SRC/route_timing.h File Reference
This graph shows which files directly or indirectly include this file:
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| boolean | try_timing_driven_route (struct s_router_opts router_opts, float **net_slack, float **net_delay, t_ivec **fb_opins_used_locally) |
| boolean | timing_driven_route_net (int inet, float pres_fac, float max_criticality, float criticality_exp, float astar_fac, float bend_cost, float *net_slack, float *pin_criticality, int *sink_order, t_rt_node **rt_node_of_sink, float T_crit, float *net_delay) |
| void | alloc_timing_driven_route_structs (float **pin_criticality_ptr, int **sink_order_ptr, t_rt_node ***rt_node_of_sink_ptr) |
| void | free_timing_driven_route_structs (float *pin_criticality, int *sink_order, t_rt_node **rt_node_of_sink) |
Function Documentation
| void alloc_timing_driven_route_structs | ( | float ** | pin_criticality_ptr, | |
| int ** | sink_order_ptr, | |||
| t_rt_node *** | rt_node_of_sink_ptr | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 186 of file route_timing.c.
00189 { 00190 00191 /* Allocates all the structures needed only by the timing-driven router. */ 00192 00193 int max_pins_per_net; 00194 float *pin_criticality; 00195 int *sink_order; 00196 t_rt_node **rt_node_of_sink; 00197 00198 max_pins_per_net = get_max_pins_per_net(); 00199 00200 pin_criticality = 00201 (float *)my_malloc((max_pins_per_net - 1) * sizeof(float)); 00202 *pin_criticality_ptr = pin_criticality - 1; /* First sink is pin #1. */ 00203 00204 sink_order = (int *)my_malloc((max_pins_per_net - 1) * sizeof(int)); 00205 *sink_order_ptr = sink_order - 1; 00206 00207 rt_node_of_sink = (t_rt_node **) my_malloc((max_pins_per_net - 1) * 00208 sizeof(t_rt_node *)); 00209 *rt_node_of_sink_ptr = rt_node_of_sink - 1; 00210 00211 alloc_route_tree_timing_structs(); 00212 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:

| void free_timing_driven_route_structs | ( | float * | pin_criticality, | |
| int * | sink_order, | |||
| t_rt_node ** | rt_node_of_sink | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 216 of file route_timing.c.
00219 { 00220 00221 /* Frees all the stuctures needed only by the timing-driven router. */ 00222 00223 free(pin_criticality + 1); /* Starts at index 1. */ 00224 free(sink_order + 1); 00225 free(rt_node_of_sink + 1); 00226 free_route_tree_timing_structs(); 00227 }
Here is the call graph for this function:

Here is the caller graph for this function:

| boolean timing_driven_route_net | ( | int | inet, | |
| float | pres_fac, | |||
| float | max_criticality, | |||
| float | criticality_exp, | |||
| float | astar_fac, | |||
| float | bend_cost, | |||
| float * | net_slack, | |||
| float * | pin_criticality, | |||
| int * | sink_order, | |||
| t_rt_node ** | rt_node_of_sink, | |||
| float | T_crit, | |||
| float * | net_delay | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 253 of file route_timing.c.
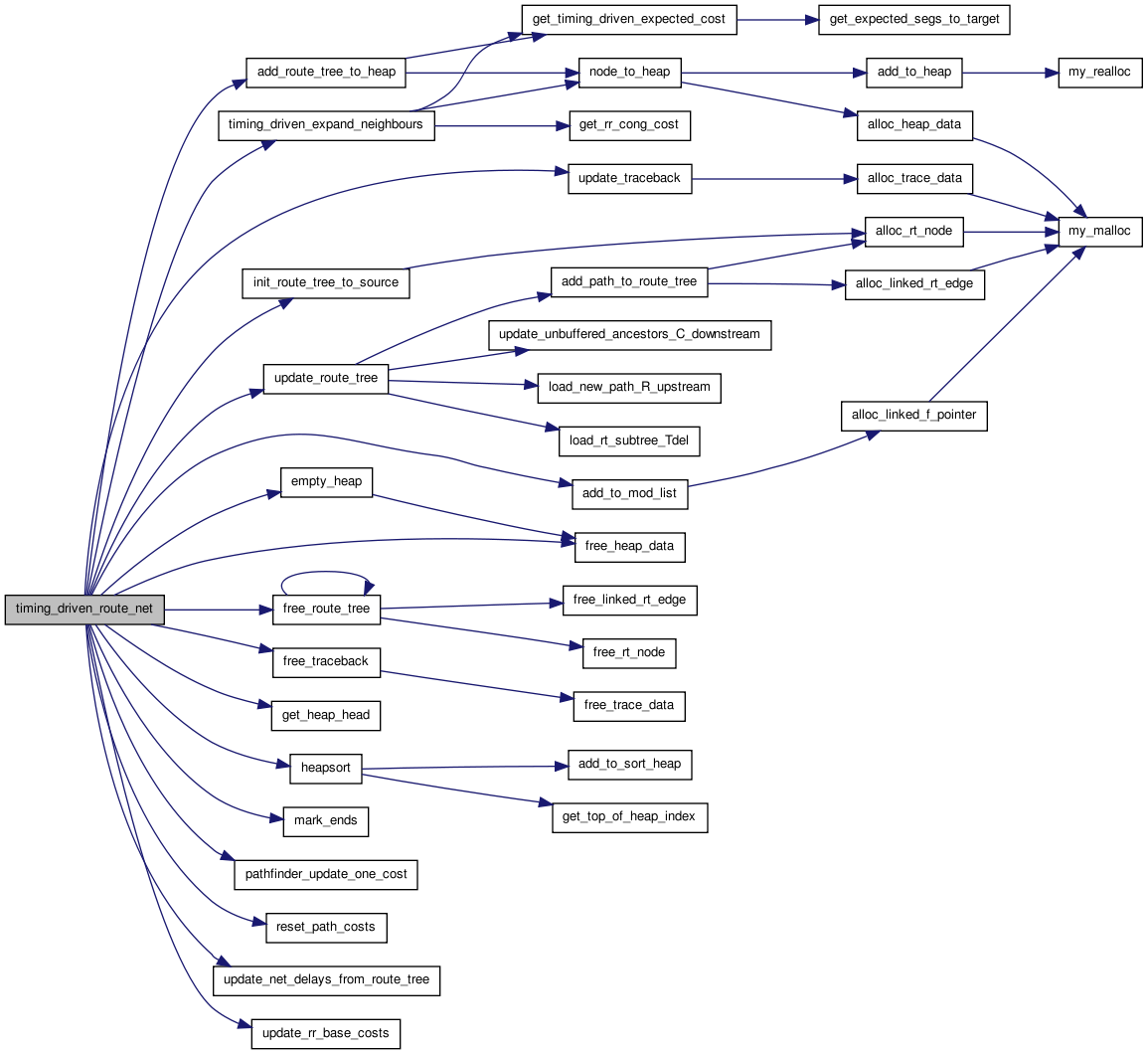
00265 { 00266 00267 /* Returns TRUE as long is found some way to hook up this net, even if that * 00268 * way resulted in overuse of resources (congestion). If there is no way * 00269 * to route this net, even ignoring congestion, it returns FALSE. In this * 00270 * case the rr_graph is disconnected and you can give up. */ 00271 00272 int ipin, num_sinks, itarget, target_pin, target_node, inode; 00273 float target_criticality, old_tcost, new_tcost, largest_criticality, 00274 pin_crit; 00275 float old_back_cost, new_back_cost; 00276 t_rt_node *rt_root; 00277 struct s_heap *current; 00278 struct s_trace *new_route_start_tptr; 00279 00280 /* Rip-up any old routing. */ 00281 00282 pathfinder_update_one_cost(trace_head[inet], -1, pres_fac); 00283 free_traceback(inet); 00284 00285 for(ipin = 1; ipin <= net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) 00286 { /* For all sinks */ 00287 pin_crit = max(max_criticality - net_slack[ipin] / T_crit, 0.); 00288 pin_crit = pow(pin_crit, criticality_exp); 00289 pin_crit = min(pin_crit, max_criticality); 00290 pin_criticality[ipin] = pin_crit; 00291 } 00292 00293 num_sinks = net[inet].num_sinks; 00294 heapsort(sink_order, pin_criticality, num_sinks); 00295 00296 /* Update base costs according to fanout and criticality rules */ 00297 00298 largest_criticality = pin_criticality[sink_order[1]]; 00299 update_rr_base_costs(inet, largest_criticality); 00300 00301 mark_ends(inet); /* Only needed to check for multiply-connected SINKs */ 00302 00303 rt_root = init_route_tree_to_source(inet); 00304 00305 for(itarget = 1; itarget <= num_sinks; itarget++) 00306 { 00307 target_pin = sink_order[itarget]; 00308 target_node = net_rr_terminals[inet][target_pin]; 00309 00310 target_criticality = pin_criticality[target_pin]; 00311 00312 add_route_tree_to_heap(rt_root, target_node, target_criticality, 00313 astar_fac); 00314 00315 current = get_heap_head(); 00316 00317 if(current == NULL) 00318 { /* Infeasible routing. No possible path for net. */ 00319 reset_path_costs(); 00320 free_route_tree(rt_root); 00321 return (FALSE); 00322 } 00323 00324 inode = current->index; 00325 00326 while(inode != target_node) 00327 { 00328 old_tcost = rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost; 00329 new_tcost = current->cost; 00330 00331 if(old_tcost > 0.99 * HUGE_FLOAT) /* First time touched. */ 00332 old_back_cost = HUGE_FLOAT; 00333 else 00334 old_back_cost = 00335 rr_node_route_inf[inode].backward_path_cost; 00336 00337 new_back_cost = current->backward_path_cost; 00338 00339 /* I only re-expand a node if both the "known" backward cost is lower * 00340 * in the new expansion (this is necessary to prevent loops from * 00341 * forming in the routing and causing havoc) *and* the expected total * 00342 * cost to the sink is lower than the old value. Different R_upstream * 00343 * values could make a path with lower back_path_cost less desirable * 00344 * than one with higher cost. Test whether or not I should disallow * 00345 * re-expansion based on a higher total cost. */ 00346 00347 if(old_tcost > new_tcost && old_back_cost > new_back_cost) 00348 { 00349 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node = 00350 current->u.prev_node; 00351 rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge = 00352 current->prev_edge; 00353 rr_node_route_inf[inode].path_cost = new_tcost; 00354 rr_node_route_inf[inode].backward_path_cost = 00355 new_back_cost; 00356 00357 if(old_tcost > 0.99 * HUGE_FLOAT) /* First time touched. */ 00358 add_to_mod_list(&rr_node_route_inf[inode]. 00359 path_cost); 00360 00361 timing_driven_expand_neighbours(current, inet, 00362 bend_cost, 00363 target_criticality, 00364 target_node, 00365 astar_fac); 00366 } 00367 00368 free_heap_data(current); 00369 current = get_heap_head(); 00370 00371 if(current == NULL) 00372 { /* Impossible routing. No path for net. */ 00373 reset_path_costs(); 00374 free_route_tree(rt_root); 00375 return (FALSE); 00376 } 00377 00378 inode = current->index; 00379 } 00380 00381 /* NB: In the code below I keep two records of the partial routing: the * 00382 * traceback and the route_tree. The route_tree enables fast recomputation * 00383 * of the Elmore delay to each node in the partial routing. The traceback * 00384 * lets me reuse all the routines written for breadth-first routing, which * 00385 * all take a traceback structure as input. Before this routine exits the * 00386 * route_tree structure is destroyed; only the traceback is needed at that * 00387 * point. */ 00388 00389 rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag--; /* Connected to this SINK. */ 00390 new_route_start_tptr = update_traceback(current, inet); 00391 rt_node_of_sink[target_pin] = update_route_tree(current); 00392 free_heap_data(current); 00393 pathfinder_update_one_cost(new_route_start_tptr, 1, pres_fac); 00394 00395 empty_heap(); 00396 reset_path_costs(); 00397 } 00398 00399 /* For later timing analysis. */ 00400 00401 update_net_delays_from_route_tree(net_delay, rt_node_of_sink, inet); 00402 free_route_tree(rt_root); 00403 return (TRUE); 00404 }
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:
| boolean try_timing_driven_route | ( | struct s_router_opts | router_opts, | |
| float ** | net_slack, | |||
| float ** | net_delay, | |||
| t_ivec ** | fb_opins_used_locally | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 50 of file route_timing.c.
00054 { 00055 00056 /* Timing-driven routing algorithm. The timing graph (includes net_slack) * 00057 * must have already been allocated, and net_delay must have been allocated. * 00058 * Returns TRUE if the routing succeeds, FALSE otherwise. */ 00059 00060 int itry, inet, ipin; 00061 boolean success, is_routable, rip_up_local_opins; 00062 float *pin_criticality; /* [1..max_pins_per_net-1]. */ 00063 int *sink_order; /* [1..max_pins_per_net-1]. */ 00064 t_rt_node **rt_node_of_sink; /* [1..max_pins_per_net-1]. */ 00065 float T_crit, pres_fac; 00066 00067 alloc_timing_driven_route_structs(&pin_criticality, &sink_order, 00068 &rt_node_of_sink); 00069 00070 /* First do one routing iteration ignoring congestion and marking all sinks * 00071 * on each net as critical to get reasonable net delay estimates. */ 00072 00073 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00074 { 00075 if(net[inet].is_global == FALSE) 00076 { 00077 for(ipin = 1; ipin <= net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) 00078 net_slack[inet][ipin] = 0.; 00079 } 00080 else 00081 { /* Set delay of global signals to zero. */ 00082 for(ipin = 1; ipin <= net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) 00083 net_delay[inet][ipin] = 0.; 00084 } 00085 } 00086 00087 T_crit = 1.; 00088 pres_fac = router_opts.first_iter_pres_fac; /* Typically 0 -> ignore cong. */ 00089 00090 for(itry = 1; itry <= router_opts.max_router_iterations; itry++) 00091 { 00092 00093 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00094 { 00095 if(net[inet].is_global == FALSE) 00096 { /* Skip global nets. */ 00097 00098 is_routable = 00099 timing_driven_route_net(inet, pres_fac, 00100 router_opts. 00101 max_criticality, 00102 router_opts. 00103 criticality_exp, 00104 router_opts.astar_fac, 00105 router_opts.bend_cost, 00106 net_slack[inet], 00107 pin_criticality, 00108 sink_order, 00109 rt_node_of_sink, 00110 T_crit, 00111 net_delay[inet]); 00112 00113 /* Impossible to route? (disconnected rr_graph) */ 00114 00115 if(!is_routable) 00116 { 00117 printf("Routing failed.\n"); 00118 free_timing_driven_route_structs 00119 (pin_criticality, sink_order, 00120 rt_node_of_sink); 00121 return (FALSE); 00122 } 00123 } 00124 } 00125 00126 /* Make sure any FB OPINs used up by subblocks being hooked directly * 00127 * to them are reserved for that purpose. */ 00128 00129 if(itry == 1) 00130 rip_up_local_opins = FALSE; 00131 else 00132 rip_up_local_opins = TRUE; 00133 00134 reserve_locally_used_opins(pres_fac, rip_up_local_opins, 00135 fb_opins_used_locally); 00136 00137 /* Pathfinder guys quit after finding a feasible route. I may want to keep * 00138 * going longer, trying to improve timing. Think about this some. */ 00139 00140 success = feasible_routing(); 00141 if(success) 00142 { 00143 printf 00144 ("Successfully routed after %d routing iterations.\n", 00145 itry); 00146 free_timing_driven_route_structs(pin_criticality, 00147 sink_order, 00148 rt_node_of_sink); 00149 #ifdef DEBUG 00150 timing_driven_check_net_delays(net_delay); 00151 #endif 00152 return (TRUE); 00153 } 00154 00155 if(itry == 1) 00156 { 00157 pres_fac = router_opts.initial_pres_fac; 00158 pathfinder_update_cost(pres_fac, 0.); /* Acc_fac=0 for first iter. */ 00159 } 00160 else 00161 { 00162 pres_fac *= router_opts.pres_fac_mult; 00163 00164 /* Avoid overflow for high iteration counts, even if acc_cost is big */ 00165 pres_fac = min (pres_fac, HUGE_FLOAT / 1e5); 00166 00167 pathfinder_update_cost(pres_fac, router_opts.acc_fac); 00168 } 00169 00170 /* Update slack values by doing another timing analysis. * 00171 * Timing_driven_route_net updated the net delay values. */ 00172 00173 load_timing_graph_net_delays(net_delay); 00174 T_crit = load_net_slack(net_slack, 0); 00175 printf("T_crit: %g.\n", T_crit); 00176 } 00177 00178 printf("Routing failed.\n"); 00179 free_timing_driven_route_structs(pin_criticality, sink_order, 00180 rt_node_of_sink); 00181 return (FALSE); 00182 }
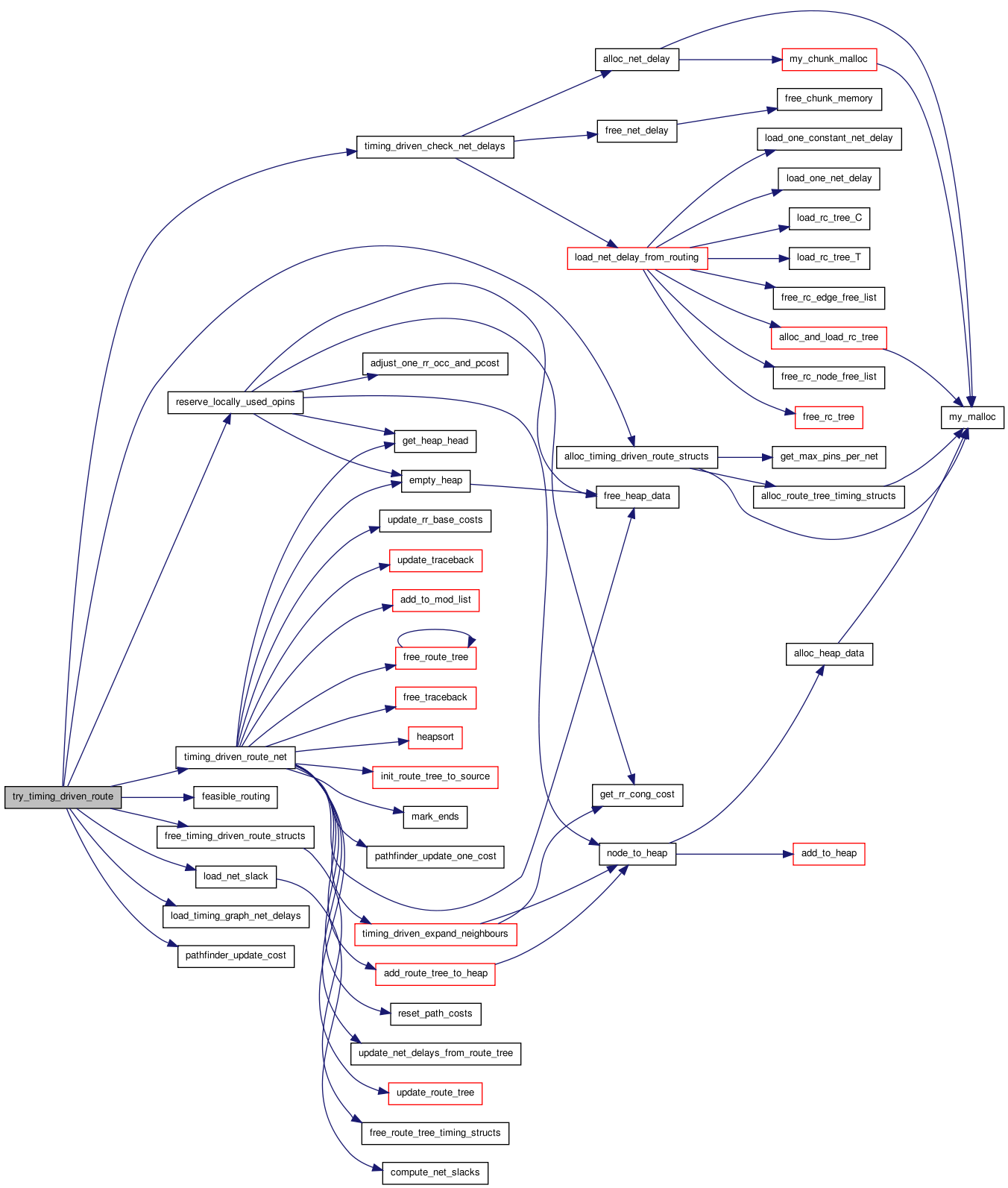
Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:

 1.6.1
1.6.1