#include <stdio.h>#include <assert.h>#include <string.h>#include "util.h"#include "physical_types.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "globals.h"#include "mst.h"#include "route_export.h"#include "route_common.h"#include "cluster_legality.h"#include "rr_graph.h" Include dependency graph for cluster_legality.c:
Include dependency graph for cluster_legality.c:Go to the source code of this file.
Function Documentation
| static boolean add_net_rr_terminal_cluster | ( | int | iblk_net, |
| t_pb * | primitive, | ||
| int | ilogical_block, | ||
| t_model_ports * | model_port, | ||
| int | ipin | ||
| ) | [static] |
Ensure at most one external input/clock source and one external output sink for net
Definition at line 84 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, net_pin;
t_port *prim_port;
const t_pb_type *pb_type;
boolean found;
int input_port;
int output_port;
int clock_port;
input_port = output_port = clock_port = 0;
pb_type = primitive->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
prim_port = NULL;
assert(pb_type->num_modes == 0);
found = FALSE;
/* TODO: This is inelegant design, I should change the primitive ports in pb_type to be input, output, or clock instead of this lookup */
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_ports && !found; i++) {
prim_port = &pb_type->ports[i];
if(pb_type->ports[i].model_port == model_port) {
found = TRUE;
} else {
if(prim_port->is_clock) {
clock_port++;
assert(prim_port->type == IN_PORT);
} else if(prim_port->type == IN_PORT) {
input_port++;
} else if(prim_port->type == OUT_PORT) {
output_port++;
} else {
assert(0);
}
}
}
if(!found) {
return FALSE;
}
if(ipin >= prim_port->num_pins) {
return FALSE;
} else {
net_pin = OPEN;
if(prim_port->is_clock) {
for(i = 1; i <= vpack_net[iblk_net].num_sinks; i++) {
if(vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block[i] == ilogical_block &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_port[i] == model_port->index &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_pin[i] == ipin) {
net_pin = i;
break;
}
}
assert(net_pin != OPEN);
net_rr_terminals[iblk_net][net_pin] =
primitive->pb_graph_node->clock_pins[clock_port][ipin].pin_count_in_cluster;
} else if(prim_port->type == IN_PORT) {
for(i = 1; i <= vpack_net[iblk_net].num_sinks; i++) {
if(vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block[i] == ilogical_block &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_port[i] == model_port->index &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_pin[i] == ipin) {
net_pin = i;
break;
}
}
assert(net_pin != OPEN);
net_rr_terminals[iblk_net][net_pin] =
primitive->pb_graph_node->input_pins[input_port][ipin].pin_count_in_cluster;
} else if(prim_port->type == OUT_PORT) {
i = 0;
if(vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block[i] == ilogical_block &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_port[i] == model_port->index &&
vpack_net[iblk_net].node_block_pin[i] == ipin) {
net_pin = i;
}
assert(net_pin != OPEN);
net_rr_terminals[iblk_net][net_pin] =
primitive->pb_graph_node->output_pins[output_port][ipin].pin_count_in_cluster;
} else {
assert(0);
}
return TRUE;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void alloc_and_load_cluster_legality_checker | ( | ) |
Legalizes routing for a cluster
Definition at line 218 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
best_routing = (struct s_trace **)my_calloc(num_logical_nets, sizeof(struct s_trace *));
nets_in_cluster = my_malloc(num_logical_nets * sizeof(int));
num_nets_in_cluster = 0;
num_nets = num_logical_nets;
/* inside a cluster, I do not consider rr_indexed_data cost, set to 1 since other costs are multiplied by it */
num_rr_indexed_data = 1;
rr_indexed_data = my_calloc(1, sizeof(t_rr_indexed_data));
rr_indexed_data[0].base_cost = 1;
/* alloc routing structures */
alloc_route_static_structs();
alloc_net_rr_terminals_cluster();
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void alloc_and_load_legalizer_for_cluster | ( | INP t_block * | clb, |
| INP int | clb_index, | ||
| INP const t_arch * | arch | ||
| ) |
Structure: Model external routing and internal routing
1. Model external routing num input pins == num external sources for input pins, fully connect them to input pins (simulates external routing) num output pins == num external sinks for output pins, fully connect them to output pins (simulates external routing) num clock pins == num external sources for clock pins, fully connect them to clock pins (simulates external routing) 2. Model internal routing
Definition at line 372 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
/* make each rr_node one correspond with pin and correspond with pin's index pin_count_in_cluster */
int i, j, k, m, index, pb_graph_rr_index;
int count_pins;
t_pb_type * pb_type;
t_pb_graph_node *pb_graph_node;
int ipin;
/* Create rr_graph */
pb_type = clb->type->pb_type;
pb_graph_node = clb->type->pb_graph_head;
num_rr_nodes = pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins + pb_type->num_input_pins +
pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_type->num_clock_pins;
if(num_rr_nodes > num_rr_intrinsic_cost) {
free(rr_intrinsic_cost);
rr_intrinsic_cost = my_calloc(num_rr_nodes, sizeof(float));
num_rr_intrinsic_cost = num_rr_nodes;
}
rr_node = my_calloc(num_rr_nodes, sizeof(t_rr_node));
clb->pb->rr_graph = rr_node;
alloc_and_load_rr_graph_for_pb_graph_node(pb_graph_node, arch, 0);
curr_cluster_index = clb_index;
/* Alloc and load rr_graph external sources and sinks */
ext_input_rr_node_index = pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
ext_output_rr_node_index = pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
ext_clock_rr_node_index = pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
max_ext_index = pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_type->num_clock_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_input_pins; i++) {
index = i + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
rr_node[index].type = SOURCE;
rr_node[index].fan_in = 0;
rr_node[index].num_edges = pb_type->num_input_pins;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].edges = my_malloc(rr_node[index].num_edges * sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].switches = my_calloc(rr_node[index].num_edges, sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
rr_intrinsic_cost[index] = 0;
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_output_pins; i++) {
index = i + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
rr_node[index].type = SINK;
rr_node[index].fan_in = pb_type->num_output_pins;
rr_node[index].num_edges = 0;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
rr_intrinsic_cost[index] = 0;
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_clock_pins; i++) {
index = i + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
rr_node[index].type = SOURCE;
rr_node[index].fan_in = 0;
rr_node[index].num_edges = pb_type->num_clock_pins;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].edges = my_malloc(rr_node[index].num_edges * sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].switches = my_calloc(rr_node[index].num_edges, sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
rr_intrinsic_cost[index] = 0;
}
ipin = 0;
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_input_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_input_pins[i]; j++) {
pb_graph_rr_index = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->num_input_pins; k++) {
index = k + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
rr_node[index].edges[ipin] = pb_graph_rr_index;
rr_node[index].switches[ipin] = arch->num_switches - 1;
}
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].pack_intrinsic_cost = MAX_SHORT; /* using an input pin should be made costly */
ipin++;
}
}
/* Must attach output pins to input pins because if a connection cannot fit using intra-cluster routing, it can also use external routing */
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_output_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_output_pins[i]; j++) {
count_pins = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_type->num_input_pins;
pb_graph_rr_index = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].edges = my_realloc(rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].edges,
(count_pins) * sizeof(int));
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].switches = my_realloc(rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].switches,
(count_pins) * sizeof(int));
ipin = 0;
for(k = 0; k < pb_graph_node->num_input_ports; k++) {
for(m = 0; m < pb_graph_node->num_input_pins[k]; m++) {
index = pb_graph_node->input_pins[k][m].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].edges[ipin + pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges] = index;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].switches[ipin + pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges] = arch->num_switches - 1;
ipin++;
}
}
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->num_output_pins; k++) {
index = k + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].edges[k + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges] = index;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].switches[k + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges] = arch->num_switches - 1;
}
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].num_edges += pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_type->num_input_pins;
rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[pb_graph_rr_index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
}
}
ipin = 0;
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_clock_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_clock_pins[i]; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->num_clock_pins; k++) {
index = k + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins;
pb_graph_rr_index = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].edges[ipin] = pb_graph_rr_index;
rr_node[index].switches[ipin] = arch->num_switches - 1;
}
ipin++;
}
}
alloc_and_load_rr_node_route_structs();
num_nets_in_cluster = 0;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void alloc_and_load_rr_graph_for_pb_graph_node | ( | INP t_pb_graph_node * | pb_graph_node, |
| INP const t_arch * | arch, | ||
| int | mode | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 254 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, j, k, index;
boolean is_primitive;
is_primitive = (pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_modes == 0);
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_input_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_input_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].pb_graph_pin = &pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j];
rr_node[index].fan_in = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].num_input_edges;
rr_node[index].num_edges = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].num_output_edges;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].edges = my_malloc(rr_node[index].num_edges * sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].switches = my_calloc(rr_node[index].num_edges, sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].net_num = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_node = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_edge = OPEN;
if(mode == 0) { /* default mode is the first mode */
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
} else {
rr_node[index].capacity = 0;
}
for(k = 0; k < pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].num_output_edges; k++) {
/* TODO: Intention was to do bus-based implementation here */
rr_node[index].edges[k] = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->output_pins[0]->pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].switches[k] = arch->num_switches - 1; /* last switch in arch switch properties is a delayless switch */
assert(pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->num_output_pins == 1);
}
rr_node[index].type = INTRA_CLUSTER_EDGE;
if(is_primitive) {
rr_node[index].type = SINK;
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_output_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_output_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].pb_graph_pin = &pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j];
rr_node[index].fan_in = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_input_edges;
rr_node[index].num_edges = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].edges = my_malloc(rr_node[index].num_edges * sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].switches = my_calloc(rr_node[index].num_edges, sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].net_num = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_node = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_edge = OPEN;
if(mode == 0) { /* Default mode is the first mode */
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
} else {
rr_node[index].capacity = 0;
}
for(k = 0; k < pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].num_output_edges; k++) {
/* TODO: Intention was to do bus-based implementation here */
rr_node[index].edges[k] = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->output_pins[0]->pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].switches[k] = arch->num_switches - 1;
assert(pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->num_output_pins == 1);
}
rr_node[index].type = INTRA_CLUSTER_EDGE;
if(is_primitive) {
rr_node[index].type = SOURCE;
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_clock_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_clock_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].pb_graph_pin = &pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j];
rr_node[index].fan_in = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].num_input_edges;
rr_node[index].num_edges = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].num_output_edges;
rr_node[index].pack_intrinsic_cost = 1 + (float)rr_node[index].num_edges / 5; /* need to normalize better than 5 */
rr_node[index].edges = my_malloc(rr_node[index].num_edges * sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].switches = my_calloc(rr_node[index].num_edges, sizeof(int));
rr_node[index].net_num = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_node = OPEN;
rr_node[index].prev_edge = OPEN;
if(mode == 0) { /* default mode is the first mode (useful for routing */
rr_node[index].capacity = 1;
} else {
rr_node[index].capacity = 0;
}
for(k = 0; k < pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].num_output_edges; k++) {
/* TODO: Intention was to do bus-based implementation here */
rr_node[index].edges[k] = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->output_pins[0]->pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].switches[k] = arch->num_switches - 1;
assert(pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].output_edges[k]->num_output_pins == 1);
}
rr_node[index].type = INTRA_CLUSTER_EDGE;
if(is_primitive) {
rr_node[index].type = SINK;
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_modes; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < pb_graph_node->pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb; k++) {
alloc_and_load_rr_graph_for_pb_graph_node(&pb_graph_node->child_pb_graph_nodes[i][j][k], arch, i);
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void alloc_net_rr_terminals_cluster | ( | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 800 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inet;
net_rr_terminals = (int **)my_malloc(num_logical_nets * sizeof(int *));
saved_net_rr_terminals = (int **)my_malloc(num_logical_nets * sizeof(int *));
for(inet = 0; inet < num_logical_nets; inet++)
{
net_rr_terminals[inet] =
(int *)my_chunk_malloc((vpack_net[inet].num_sinks + 1) *
sizeof(int), &rr_mem_chunk_list_head,
&chunk_bytes_avail,
&chunk_next_avail_mem);
saved_net_rr_terminals[inet] = (int *)my_malloc((vpack_net[inet].num_sinks + 1) * sizeof(int));
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void breadth_first_add_source_to_heap_cluster | ( | int | inet | ) | [static] |
Adds the SOURCE of this net to the heap. Used to start a net's routing.
Definition at line 766 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inode;
float cost;
inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][0]; /* SOURCE */
cost = get_rr_cong_cost(inode);
node_to_heap(inode, cost, NO_PREVIOUS, NO_PREVIOUS, OPEN, OPEN);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void breadth_first_expand_neighbours_cluster | ( | int | inode, |
| float | pcost, | ||
| int | inet, | ||
| boolean | first_time | ||
| ) | [static] |
Puts all the rr_nodes adjacent to inode on the heap. rr_nodes outside the expanded bounding box specified in route_bb are not added to the heap. pcost is the path_cost to get to inode.
Definition at line 741 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int iconn, to_node, num_edges;
float tot_cost;
num_edges = rr_node[inode].num_edges;
for(iconn = 0; iconn < num_edges; iconn++)
{
to_node = rr_node[inode].edges[iconn];
/*if(first_time) { */
tot_cost = pcost + get_rr_cong_cost(to_node) * rr_node_intrinsic_cost(to_node);
/*
} else {
tot_cost = pcost + get_rr_cong_cost(to_node);
}*/
node_to_heap(to_node, tot_cost, inode, iconn, OPEN, OPEN);
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void breadth_first_expand_trace_segment_cluster | ( | struct s_trace * | start_ptr, |
| int | remaining_connections_to_sink | ||
| ) | [static] |
Adds all the rr_nodes in the traceback segment starting at tptr (and continuing to the end of the traceback) to the heap with a cost of zero. This allows expansion to begin from the existing wiring. The remaining_connections_to_sink value is 0 if the route segment ending at this location is the last one to connect to the SINK ending the route segment. This is the usual case. If it is not the last connection this net must make to this SINK, I have a hack to ensure the next connection to this SINK goes through a different IPIN. Without this hack, the router would always put all the connections from this net to this SINK through the same IPIN. With LUTs or cluster-based logic blocks, you should never have a net connecting to two logically-equivalent pins on the same logic block, so the hack will never execute. If your logic block is an and-gate, however, nets might connect to two and-inputs on the same logic block, and since the and-inputs are logically-equivalent, this means two connections to the same SINK.
Definition at line 717 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
struct s_trace *tptr;
tptr = start_ptr;
/* For intra-cluster routing, logical equivalence does not occur, so it is impossible to get a value bigger than 0 */
assert(remaining_connections_to_sink == 0);
while(tptr != NULL)
{
node_to_heap(tptr->index, 0., NO_PREVIOUS, NO_PREVIOUS,
OPEN, OPEN);
tptr = tptr->next;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
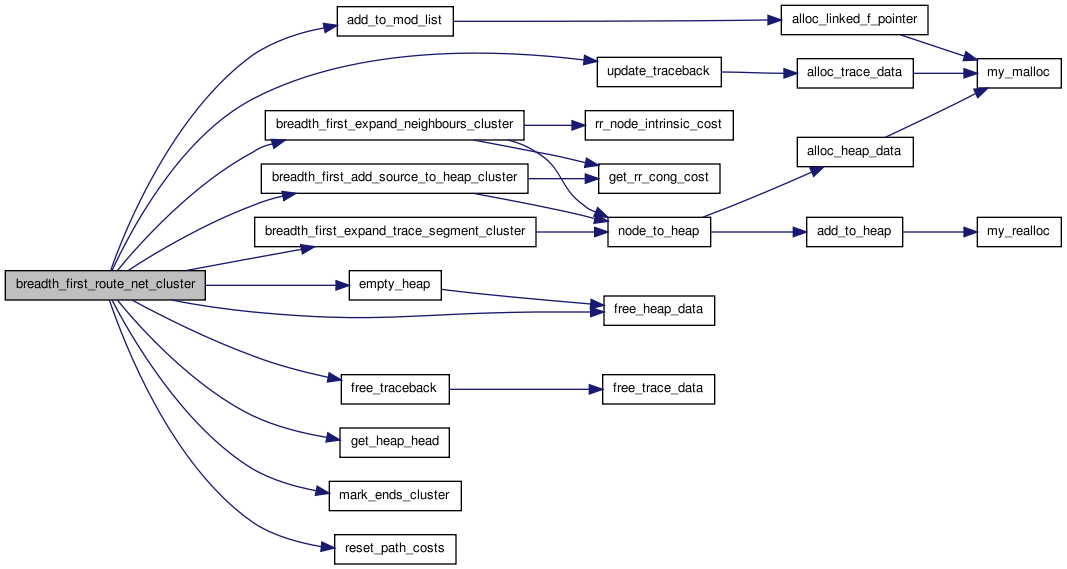
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean breadth_first_route_net_cluster | ( | int | inet | ) | [static] |
Uses a maze routing (Dijkstra's) algorithm to route a net. The net begins at the net output, and expands outward until it hits a target pin. The algorithm is then restarted with the entire first wire segment included as part of the source this time. For an n-pin net, the maze router is invoked n-1 times to complete all the connections. Inet is the index of the net to be routed. If this routine finds that a net *cannot* be connected (due to a complete lack of potential paths, rather than congestion), it returns FALSE, as routing is impossible on this architecture. Otherwise it returns TRUE.
Definition at line 620 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, inode, prev_node, remaining_connections_to_sink;
float pcost, new_pcost;
struct s_heap *current;
struct s_trace *tptr;
boolean first_time;
free_traceback(inet);
breadth_first_add_source_to_heap_cluster(inet);
mark_ends_cluster(inet);
tptr = NULL;
remaining_connections_to_sink = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; i++)
{ /* Need n-1 wires to connect n pins */
/* Do not connect open terminals */
if(net_rr_terminals[inet][i] == OPEN)
continue;
/* Expand and begin routing */
breadth_first_expand_trace_segment_cluster(tptr,
remaining_connections_to_sink);
current = get_heap_head();
if(current == NULL)
{ /* Infeasible routing. No possible path for net. */
reset_path_costs(); /* Clean up before leaving. */
return (FALSE);
}
inode = current->index;
while(rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag == 0)
{
pcost = rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost;
new_pcost = current->cost;
if(pcost > new_pcost)
{ /* New path is lowest cost. */
rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = new_pcost;
prev_node = current->u.prev_node;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = prev_node;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge =
current->prev_edge;
first_time = FALSE;
if(pcost > 0.99 * HUGE_FLOAT) /* First time touched. */ {
add_to_mod_list(&rr_node_route_inf[inode].
path_cost);
first_time = TRUE;
}
breadth_first_expand_neighbours_cluster(inode, new_pcost, inet, first_time);
}
free_heap_data(current);
current = get_heap_head();
if(current == NULL)
{ /* Impossible routing. No path for net. */
reset_path_costs();
return (FALSE);
}
inode = current->index;
}
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag--; /* Connected to this SINK. */
remaining_connections_to_sink =
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag;
tptr = update_traceback(current, inet);
free_heap_data(current);
}
empty_heap();
reset_path_costs();
return (TRUE);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
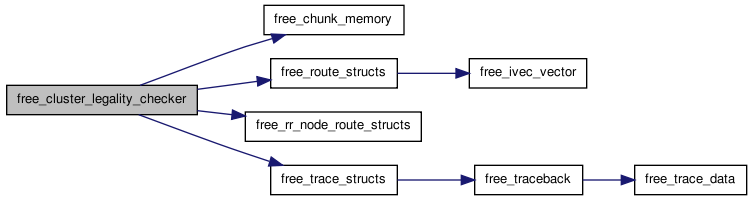
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_cluster_legality_checker | ( | ) |
Definition at line 235 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inet;
free(rr_indexed_data);
free_rr_node_route_structs();
free_route_structs(NULL);
free_trace_structs();
free_chunk_memory(rr_mem_chunk_list_head);
rr_mem_chunk_list_head = NULL;
for(inet = 0; inet < num_logical_nets; inet++)
{
free(saved_net_rr_terminals[inet]);
}
free(net_rr_terminals);
free(saved_net_rr_terminals);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_legalizer_for_cluster | ( | INP t_block * | clb | ) |
Definition at line 500 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i;
free_rr_node_route_structs();
for(i = 0; i < num_rr_nodes; i++) {
if(clb->pb->rr_graph[i].edges != NULL) {
free(clb->pb->rr_graph[i].edges);
}
if(clb->pb->rr_graph[i].switches != NULL) {
free(clb->pb->rr_graph[i].switches);
}
}
free(clb->pb->rr_graph);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_num_violated_nets | ( | ) | [static] |
| static boolean is_net_in_cluster | ( | INP int | inet | ) | [static] |
load rr_node for source and sinks of net if exists, return FALSE otherwise. Todo: Note this is an inefficient way to determine port, better to use a lookup, worry about this if runtime becomes an issue
Definition at line 73 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++) {
if(nets_in_cluster[i] == inet) {
return TRUE;
}
}
return FALSE;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| boolean is_pin_open | ( | int | i | ) |
Definition at line 1051 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
return (rr_node[i].occ == 0);
}
| static void mark_ends_cluster | ( | int | inet | ) | [static] |
Mark all the SINKs of this net as targets by setting their target flags to the number of times the net must connect to each SINK. Note that this number can occassionally be greater than 1 -- think of connecting the same net to two inputs of an and-gate (and-gate inputs are logically equivalent, so both will connect to the same SINK).
Definition at line 784 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int ipin, inode;
for(ipin = 1; ipin <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++)
{
inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][ipin];
if(inode == OPEN)
continue;
rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag++;
assert(rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag == 1);
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void print_intra_cluster_route | ( | char * | route_file | ) | [static] |
Prints out the routing to file route_file.
Definition at line 1058 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inet, inode;
t_rr_type rr_type;
struct s_trace *tptr;
char *name_type[] =
{ "SOURCE", "SINK", "IPIN", "OPIN", "CHANX", "CHANY", "INTRA_CLUSTER_EDGE" };
FILE *fp;
fp = my_fopen(route_file, "w", 0);
fprintf(fp, "\nRouting:");
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++)
{
if(vpack_net[inet].num_sinks == FALSE)
{
fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s)\n\n", inet, vpack_net[inet].name);
fprintf(fp, "\n\n Used in local cluster only, reserved one CLB pin\n\n");
} else if(trace_head[inet]){
fprintf(fp, "\n\nNet %d (%s)\n\n", inet, vpack_net[inet].name);
tptr = trace_head[inet];
while(tptr != NULL)
{
inode = tptr->index;
rr_type = rr_node[inode].type;
fprintf(fp, "%6s %d ", name_type[rr_type], inode);
/* Uncomment line below if you're debugging and want to see the switch types *
* used in the routing. */
/* fprintf (fp, "Switch: %d", tptr->iswitch); */
fprintf(fp, "\n");
tptr = tptr->next;
}
}
}
fclose(fp);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:| static boolean reload_ext_net_rr_terminal_cluster | ( | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 169 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, j, net_index;
boolean has_ext_sink, has_ext_source;
int curr_ext_output, curr_ext_input, curr_ext_clock;
curr_ext_input = ext_input_rr_node_index;
curr_ext_output = ext_output_rr_node_index;
curr_ext_clock = ext_clock_rr_node_index;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++)
{
net_index = nets_in_cluster[i];
has_ext_sink = FALSE;
has_ext_source = (logical_block[vpack_net[net_index].node_block[0]].clb_index != curr_cluster_index);
if(has_ext_source) {
/* Instantiate a source of this net */
if(vpack_net[net_index].is_global) {
net_rr_terminals[net_index][0] = curr_ext_clock;
curr_ext_clock++;
} else {
net_rr_terminals[net_index][0] = curr_ext_input;
curr_ext_input++;
}
}
for(j = 1; j <= vpack_net[net_index].num_sinks; j++) {
if(logical_block[vpack_net[net_index].node_block[j]].clb_index != curr_cluster_index) {
if(has_ext_sink || has_ext_source) {
/* Only need one node driving external routing, either this cluster drives external routing or another cluster does it */
net_rr_terminals[net_index][j] = OPEN;
} else {
/* External sink, only need to route once, externally routing will take care of the rest */
net_rr_terminals[net_index][j] = curr_ext_output;
curr_ext_output++;
has_ext_sink = TRUE;
}
}
}
if( curr_ext_input > ext_output_rr_node_index ||
curr_ext_output > ext_clock_rr_node_index ||
curr_ext_clock > max_ext_index) {
/* failed, not enough pins of proper type, overran index */
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void reset_legalizer_for_cluster | ( | t_block * | clb | ) |
Definition at line 515 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++) {
free_traceback(nets_in_cluster[i]);
trace_head[nets_in_cluster[i]] = best_routing[nets_in_cluster[i]];
free_traceback(nets_in_cluster[i]);
best_routing[nets_in_cluster[i]] = NULL;
}
free_rr_node_route_structs();
num_nets_in_cluster = 0;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void restore_routing_cluster | ( | ) | [static] |
Deallocates any current routing in trace_head, and replaces it with the routing in best_routing. Best_routing is set to NULL to show that it no longer points to a valid routing. NOTE: trace_tail is not restored -- it is set to all NULLs since it is only used in update_traceback. If you need trace_tail restored, modify this routine. Also restores the locally used opin data.
Definition at line 967 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inet, i, j;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++)
{
inet = nets_in_cluster[i];
pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], -1, pres_fac);
/* Free any current routing. */
free_traceback(inet);
/* Set the current routing to the saved one. */
trace_head[inet] = best_routing[inet];
best_routing[inet] = NULL; /* No stored routing. */
/* restore net terminals */
for(j = 0; j <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; j++) {
net_rr_terminals[inet][j] = saved_net_rr_terminals[inet][j];
}
/* restore old routing */
pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], 1, pres_fac);
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static float rr_node_intrinsic_cost | ( | int | inode | ) | [static] |
This is a tie breaker to avoid using nodes with more edges whenever possible
Definition at line 1105 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
float value;
value = rr_node[inode].pack_intrinsic_cost;
return value;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void save_and_reset_routing_cluster | ( | ) | [static] |
This routing frees any routing currently held in best routing, then copies over the current routing (held in trace_head), and finally sets trace_head and trace_tail to all NULLs so that the connection to the saved routing is broken. This is necessary so that the next iteration of the router does not free the saved routing elements. Also, the routing path costs and net_rr_terminals is stripped from the existing rr_graph so that the saved routing does not affect the graph
Definition at line 930 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int inet, i, j;
struct s_trace *tempptr;
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++)
{
inet = nets_in_cluster[i];
for(j = 0; j <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; j++) {
saved_net_rr_terminals[inet][j] = net_rr_terminals[inet][j];
}
/* Free any previously saved routing. It is no longer best. */
/* Also Save a pointer to the current routing in best_routing. */
pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], -1, pres_fac);
tempptr = trace_head[inet];
trace_head[inet] = best_routing[inet];
free_traceback(inet);
best_routing[inet] = tempptr;
/* Set the current (working) routing to NULL so the current trace *
* elements won't be reused by the memory allocator. */
trace_head[inet] = NULL;
trace_tail[inet] = NULL;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void save_cluster_solution | ( | ) |
This routine updates the occupancy and pres_cost of the rr_nodes that are affected by the portion of the routing of one net that starts at route_segment_start. If route_segment_start is trace_head[inet], the cost of all the nodes in the routing of net inet are updated. If add_or_sub is -1 the net (or net portion) is ripped up, if it is 1 the net is added to the routing. The size of pres_fac determines how severly oversubscribed rr_nodes are penalized.
Definition at line 1002 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, j, net_index;
struct s_trace *tptr, *prev;
int inode;
for(i = 0; i < max_ext_index; i++) {
rr_node[i].net_num = OPEN;
rr_node[i].prev_edge = OPEN;
rr_node[i].prev_node = OPEN;
}
for(i = 0; i < num_nets_in_cluster; i++) {
prev = NULL;
net_index = nets_in_cluster[i];
tptr = trace_head[net_index];
if(tptr == NULL) /* No routing yet. */
return;
for(;;)
{
inode = tptr->index;
rr_node[inode].net_num = net_index;
if(prev != NULL) {
rr_node[inode].prev_node = prev->index;
for(j = 0; j < rr_node[prev->index].num_edges; j++) {
if(rr_node[prev->index].edges[j] == inode) {
rr_node[inode].prev_edge = j;
break;
}
}
assert(j != rr_node[prev->index].num_edges);
} else {
rr_node[inode].prev_node = OPEN;
rr_node[inode].prev_edge = OPEN;
}
if(rr_node[inode].type == SINK)
{
tptr = tptr->next; /* Skip next segment. */
if(tptr == NULL)
break;
}
prev = tptr;
tptr = tptr->next;
} /* End while loop -- did an entire traceback. */
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void set_pb_mode | ( | t_pb * | pb, |
| int | mode, | ||
| int | isOn | ||
| ) |
turns on mode for a pb by setting capacity of its rr_nodes to 1
Definition at line 1112 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int i, j, index;
int i_pb_type, i_pb_inst;
const t_pb_type *pb_type;
t_pb_graph_node *pb_graph_node;
pb_type = pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
for(i_pb_type = 0; i_pb_type < pb_type->modes[mode].num_pb_type_children; i_pb_type++) {
for(i_pb_inst = 0; i_pb_inst < pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i_pb_type].num_pb; i_pb_inst++) {
pb_graph_node = &pb->pb_graph_node->child_pb_graph_nodes[mode][i_pb_type][i_pb_inst];
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_input_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_input_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].capacity = isOn;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_output_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_output_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].capacity = isOn;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < pb_graph_node->num_clock_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_graph_node->num_clock_pins[i]; j++) {
index = pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
rr_node[index].capacity = isOn;
}
}
}
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
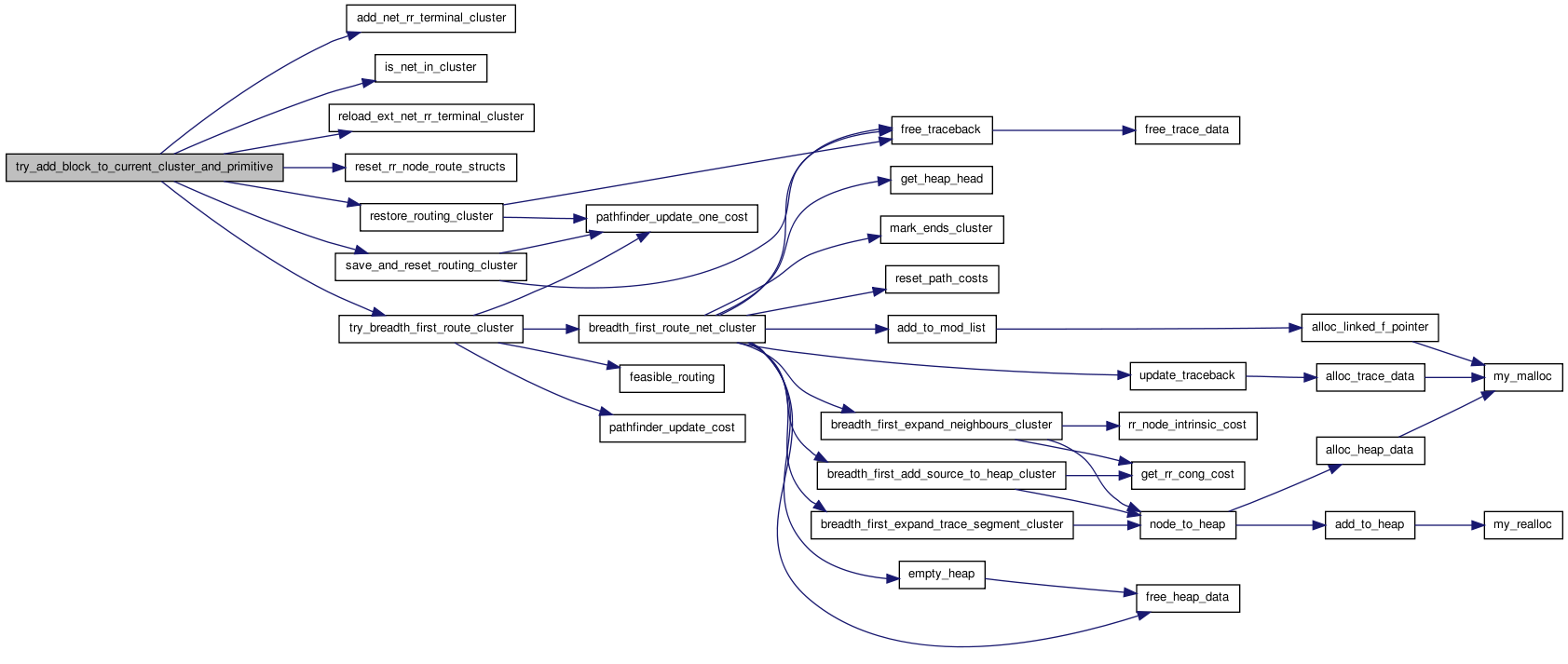
Here is the caller graph for this function:| enum e_block_pack_status try_add_block_to_current_cluster_and_primitive | ( | INP int | iblock, |
| INP t_pb * | primitive | ||
| ) |
Allocates and loads the net_rr_terminals data structure. For each net it stores the rr_node index of the SOURCE of the net and all the SINKs of the net. [0..num_logical_nets-1][0..num_pins-1].
Definition at line 825 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
int ipin, iblk_net;
int orig_num_nets_in_cluster;
boolean success, found;
t_model_ports *port;
success = FALSE;
found = FALSE;
assert(primitive->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_modes == 0); /* check if primitive */
assert(primitive->logical_block == OPEN && logical_block[iblock].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER); /* check if primitive and block is open */
/* check if block type matches primitive type */
if(logical_block[iblock].model != primitive->pb_graph_node->pb_type->model) {
/* End early, model is incompatible */
return BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE;
}
orig_num_nets_in_cluster = num_nets_in_cluster;
save_and_reset_routing_cluster();
/* try pack it in */
assert(primitive->logical_block == OPEN);
assert(logical_block[iblock].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER);
primitive->logical_block = iblock;
logical_block[iblock].pb = primitive;
logical_block[iblock].clb_index = curr_cluster_index;
/* for each net of logical block, check if it is in cluster, if not add it */
/* also check if pins on primitive can fit logical block */
port = logical_block[iblock].model->inputs;
success = TRUE;
while(port && success) {
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size && success; ipin++) {
if(port->is_clock) {
assert(port->size == 1);
iblk_net = logical_block[iblock].clock_net;
} else {
iblk_net = logical_block[iblock].input_nets[port->index][ipin];
}
if(iblk_net == OPEN) {
continue;
}
if(!is_net_in_cluster(iblk_net)){
nets_in_cluster[num_nets_in_cluster] = iblk_net;
num_nets_in_cluster++;
}
success = add_net_rr_terminal_cluster(iblk_net, primitive, iblock, port, ipin);
}
port = port->next;
}
port = logical_block[iblock].model->outputs;
while(port && success) {
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size && success; ipin++) {
iblk_net = logical_block[iblock].output_nets[port->index][ipin];
if(iblk_net == OPEN) {
continue;
}
if(!is_net_in_cluster(iblk_net)){
nets_in_cluster[num_nets_in_cluster] = iblk_net;
num_nets_in_cluster++;
}
success = add_net_rr_terminal_cluster(iblk_net, primitive, iblock, port, ipin);
}
port = port->next;
}
if(success) {
success = reload_ext_net_rr_terminal_cluster();
}
if(success) {
/* route it */
reset_rr_node_route_structs(); /* Clear all prior rr_graph history */
success = try_breadth_first_route_cluster(); /* route from scratch */
}
if(success) {
return BLK_PASSED;
} else {
/* Cannot pack, restore cluster */
primitive->logical_block = OPEN;
logical_block[iblock].pb = NULL;
logical_block[iblock].clb_index = NO_CLUSTER;
restore_routing_cluster();
num_nets_in_cluster = orig_num_nets_in_cluster;
return BLK_FAILED_ROUTE;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean try_breadth_first_route_cluster | ( | ) | [static] |
internal_nets: index of nets to route [0..num_internal_nets - 1] Iterated maze router ala Pathfinder Negotiated Congestion algorithm, (FPGA 95 p. 111). Returns TRUE if it can route this FPGA, FALSE if it can't.
Definition at line 537 of file cluster_legality.c.
{
/* For different modes, when a mode is turned on, I set the max occupancy of all rr_nodes in the mode to 1 and all others to 0 */
/* TODO: There is a bug for route-throughs where edges in route-throughs do not get turned off because the rr_edge is in a particular mode but the two rr_nodes are outside */
boolean success, is_routable;
int itry, inet, net_index;
struct s_router_opts router_opts;
/* Usually the first iteration uses a very small (or 0) pres_fac to find *
* the shortest path and get a congestion map. For fast compiles, I set *
* pres_fac high even for the first iteration. */
/* sets up a fast breadth-first router */
router_opts.first_iter_pres_fac = 10;
router_opts.max_router_iterations = 20;
router_opts.initial_pres_fac = 10;
router_opts.pres_fac_mult = 2;
router_opts.acc_fac = 1;
pres_fac = router_opts.first_iter_pres_fac;
for(itry = 1; itry <= router_opts.max_router_iterations; itry++)
{
for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets_in_cluster; inet++)
{
net_index = nets_in_cluster[inet];
pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[net_index], -1,
pres_fac);
is_routable =
breadth_first_route_net_cluster(net_index);
/* Impossible to route? (disconnected rr_graph) */
if(!is_routable)
{
/* TODO: Inelegant, can be more intelligent */
printf("Failed routing net %s\n", vpack_net[net_index].name);
printf("Routing failed. Disconnected rr_graph\n");
return FALSE;
}
pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[net_index], 1,
pres_fac);
}
success = feasible_routing();
if(success)
{
return (TRUE);
}
if(itry == 1)
pres_fac = router_opts.initial_pres_fac;
else
pres_fac *= router_opts.pres_fac_mult;
pres_fac = min (pres_fac, HUGE_FLOAT / 1e5);
pathfinder_update_cost(pres_fac, router_opts.acc_fac);
}
return (FALSE);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Variable Documentation
struct s_trace** best_routing [static] |
Definition at line 18 of file cluster_legality.c.
int chunk_bytes_avail = 0 [static] |
Definition at line 16 of file cluster_legality.c.
char* chunk_next_avail_mem = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 17 of file cluster_legality.c.
int curr_cluster_index [static] |
Definition at line 23 of file cluster_legality.c.
Definition at line 25 of file cluster_legality.c.
int ext_input_rr_node_index [static] |
Definition at line 25 of file cluster_legality.c.
Definition at line 25 of file cluster_legality.c.
| int max_ext_index |
Definition at line 25 of file cluster_legality.c.
int* nets_in_cluster [static] |
nets_in_cluster: array of all nets contained in the cluster [0..num_nets_in_cluster-1]
Definition at line 21 of file cluster_legality.c.
int num_nets_in_cluster [static] |
Definition at line 22 of file cluster_legality.c.
int num_rr_intrinsic_cost = 0 [static] |
Definition at line 29 of file cluster_legality.c.
float pres_fac [static] |
Definition at line 27 of file cluster_legality.c.
float* rr_intrinsic_cost [static] |
Definition at line 28 of file cluster_legality.c.
struct s_linked_vptr* rr_mem_chunk_list_head = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 15 of file cluster_legality.c.
int** saved_net_rr_terminals [static] |
Definition at line 26 of file cluster_legality.c.