#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <assert.h>#include <time.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "vpr_utils.h"#include "globals.h"#include "mst.h"#include "route_export.h"#include "route_common.h"#include "route_tree_timing.h"#include "route_timing.h"#include "route_breadth_first.h"#include "route_directed_search.h"#include "place_and_route.h"#include "rr_graph.h"#include "read_xml_arch_file.h" Include dependency graph for route_common.c:
Include dependency graph for route_common.c:Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
| #define | NCHUNK 200 |
Functions | |
| static void | free_trace_data (struct s_trace *tptr) |
| static void | load_route_bb (int bb_factor) |
| static struct s_trace * | alloc_trace_data (void) |
| static void | add_to_heap (struct s_heap *hptr) |
| static struct s_heap * | alloc_heap_data (void) |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | alloc_linked_f_pointer (void) |
| static t_ivec ** | alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally () |
| static void | adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost (int inode, int add_or_sub, float pres_fac) |
| void | save_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | restore_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | get_serial_num (void) |
| boolean | try_route (int width_fac, struct s_router_opts router_opts, struct s_det_routing_arch det_routing_arch, t_segment_inf *segment_inf, t_timing_inf timing_inf, float **net_slack, float **net_delay, t_chan_width_dist chan_width_dist, t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally, t_mst_edge **mst, boolean *Fc_clipped) |
| boolean | feasible_routing (void) |
| void | pathfinder_update_one_cost (struct s_trace *route_segment_start, int add_or_sub, float pres_fac) |
| void | pathfinder_update_cost (float pres_fac, float acc_fac) |
| void | init_route_structs (int bb_factor) |
| struct s_trace * | update_traceback (struct s_heap *hptr, int inet) |
| void | reset_path_costs (void) |
| float | get_rr_cong_cost (int inode) |
| void | mark_ends (int inet) |
| void | node_to_heap (int inode, float cost, int prev_node, int prev_edge, float backward_path_cost, float R_upstream) |
| void | free_traceback (int inet) |
| t_ivec ** | alloc_route_structs () |
| void | alloc_route_static_structs () |
| struct s_trace ** | alloc_saved_routing (t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally, t_ivec ***saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr) |
| void | free_trace_structs (void) |
| void | free_route_structs (t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | free_saved_routing (struct s_trace **best_routing, t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally) |
| void | alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs (void) |
| void | reset_rr_node_route_structs (void) |
| void | free_rr_node_route_structs (void) |
| void | add_to_mod_list (float *fptr) |
| boolean | is_empty_heap (void) |
| struct s_heap * | get_heap_head (void) |
| void | empty_heap (void) |
| void | free_heap_data (struct s_heap *hptr) |
| void | invalidate_heap_entries (int sink_node, int ipin_node) |
| void | print_route (char *route_file) |
| void | reserve_locally_used_opins (float pres_fac, boolean rip_up_local_opins, t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally) |
Variables | |
| t_rr_node_route_inf * | rr_node_route_inf = NULL |
| struct s_bb * | route_bb = NULL |
| static struct s_heap ** | heap |
| static int | heap_size |
| static int | heap_tail |
| static struct s_heap * | heap_free_head = NULL |
| static struct s_trace * | trace_free_head = NULL |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | rr_modified_head = NULL |
| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * | linked_f_pointer_free_head = NULL |
Define Documentation
| #define NCHUNK 200 |
# of various structs malloced at a time.
Definition at line 1147 of file route_common.c.
Function Documentation
| static void add_to_heap | ( | struct s_heap * | hptr | ) | [static] |
Adds an item to the heap, expanding the heap if necessary.
Definition at line 1050 of file route_common.c.
{
int ito, ifrom;
struct s_heap *temp_ptr;
if(heap_tail > heap_size)
{ /* Heap is full */
heap_size *= 2;
heap = my_realloc((void *)(heap + 1), heap_size *
sizeof(struct s_heap *));
heap--; /* heap goes from [1..heap_size] */
}
heap[heap_tail] = hptr;
ifrom = heap_tail;
ito = ifrom / 2;
heap_tail++;
while((ito >= 1) && (heap[ifrom]->cost < heap[ito]->cost))
{
temp_ptr = heap[ito];
heap[ito] = heap[ifrom];
heap[ifrom] = temp_ptr;
ifrom = ito;
ito = ifrom / 2;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void add_to_mod_list | ( | float * | fptr | ) |
This routine adds the floating point pointer (fptr) into a linked list that indicates all the pathcosts that have been modified thus far.
Definition at line 1033 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_linked_f_pointer *mod_ptr;
mod_ptr = alloc_linked_f_pointer();
/* Add this element to the start of the modified list. */
mod_ptr->next = rr_modified_head;
mod_ptr->fptr = fptr;
rr_modified_head = mod_ptr;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost | ( | int | inode, |
| int | add_or_sub, | ||
| float | pres_fac | ||
| ) | [static] |
Increments or decrements (depending on add_or_sub) the occupancy of one rr_node, and adjusts the present cost of that node appropriately.
Definition at line 1507 of file route_common.c.
{
int occ, capacity;
occ = rr_node[inode].occ + add_or_sub;
capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity;
rr_node[inode].occ = occ;
if(occ < capacity)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.;
}
else
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) *
pres_fac;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static t_ivec ** alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally | ( | ) | [static] |
Allocates and loads the data needed to make the router reserve some CLB output pins for connections made locally within a CLB (if the netlist specifies that this is necessary).
Definition at line 786 of file route_common.c.
{
t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally;
int iblk, clb_pin, iclass, num_local_opins;
int class_low, class_high;
t_type_ptr type;
clb_opins_used_locally =
(t_ivec **) my_malloc(num_blocks * sizeof(t_ivec *));
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
get_class_range_for_block(iblk, &class_low, &class_high);
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk] =
(t_ivec *) my_malloc(type->num_class * sizeof(t_ivec));
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem = 0;
for(clb_pin = 0; clb_pin < type->num_pins; clb_pin++)
{
/* Subblock output used only locally, but must connect to a CLB OPIN? */
if(block[iblk].nets[clb_pin] != OPEN
&& clb_net[block[iblk].nets[clb_pin]].num_sinks == 0)
{
iclass = type->pin_class[clb_pin];
/* Check to make sure class is in same range as that assigned to block */
assert(iclass >= class_low
&& iclass <= class_high);
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem++;
}
}
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opins =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
if(num_local_opins == 0)
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list = NULL;
else
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list =
(int *)my_malloc(num_local_opins * sizeof(int));
}
}
return (clb_opins_used_locally);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs | ( | void | ) |
Allocates some extra information about each rr_node that is used only during routing.
Definition at line 904 of file route_common.c.
{
int inode;
if(rr_node_route_inf != NULL)
{
printf("Error in alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs: \n"
"old rr_node_route_inf array exists.\n");
exit(1);
}
rr_node_route_inf = my_malloc(num_rr_nodes * sizeof(t_rr_node_route_inf));
for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = NO_PREVIOUS;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge = NO_PREVIOUS;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost = 1.;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = HUGE_FLOAT;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag = 0;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static struct s_heap * alloc_heap_data | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
Definition at line 1151 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
struct s_heap *temp_ptr;
if(heap_free_head == NULL)
{ /* No elements on the free list */
heap_free_head = (struct s_heap *)my_malloc(NCHUNK *
sizeof(struct
s_heap));
/* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer *
* somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory *
* for post-routing stages, look into it. */
for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++)
(heap_free_head + i)->u.next = heap_free_head + i + 1;
(heap_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->u.next = NULL;
}
temp_ptr = heap_free_head;
heap_free_head = heap_free_head->u.next;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_heap_allocated++;
#endif
return (temp_ptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static struct s_linked_f_pointer * alloc_linked_f_pointer | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
This routine returns a linked list element with a float pointer as the node data.
Definition at line 1256 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
struct s_linked_f_pointer *temp_ptr;
if(linked_f_pointer_free_head == NULL)
{
/* No elements on the free list */
linked_f_pointer_free_head = (struct s_linked_f_pointer *)
my_malloc(NCHUNK * sizeof(struct s_linked_f_pointer));
/* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer *
* somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory *
* for post-routing stages, look into it. */
for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++)
{
(linked_f_pointer_free_head + i)->next =
linked_f_pointer_free_head + i + 1;
}
(linked_f_pointer_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->next = NULL;
}
temp_ptr = linked_f_pointer_free_head;
linked_f_pointer_free_head = linked_f_pointer_free_head->next;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_linked_f_pointer_allocated++;
#endif
return (temp_ptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void alloc_route_static_structs | ( | ) |
Definition at line 715 of file route_common.c.
{
trace_head = (struct s_trace **)my_calloc(num_nets,
sizeof(struct s_trace *));
trace_tail = (struct s_trace **)my_malloc(num_nets *
sizeof(struct s_trace *));
heap_size = nx * ny;
heap = (struct s_heap **)my_malloc(heap_size * sizeof(struct s_heap *));
heap--; /* heap stores from [1..heap_size] */
heap_tail = 1;
route_bb = (struct s_bb *)my_malloc(num_nets * sizeof(struct s_bb));
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| t_ivec** alloc_route_structs | ( | ) |
Allocates the data structures needed for routing.
Definition at line 704 of file route_common.c.
{
t_ivec **clb_opins_used_locally;
alloc_route_static_structs();
clb_opins_used_locally =
alloc_and_load_clb_opins_used_locally();
return (clb_opins_used_locally);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| struct s_trace** alloc_saved_routing | ( | t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally, |
| t_ivec *** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr | ||
| ) | [read] |
Allocates data structures into which the key routing data can be saved, allowing the routing to be recovered later (e.g. after a another routing is attempted).
Definition at line 734 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_trace **best_routing;
t_ivec **saved_clb_opins_used_locally;
int iblk, iclass, num_local_opins;
t_type_ptr type;
best_routing = (struct s_trace **)my_calloc(num_nets,
sizeof(struct s_trace *));
saved_clb_opins_used_locally =
(t_ivec **) my_malloc(num_blocks * sizeof(t_ivec *));
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk] =
(t_ivec *) my_malloc(type->num_class * sizeof(t_ivec));
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opins =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem =
num_local_opins;
if(num_local_opins == 0)
{
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list =
NULL;
}
else
{
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list =
(int *)my_malloc(num_local_opins *
sizeof(int));
}
}
}
*saved_clb_opins_used_locally_ptr = saved_clb_opins_used_locally;
return (best_routing);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static struct s_trace * alloc_trace_data | ( | void | ) | [static, read] |
Definition at line 1212 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
struct s_trace *temp_ptr;
if(trace_free_head == NULL)
{ /* No elements on the free list */
trace_free_head = (struct s_trace *)my_malloc(NCHUNK *
sizeof(struct
s_trace));
/* If I want to free this memory, I have to store the original pointer *
* somewhere. Not worthwhile right now -- if you need more memory *
* for post-routing stages, look into it. */
for(i = 0; i < NCHUNK - 1; i++)
(trace_free_head + i)->next = trace_free_head + i + 1;
(trace_free_head + NCHUNK - 1)->next = NULL;
}
temp_ptr = trace_free_head;
trace_free_head = trace_free_head->next;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_trace_allocated++;
#endif
return (temp_ptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void empty_heap | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 1136 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 1; i < heap_tail; i++)
free_heap_data(heap[i]);
heap_tail = 1;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| boolean feasible_routing | ( | void | ) |
This routine checks to see if this is a resource-feasible routing. That is, are all rr_node capacity limitations respected? It assumes that the occupancy arrays are up to date when it is called.
Definition at line 349 of file route_common.c.
{
int inode;
for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++) {
if(rr_node[inode].occ > rr_node[inode].capacity) {
return (FALSE);
}
}
return (TRUE);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_heap_data | ( | struct s_heap * | hptr | ) |
Definition at line 1182 of file route_common.c.
{
hptr->u.next = heap_free_head;
heap_free_head = hptr;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_heap_allocated--;
#endif
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_route_structs | ( | t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally | ) |
Frees the temporary storage needed only during the routing. The final routing result is not freed.
Definition at line 858 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
free(heap + 1);
free(route_bb);
heap = NULL; /* Defensive coding: crash hard if I use these. */
route_bb = NULL;
if(clb_opins_used_locally != NULL) {
for(i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++)
{
free_ivec_vector(clb_opins_used_locally[i], 0,
block[i].type->num_class - 1);
}
free(clb_opins_used_locally);
}
/* NB: Should use my chunk_malloc for tptr, hptr, and mod_ptr structures. *
* I could free everything except the tptrs at the end then. */
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_rr_node_route_structs | ( | void | ) |
Frees the extra information about each rr_node that is needed only during routing.
Definition at line 954 of file route_common.c.
{
free(rr_node_route_inf);
rr_node_route_inf = NULL; /* Mark as free */
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Frees the data structures needed to save a routing.
Definition at line 886 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
free(best_routing);
for(i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++)
{
free_ivec_vector(saved_clb_opins_used_locally[i], 0,
block[i].type->num_class - 1);
}
free(saved_clb_opins_used_locally);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void free_trace_data | ( | struct s_trace * | tptr | ) | [static] |
Puts the traceback structure pointed to by tptr on the free list.
Definition at line 1243 of file route_common.c.
{
tptr->next = trace_free_head;
trace_free_head = tptr;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_trace_allocated--;
#endif
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_trace_structs | ( | void | ) |
the trace lists are only freed after use by the timing-driven placer. Do not free them after use by the router, since stats, and draw routines use the trace values
Definition at line 841 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets; i++)
free_traceback(i);
free(trace_head);
free(trace_tail);
trace_head = NULL;
trace_tail = NULL;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_traceback | ( | int | inet | ) |
Puts the entire traceback (old routing) for this net on the free list and sets the trace_head pointers etc. for the net to NULL.
Definition at line 683 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_trace *tptr, *tempptr;
tptr = trace_head[inet];
while(tptr != NULL)
{
tempptr = tptr->next;
free_trace_data(tptr);
tptr = tempptr;
}
trace_head[inet] = NULL;
trace_tail[inet] = NULL;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| struct s_heap* get_heap_head | ( | void | ) | [read] |
Returns a pointer to the smallest element on the heap, or NULL if the heap is empty. Invalid (index == OPEN) entries on the heap are never returned -- they are just skipped over.
Definition at line 1090 of file route_common.c.
{
int ito, ifrom;
struct s_heap *heap_head, *temp_ptr;
do
{
if(heap_tail == 1)
{ /* Empty heap. */
printf("Empty heap occurred in get_heap_head.\n");
printf
("Some blocks are impossible to connect in this architecture.\n");
return (NULL);
}
heap_head = heap[1]; /* Smallest element. */
/* Now fix up the heap */
heap_tail--;
heap[1] = heap[heap_tail];
ifrom = 1;
ito = 2 * ifrom;
while(ito < heap_tail)
{
if(heap[ito + 1]->cost < heap[ito]->cost)
ito++;
if(heap[ito]->cost > heap[ifrom]->cost)
break;
temp_ptr = heap[ito];
heap[ito] = heap[ifrom];
heap[ifrom] = temp_ptr;
ifrom = ito;
ito = 2 * ifrom;
}
}
while(heap_head->index == OPEN); /* Get another one if invalid entry. */
return (heap_head);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| float get_rr_cong_cost | ( | int | inode | ) |
Returns the *congestion* cost of using this rr_node.
Definition at line 617 of file route_common.c.
{
short cost_index;
float cost;
cost_index = rr_node[inode].cost_index;
cost = rr_indexed_data[cost_index].base_cost *
rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost *
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost;
return (cost);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void get_serial_num | ( | void | ) |
This routine finds a "magic cookie" for the routing and prints it. Use this number as a routing serial number to ensure that programming changes do not break the router.
Definition at line 212 of file route_common.c.
{
int inet, serial_num, inode;
struct s_trace *tptr;
serial_num = 0;
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
/* Global nets will have null trace_heads (never routed) so they *
* are not included in the serial number calculation. */
tptr = trace_head[inet];
while(tptr != NULL)
{
inode = tptr->index;
serial_num +=
(inet + 1) * (rr_node[inode].xlow * (nx + 1) -
rr_node[inode].yhigh);
serial_num -= rr_node[inode].ptc_num * (inet + 1) * 10;
serial_num -= rr_node[inode].type * (inet + 1) * 100;
serial_num %= 2000000000; /* Prevent overflow */
tptr = tptr->next;
}
}
printf("Serial number (magic cookie) for the routing is: %d\n",
serial_num);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void init_route_structs | ( | int | bb_factor | ) |
Call this before you route any nets. It frees any old traceback and sets the list of rr_nodes touched to empty.
Definition at line 461 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets; i++)
free_traceback(i);
load_route_bb(bb_factor);
/* Check that things that should have been emptied after the last routing *
* really were. */
if(rr_modified_head != NULL)
{
printf
("Error in init_route_structs. List of modified rr nodes is \n"
"not empty.\n");
exit(1);
}
if(heap_tail != 1)
{
printf("Error in init_route_structs. Heap is not empty.\n");
exit(1);
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void invalidate_heap_entries | ( | int | sink_node, |
| int | ipin_node | ||
| ) |
Marks all the heap entries consisting of sink_node, where it was reached via ipin_node, as invalid (OPEN). Used only by the breadth_first router and even then only in rare circumstances.
Definition at line 1197 of file route_common.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 1; i < heap_tail; i++)
{
if(heap[i]->index == sink_node
&& heap[i]->u.prev_node == ipin_node)
heap[i]->index = OPEN; /* Invalid. */
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| boolean is_empty_heap | ( | void | ) |
WMF: peeking accessor :)
Definition at line 1080 of file route_common.c.
{
return (heap_tail == 1);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void load_route_bb | ( | int | bb_factor | ) | [static] |
This routine loads the bounding box arrays used to limit the space searched by the maze router when routing each net. The search is limited to channels contained with the net bounding box expanded by bb_factor channels on each side. For example, if bb_factor is 0, the maze router must route each net within its bounding box. If bb_factor = nx, the maze router will search every channel in the FPGA if necessary. The bounding boxes returned by this routine are different from the ones used by the placer in that they are clipped to lie within (0,0) and (nx+1,ny+1) rather than (1,1) and (nx,ny).
Definition at line 974 of file route_common.c.
{
int k, xmax, ymax, xmin, ymin, x, y, inet;
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
x = block[clb_net[inet].node_block[0]].x;
y = block[clb_net[inet].node_block[0]].y + block[clb_net[inet].node_block[0]].type->pin_height[clb_net[inet].node_block_pin[0]];
xmin = x;
ymin = y;
xmax = x;
ymax = y;
for(k = 1; k <= clb_net[inet].num_sinks; k++)
{
x = block[clb_net[inet].node_block[k]].x;
y = block[clb_net[inet].node_block[k]].y + block[clb_net[inet].node_block[k]].type->pin_height[clb_net[inet].node_block_pin[k]];
if(x < xmin)
{
xmin = x;
}
else if(x > xmax)
{
xmax = x;
}
if(y < ymin)
{
ymin = y;
}
else if(y > ymax)
{
ymax = y;
}
}
/* Want the channels on all 4 sides to be usuable, even if bb_factor = 0. */
xmin -= 1;
ymin -= 1;
/* Expand the net bounding box by bb_factor, then clip to the physical *
* chip area. */
route_bb[inet].xmin = max(xmin - bb_factor, 0);
route_bb[inet].xmax = min(xmax + bb_factor, nx + 1);
route_bb[inet].ymin = max(ymin - bb_factor, 0);
route_bb[inet].ymax = min(ymax + bb_factor, ny + 1);
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void mark_ends | ( | int | inet | ) |
Mark all the SINKs of this net as targets by setting their target flags to the number of times the net must connect to each SINK. Note that this number can occassionally be greater than 1 -- think of connecting the same net to two inputs of an and-gate (and-gate inputs are logically equivalent, so both will connect to the same SINK).
Definition at line 636 of file route_common.c.
{
int ipin, inode;
for(ipin = 1; ipin <= clb_net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++)
{
inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][ipin];
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag++;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void node_to_heap | ( | int | inode, |
| float | cost, | ||
| int | prev_node, | ||
| int | prev_edge, | ||
| float | backward_path_cost, | ||
| float | R_upstream | ||
| ) |
Puts an rr_node on the heap, if the new cost given is lower than the current path_cost to this channel segment. The index of its predecessor is stored to make traceback easy. The index of the edge used to get from its predecessor to it is also stored to make timing analysis, etc. easy. The backward_path_cost and R_upstream values are used only by the timing-driven router -- the breadth-first router ignores them.
Definition at line 656 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_heap *hptr;
if(cost >= rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost)
return;
hptr = alloc_heap_data();
hptr->index = inode;
hptr->cost = cost;
hptr->u.prev_node = prev_node;
hptr->prev_edge = prev_edge;
hptr->backward_path_cost = backward_path_cost;
hptr->R_upstream = R_upstream;
add_to_heap(hptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void pathfinder_update_cost | ( | float | pres_fac, |
| float | acc_fac | ||
| ) |
This routine recomputes the pres_cost and acc_cost of each routing resource for the pathfinder algorithm after all nets have been routed. It updates the accumulated cost to by adding in the number of extra signals sharing a resource right now (i.e. after each complete iteration) times acc_fac. It also updates pres_cost, since pres_fac may have changed. THIS ROUTINE ASSUMES THE OCCUPANCY VALUES IN RR_NODE ARE UP TO DATE.
Definition at line 428 of file route_common.c.
{
int inode, occ, capacity;
for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++)
{
occ = rr_node[inode].occ;
capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity;
if(occ > capacity)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost +=
(occ - capacity) * acc_fac;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost =
1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) * pres_fac;
}
/* If occ == capacity, we don't need to increase acc_cost, but a change *
* in pres_fac could have made it necessary to recompute the cost anyway. */
else if(occ == capacity)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1. + pres_fac;
}
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void pathfinder_update_one_cost | ( | struct s_trace * | route_segment_start, |
| int | add_or_sub, | ||
| float | pres_fac | ||
| ) |
This routine updates the occupancy and pres_cost of the rr_nodes that are affected by the portion of the routing of one net that starts at route_segment_start. If route_segment_start is trace_head[inet], the cost of all the nodes in the routing of net inet are updated. If add_or_sub is -1 the net (or net portion) is ripped up, if it is 1 the net is added to the routing. The size of pres_fac determines how severly oversubscribed rr_nodes are penalized.
Definition at line 372 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_trace *tptr;
int inode, occ, capacity;
tptr = route_segment_start;
if(tptr == NULL) /* No routing yet. */
return;
for(;;)
{
inode = tptr->index;
occ = rr_node[inode].occ + add_or_sub;
capacity = rr_node[inode].capacity;
rr_node[inode].occ = occ;
/* pres_cost is Pn in the Pathfinder paper. I set my pres_cost according to *
* the overuse that would result from having ONE MORE net use this routing *
* node. */
if(occ < capacity)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.;
}
else
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost =
1. + (occ + 1 - capacity) * pres_fac;
}
if(rr_node[inode].type == SINK)
{
tptr = tptr->next; /* Skip next segment. */
if(tptr == NULL)
break;
}
tptr = tptr->next;
} /* End while loop -- did an entire traceback. */
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void print_route | ( | char * | route_file | ) |
Prints out the routing to file route_file.
Definition at line 1293 of file route_common.c.
{
int inet, inode, ipin, bnum, ilow, jlow, node_block_pin, iclass;
t_rr_type rr_type;
struct s_trace *tptr;
char *name_type[] =
{ "SOURCE", "SINK", "IPIN", "OPIN", "CHANX", "CHANY", "INTRA_CLUSTER_EDGE" };
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(route_file, "w");
fprintf(fp, "Array size: %d x %d logic blocks.\n", nx, ny);
fprintf(fp, "\nRouting:");
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
if(clb_net[inet].is_global == FALSE)
{
if(clb_net[inet].num_sinks == FALSE)
{
fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s)\n\n", inet, clb_net[inet].name);
fprintf(fp, "\n\n Used in local cluster only, reserved one CLB pin\n\n");
} else {
fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s)\n\n", inet, clb_net[inet].name);
tptr = trace_head[inet];
while(tptr != NULL)
{
inode = tptr->index;
rr_type = rr_node[inode].type;
ilow = rr_node[inode].xlow;
jlow = rr_node[inode].ylow;
fprintf(fp, "%6s (%d,%d) ", name_type[rr_type],
ilow, jlow);
if((ilow != rr_node[inode].xhigh) || (jlow !=
rr_node
[inode].
yhigh))
fprintf(fp, "to (%d,%d) ",
rr_node[inode].xhigh,
rr_node[inode].yhigh);
switch (rr_type)
{
case IPIN:
case OPIN:
if(grid[ilow][jlow].type == IO_TYPE)
{
fprintf(fp, " Pad: ");
}
else
{ /* IO Pad. */
fprintf(fp, " Pin: ");
}
break;
case CHANX:
case CHANY:
fprintf(fp, " Track: ");
break;
case SOURCE:
case SINK:
if(grid[ilow][jlow].type == IO_TYPE)
{
fprintf(fp, " Pad: ");
}
else
{ /* IO Pad. */
fprintf(fp, " Class: ");
}
break;
default:
printf
("Error in print_route: Unexpected traceback element "
"type: %d (%s).\n", rr_type,
name_type[rr_type]);
exit(1);
break;
}
fprintf(fp, "%d ", rr_node[inode].ptc_num);
/* Uncomment line below if you're debugging and want to see the switch types *
* used in the routing. */
/* fprintf (fp, "Switch: %d", tptr->iswitch); */
fprintf(fp, "\n");
tptr = tptr->next;
}
}
}
else
{ /* Global net. Never routed. */
fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s): global net connecting:\n\n",
inet, clb_net[inet].name);
for(ipin = 0; ipin <= clb_net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++)
{
bnum = clb_net[inet].node_block[ipin];
node_block_pin = clb_net[inet].node_block_pin[ipin];
iclass =
block[bnum].type->pin_class[node_block_pin];
fprintf(fp,
"Block %s (#%d) at (%d, %d), Pin class %d.\n",
block[bnum].name, bnum, block[bnum].x,
block[bnum].y, iclass);
}
}
}
fclose(fp);
#ifdef CREATE_ECHO_FILES
fp = my_fopen("mem.echo", "w", 0);
fprintf(fp, "\nNum_heap_allocated: %d Num_trace_allocated: %d\n",
num_heap_allocated, num_trace_allocated);
fprintf(fp, "Num_linked_f_pointer_allocated: %d\n",
num_linked_f_pointer_allocated);
fclose(fp);
#endif /* CREATE_ECHO_FILES */
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void reserve_locally_used_opins | ( | float | pres_fac, |
| boolean | rip_up_local_opins, | ||
| t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 1426 of file route_common.c.
{
/* In the past, this function implicitly allowed LUT duplication when there are free LUTs.
This was especially important for logical equivalence; however, now that we have a very general
logic cluster, it does not make sense to allow LUT duplication implicitly. we'll need to look into how we want to handle this case
*/
int iblk, num_local_opin, inode, from_node, iconn, num_edges, to_node;
int iclass, ipin;
float cost;
struct s_heap *heap_head_ptr;
t_type_ptr type;
if(rip_up_local_opins)
{
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opin =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
/* Always 0 for pads and for RECEIVER (IPIN) classes */
for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opin; ipin++)
{
inode =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].
list[ipin];
adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost(inode, -1,
pres_fac);
}
}
}
}
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opin =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
/* Always 0 for pads and for RECEIVER (IPIN) classes */
if(num_local_opin != 0)
{ /* Have to reserve (use) some OPINs */
from_node = rr_blk_source[iblk][iclass];
num_edges = rr_node[from_node].num_edges;
for(iconn = 0; iconn < num_edges; iconn++)
{
to_node = rr_node[from_node].edges[iconn];
cost = get_rr_cong_cost(to_node);
node_to_heap(to_node, cost, OPEN, OPEN,
0., 0.);
}
for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opin; ipin++)
{
heap_head_ptr = get_heap_head();
inode = heap_head_ptr->index;
adjust_one_rr_occ_and_pcost(inode, 1,
pres_fac);
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].
list[ipin] = inode;
free_heap_data(heap_head_ptr);
}
empty_heap();
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void reset_path_costs | ( | void | ) |
The routine sets the path_cost to HUGE_FLOAT for all channel segments touched by previous routing phases.
Definition at line 572 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_linked_f_pointer *mod_ptr;
#ifdef DEBUG
int num_mod_ptrs;
#endif
/* The traversal method below is slightly painful to make it faster. */
if(rr_modified_head != NULL)
{
mod_ptr = rr_modified_head;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_mod_ptrs = 1;
#endif
while(mod_ptr->next != NULL)
{
*(mod_ptr->fptr) = HUGE_FLOAT;
mod_ptr = mod_ptr->next;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_mod_ptrs++;
#endif
}
*(mod_ptr->fptr) = HUGE_FLOAT; /* Do last one. */
/* Reset the modified list and put all the elements back in the free *
* list. */
mod_ptr->next = linked_f_pointer_free_head;
linked_f_pointer_free_head = rr_modified_head;
rr_modified_head = NULL;
#ifdef DEBUG
num_linked_f_pointer_allocated -= num_mod_ptrs;
#endif
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void reset_rr_node_route_structs | ( | void | ) |
Allocates some extra information about each rr_node that is used only during routing.
Definition at line 933 of file route_common.c.
{
int inode;
assert(rr_node_route_inf != NULL);
for(inode = 0; inode < num_rr_nodes; inode++)
{
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = NO_PREVIOUS;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge = NO_PREVIOUS;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].pres_cost = 1.;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].acc_cost = 1.;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = HUGE_FLOAT;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag = 0;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void restore_routing | ( | struct s_trace ** | best_routing, |
| t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally, | ||
| t_ivec ** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally | ||
| ) |
Deallocates any current routing in trace_head, and replaces it with the routing in best_routing. Best_routing is set to NULL to show that it no longer points to a valid routing. NOTE: trace_tail is not restored -- it is set to all NULLs since it is only used in update_traceback. If you need trace_tail restored, modify this routine. Also restores the locally used opin data.
Definition at line 168 of file route_common.c.
{
int inet, iblk, ipin, iclass, num_local_opins;
t_type_ptr type;
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
/* Free any current routing. */
free_traceback(inet);
/* Set the current routing to the saved one. */
trace_head[inet] = best_routing[inet];
best_routing[inet] = NULL; /* No stored routing. */
}
/* Save which OPINs are locally used. */
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opins =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opins; ipin++)
{
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].list[ipin] =
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].
list[ipin];
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void save_routing | ( | struct s_trace ** | best_routing, |
| t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally, | ||
| t_ivec ** | saved_clb_opins_used_locally | ||
| ) |
This routing frees any routing currently held in best routing, then copies over the current routing (held in trace_head), and finally sets trace_head and trace_tail to all NULLs so that the connection to the saved routing is broken. This is necessary so that the next iteration of the router does not free the saved routing elements. Also saves any data about locally used clb_opins, since this is also part of the routing.
Definition at line 109 of file route_common.c.
{
int inet, iblk, iclass, ipin, num_local_opins;
struct s_trace *tptr, *tempptr;
t_type_ptr type;
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
/* Free any previously saved routing. It is no longer best. */
tptr = best_routing[inet];
while(tptr != NULL)
{
tempptr = tptr->next;
free_trace_data(tptr);
tptr = tempptr;
}
/* Save a pointer to the current routing in best_routing. */
best_routing[inet] = trace_head[inet];
/* Set the current (working) routing to NULL so the current trace *
* elements won't be reused by the memory allocator. */
trace_head[inet] = NULL;
trace_tail[inet] = NULL;
}
/* Save which OPINs are locally used. */
for(iblk = 0; iblk < num_blocks; iblk++)
{
type = block[iblk].type;
for(iclass = 0; iclass < type->num_class; iclass++)
{
num_local_opins =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].nelem;
for(ipin = 0; ipin < num_local_opins; ipin++)
{
saved_clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].
list[ipin] =
clb_opins_used_locally[iblk][iclass].
list[ipin];
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
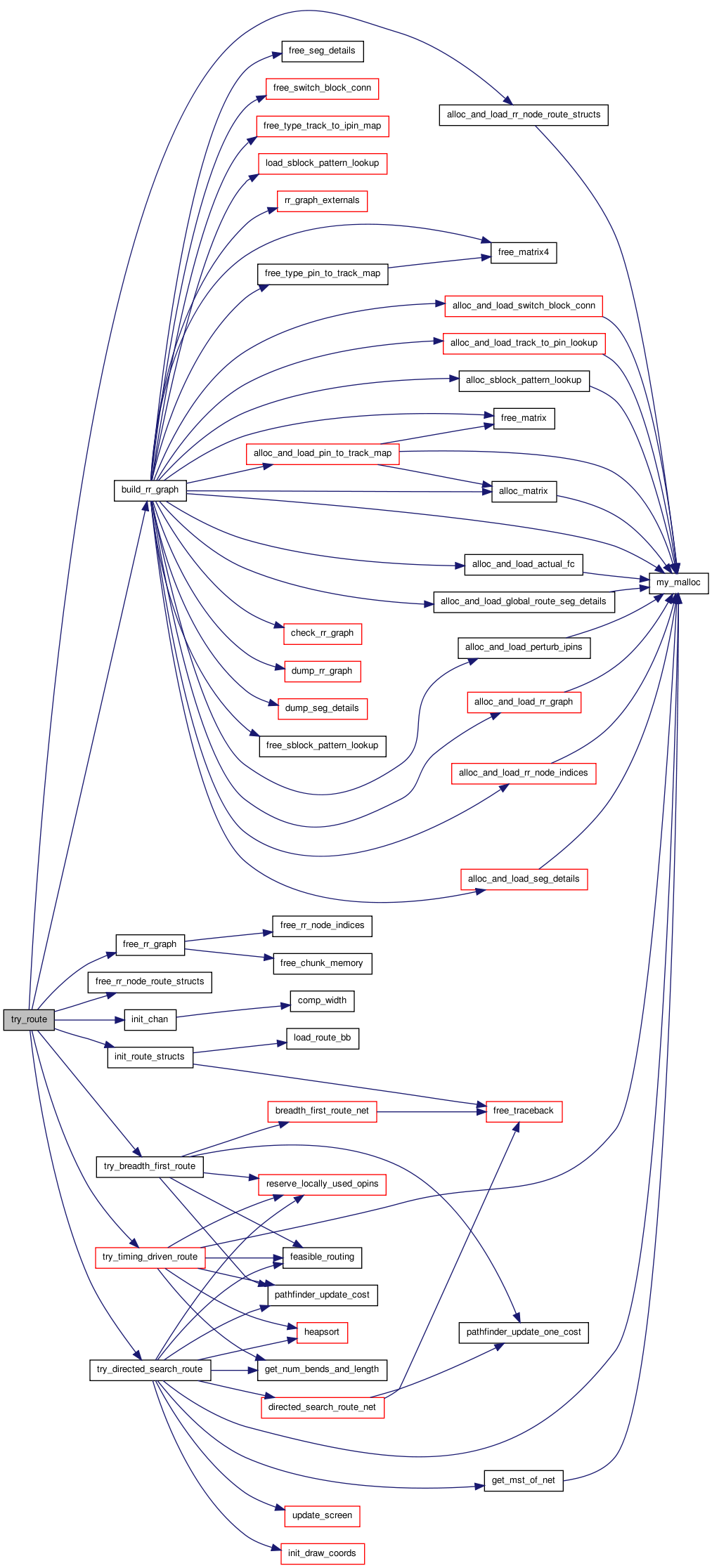
Here is the caller graph for this function:| boolean try_route | ( | int | width_fac, |
| struct s_router_opts | router_opts, | ||
| struct s_det_routing_arch | det_routing_arch, | ||
| t_segment_inf * | segment_inf, | ||
| t_timing_inf | timing_inf, | ||
| float ** | net_slack, | ||
| float ** | net_delay, | ||
| t_chan_width_dist | chan_width_dist, | ||
| t_ivec ** | clb_opins_used_locally, | ||
| t_mst_edge ** | mst, | ||
| boolean * | Fc_clipped | ||
| ) |
Attempts a routing via an iterated maze router algorithm. Width_fac specifies the relative width of the channels, while the members of router_opts determine the value of the costs assigned to routing resource node, etc. det_routing_arch describes the detailed routing architecture (connection and switch boxes) of the FPGA; it is used only if a DETAILED routing has been selected.
Definition at line 253 of file route_common.c.
{
int tmp;
clock_t begin, end;
boolean success;
t_graph_type graph_type;
if(router_opts.route_type == GLOBAL) {
graph_type = GRAPH_GLOBAL;
} else {
graph_type = (det_routing_arch.directionality ==
BI_DIRECTIONAL ? GRAPH_BIDIR : GRAPH_UNIDIR);
}
/* Set the channel widths */
init_chan(width_fac, chan_width_dist);
/* Free any old routing graph, if one exists. */
free_rr_graph();
begin = clock();
/* Set up the routing resource graph defined by this FPGA architecture. */
build_rr_graph(graph_type,
num_types, type_descriptors, nx, ny, grid,
chan_width_x[0], NULL,
det_routing_arch.switch_block_type, det_routing_arch.Fs,
det_routing_arch.num_segment, det_routing_arch.num_switch, segment_inf,
det_routing_arch.global_route_switch,
det_routing_arch.delayless_switch, timing_inf,
det_routing_arch.wire_to_ipin_switch,
router_opts.base_cost_type, &tmp);
end = clock();
#ifdef CLOCKS_PER_SEC
printf("build rr_graph took %g seconds\n", (float)(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
#else
printf("build rr_graph took %g seconds\n", (float)(end - begin) / CLK_PER_SEC);
#endif
/* Allocate and load some additional rr_graph information needed only by *
* the router. */
alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs();
init_route_structs(router_opts.bb_factor);
if(router_opts.router_algorithm == BREADTH_FIRST)
{
printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: BREADTH_FIRST.\n");
success =
try_breadth_first_route(router_opts, clb_opins_used_locally,
width_fac);
}
else if(router_opts.router_algorithm == TIMING_DRIVEN)
{ /* TIMING_DRIVEN route */
printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: TIMING_DRIVEN.\n");
assert(router_opts.route_type != GLOBAL);
success =
try_timing_driven_route(router_opts, net_slack, net_delay,
clb_opins_used_locally);
}
else
{ /* Directed Search Routability Driven */
printf("Confirming Router Algorithm: DIRECTED_SEARCH.\n");
success =
try_directed_search_route(router_opts, clb_opins_used_locally,
width_fac, mst);
}
free_rr_node_route_structs();
return (success);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
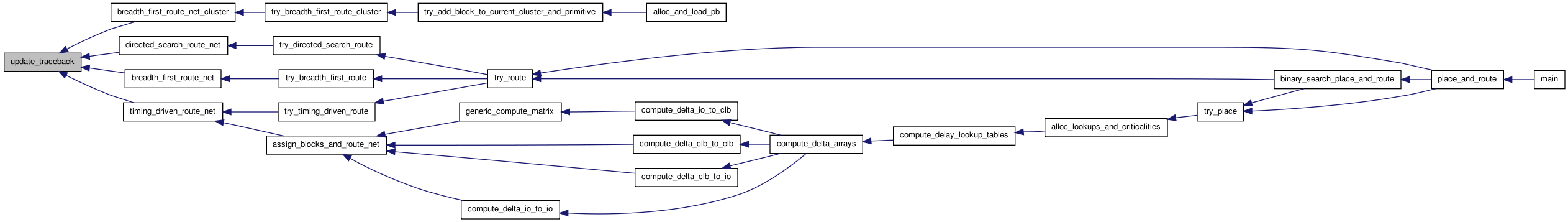
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:This routine adds the most recently finished wire segment to the traceback linked list. The first connection starts with the net SOURCE and begins at the structure pointed to by trace_head[inet]. Each connection ends with a SINK. After each SINK, the next connection begins (if the net has more than 2 pins). The first element after the SINK gives the routing node on a previous piece of the routing, which is the link from the existing net to this new piece of the net. In each traceback I start at the end of a path and trace back through its predecessors to the beginning. I have stored information on the predecesser of each node to make traceback easy -- this sacrificies some memory for easier code maintenance. This routine returns a pointer to the first "new" node in the traceback (node not previously in trace).
Definition at line 503 of file route_common.c.
{
struct s_trace *tptr, *prevptr, *temptail, *ret_ptr;
int inode;
short iedge;
#ifdef DEBUG
t_rr_type rr_type;
#endif
inode = hptr->index;
#ifdef DEBUG
rr_type = rr_node[inode].type;
if(rr_type != SINK)
{
printf("Error in update_traceback. Expected type = SINK (%d).\n",
SINK);
printf("Got type = %d while tracing back net %d.\n", rr_type,
inet);
exit(1);
}
#endif
tptr = alloc_trace_data(); /* SINK on the end of the connection */
tptr->index = inode;
tptr->iswitch = OPEN;
tptr->next = NULL;
temptail = tptr; /* This will become the new tail at the end */
/* of the routine. */
/* Now do it's predecessor. */
inode = hptr->u.prev_node;
iedge = hptr->prev_edge;
while(inode != NO_PREVIOUS)
{
prevptr = alloc_trace_data();
prevptr->index = inode;
prevptr->iswitch = rr_node[inode].switches[iedge];
prevptr->next = tptr;
tptr = prevptr;
iedge = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge;
inode = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node;
}
if(trace_tail[inet] != NULL)
{
trace_tail[inet]->next = tptr; /* Traceback ends with tptr */
ret_ptr = tptr->next; /* First new segment. */
}
else
{ /* This was the first "chunk" of the net's routing */
trace_head[inet] = tptr;
ret_ptr = tptr; /* Whole traceback is new. */
}
trace_tail[inet] = temptail;
return (ret_ptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Variable Documentation
Indexed from [1..heap_size]
Definition at line 30 of file route_common.c.
struct s_heap* heap_free_head = NULL [static] |
For managing my own list of currently free heap data structures.
Definition at line 35 of file route_common.c.
int heap_size [static] |
Number of slots in the heap array
Definition at line 31 of file route_common.c.
int heap_tail [static] |
Index of first unused slot in the heap array
Definition at line 32 of file route_common.c.
struct s_linked_f_pointer* linked_f_pointer_free_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 47 of file route_common.c.
[0..num_nets-1]. Limits area in which each net must be routed.
Definition at line 24 of file route_common.c.
struct s_linked_f_pointer* rr_modified_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 46 of file route_common.c.
| t_rr_node_route_inf* rr_node_route_inf = NULL |
[0..num_rr_nodes-1]
Definition at line 22 of file route_common.c.
struct s_trace* trace_free_head = NULL [static] |
For managing my own list of currently free trace data structures.
Definition at line 38 of file route_common.c.