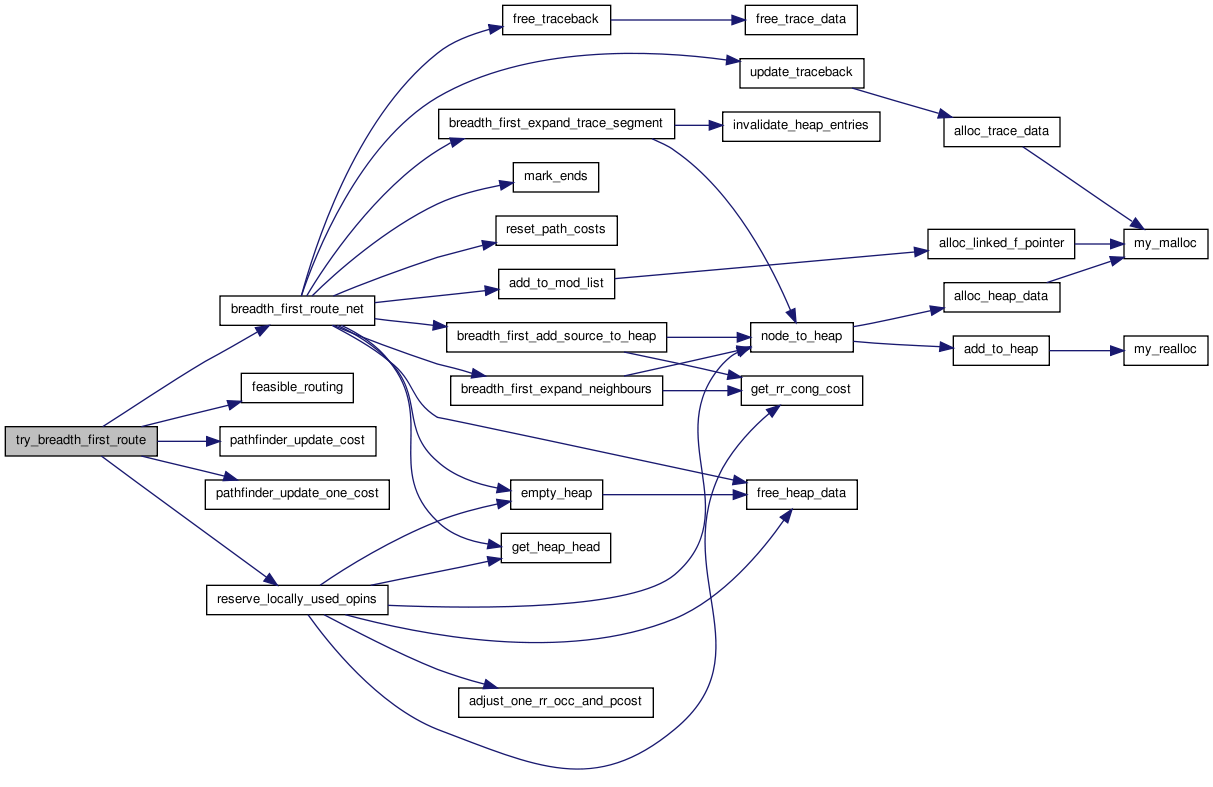
Here is the caller graph for this function:

 1.6.1
1.6.1