SRC/route_tree_timing.c File Reference
#include <stdio.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "globals.h"#include "route_common.h"#include "route_tree_timing.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Define Documentation
| #define NO_ROUTE_THROUGHS 1 |
Function Documentation
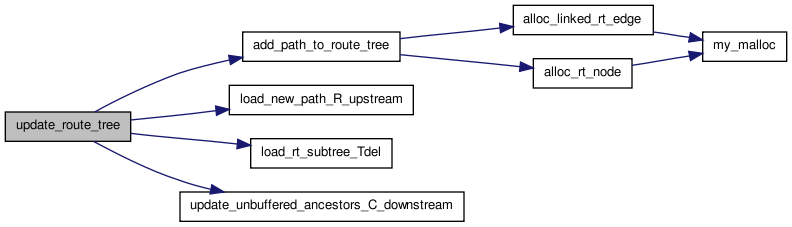
| static t_rt_node * add_path_to_route_tree | ( | struct s_heap * | hptr, | |
| t_rt_node ** | sink_rt_node_ptr | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 256 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00258 { 00259 00260 /* Adds the most recent wire segment, ending at the SINK indicated by hptr, * 00261 * to the routing tree. It returns the first (most upstream) new rt_node, * 00262 * and (via a pointer) the rt_node of the new SINK. */ 00263 00264 int inode, remaining_connections_to_sink; 00265 short iedge, iswitch; 00266 float C_downstream; 00267 t_rt_node *rt_node, *downstream_rt_node, *sink_rt_node; 00268 t_linked_rt_edge *linked_rt_edge; 00269 00270 00271 inode = hptr->index; 00272 00273 #ifdef DEBUG 00274 if(rr_node[inode].type != SINK) 00275 { 00276 printf 00277 ("Error in add_path_to_route_tree. Expected type = SINK (%d).\n", 00278 SINK); 00279 printf("Got type = %d.", rr_node[inode].type); 00280 exit(1); 00281 } 00282 #endif 00283 00284 remaining_connections_to_sink = rr_node_route_inf[inode].target_flag; 00285 sink_rt_node = alloc_rt_node(); 00286 sink_rt_node->u.child_list = NULL; 00287 sink_rt_node->inode = inode; 00288 C_downstream = rr_node[inode].C; 00289 sink_rt_node->C_downstream = C_downstream; 00290 rr_node_to_rt_node[inode] = sink_rt_node; 00291 00292 /* In the code below I'm marking SINKs and IPINs as not to be re-expanded. * 00293 * Undefine NO_ROUTE_THROUGHS if you want route-throughs or ipin doglegs. * 00294 * It makes the code more efficient (though not vastly) to prune this way * 00295 * when there aren't route-throughs or ipin doglegs. */ 00296 00297 #define NO_ROUTE_THROUGHS 1 /* Can't route through unused FB outputs */ 00298 00299 #ifdef NO_ROUTE_THROUGHS 00300 sink_rt_node->re_expand = FALSE; 00301 #else 00302 if(remaining_connections_to_sink == 0) 00303 { /* Usual case */ 00304 sink_rt_node->re_expand = TRUE; 00305 } 00306 00307 /* Weird case. This net connects several times to the same SINK. Thus I * 00308 * can't re_expand this node as part of the partial routing for subsequent * 00309 * connections, since I need to reach it again via another path. */ 00310 00311 else 00312 { 00313 sink_rt_node->re_expand = FALSE; 00314 } 00315 #endif 00316 00317 00318 /* Now do it's predecessor. */ 00319 00320 downstream_rt_node = sink_rt_node; 00321 inode = hptr->u.prev_node; 00322 iedge = hptr->prev_edge; 00323 iswitch = rr_node[inode].switches[iedge]; 00324 00325 /* For all "new" nodes in the path */ 00326 00327 while(rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node != NO_PREVIOUS) 00328 { 00329 linked_rt_edge = alloc_linked_rt_edge(); 00330 linked_rt_edge->child = downstream_rt_node; 00331 linked_rt_edge->iswitch = iswitch; 00332 linked_rt_edge->next = NULL; 00333 00334 rt_node = alloc_rt_node(); 00335 downstream_rt_node->parent_node = rt_node; 00336 downstream_rt_node->parent_switch = iswitch; 00337 00338 rt_node->u.child_list = linked_rt_edge; 00339 rt_node->inode = inode; 00340 00341 if(switch_inf[iswitch].buffered == FALSE) 00342 C_downstream += rr_node[inode].C; 00343 else 00344 C_downstream = rr_node[inode].C; 00345 00346 rt_node->C_downstream = C_downstream; 00347 rr_node_to_rt_node[inode] = rt_node; 00348 00349 #ifdef NO_ROUTE_THROUGHS 00350 if(rr_node[inode].type == IPIN) 00351 rt_node->re_expand = FALSE; 00352 else 00353 rt_node->re_expand = TRUE; 00354 00355 #else 00356 if(remaining_connections_to_sink == 0) 00357 { /* Normal case */ 00358 rt_node->re_expand = TRUE; 00359 } 00360 else 00361 { /* This is the IPIN before a multiply-connected SINK */ 00362 rt_node->re_expand = FALSE; 00363 00364 /* Reset flag so wire segments get reused */ 00365 00366 remaining_connections_to_sink = 0; 00367 } 00368 #endif 00369 00370 downstream_rt_node = rt_node; 00371 iedge = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_edge; 00372 inode = rr_node_route_inf[inode].prev_node; 00373 iswitch = rr_node[inode].switches[iedge]; 00374 } 00375 00376 /* Inode is the join point to the old routing */ 00377 00378 rt_node = rr_node_to_rt_node[inode]; 00379 00380 linked_rt_edge = alloc_linked_rt_edge(); 00381 linked_rt_edge->child = downstream_rt_node; 00382 linked_rt_edge->iswitch = iswitch; 00383 linked_rt_edge->next = rt_node->u.child_list; 00384 rt_node->u.child_list = linked_rt_edge; 00385 00386 downstream_rt_node->parent_node = rt_node; 00387 downstream_rt_node->parent_switch = iswitch; 00388 00389 *sink_rt_node_ptr = sink_rt_node; 00390 return (downstream_rt_node); 00391 }


| static t_linked_rt_edge * alloc_linked_rt_edge | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 152 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00153 { 00154 00155 /* Allocates a new linked_rt_edge, from the free list if possible, from the * 00156 * free store otherwise. */ 00157 00158 t_linked_rt_edge *linked_rt_edge; 00159 00160 linked_rt_edge = rt_edge_free_list; 00161 00162 if(linked_rt_edge != NULL) 00163 { 00164 rt_edge_free_list = linked_rt_edge->next; 00165 } 00166 else 00167 { 00168 linked_rt_edge = (t_linked_rt_edge *) my_malloc(sizeof 00169 (t_linked_rt_edge)); 00170 } 00171 00172 return (linked_rt_edge); 00173 }


| void alloc_route_tree_timing_structs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 61 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00062 { 00063 00064 /* Allocates any structures needed to build the routing trees. */ 00065 00066 if(rr_node_to_rt_node != NULL || rt_node_free_list != NULL || 00067 rt_node_free_list != NULL) 00068 { 00069 printf("Error in alloc_route_tree_timing_structs: old structures " 00070 "already exist.\n"); 00071 exit(1); 00072 } 00073 00074 rr_node_to_rt_node = (t_rt_node **) my_malloc(num_rr_nodes * 00075 sizeof(t_rt_node *)); 00076 }


| static t_rt_node * alloc_rt_node | ( | void | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 117 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00118 { 00119 00120 /* Allocates a new rt_node, from the free list if possible, from the free * 00121 * store otherwise. */ 00122 00123 t_rt_node *rt_node; 00124 00125 rt_node = rt_node_free_list; 00126 00127 if(rt_node != NULL) 00128 { 00129 rt_node_free_list = rt_node->u.next; 00130 } 00131 else 00132 { 00133 rt_node = (t_rt_node *) my_malloc(sizeof(t_rt_node)); 00134 } 00135 00136 return (rt_node); 00137 }


| static void free_linked_rt_edge | ( | t_linked_rt_edge * | rt_edge | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 177 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00178 { 00179 00180 /* Adds the rt_edge to the rt_edge free list. */ 00181 00182 rt_edge->next = rt_edge_free_list; 00183 rt_edge_free_list = rt_edge; 00184 }

| void free_route_tree | ( | t_rt_node * | rt_node | ) |
Definition at line 529 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00530 { 00531 00532 /* Puts the rt_nodes and edges in the tree rooted at rt_node back on the * 00533 * free lists. Recursive, depth-first post-order traversal. */ 00534 00535 t_rt_node *child_node; 00536 t_linked_rt_edge *rt_edge, *next_edge; 00537 00538 rt_edge = rt_node->u.child_list; 00539 00540 while(rt_edge != NULL) 00541 { /* For all children */ 00542 child_node = rt_edge->child; 00543 free_route_tree(child_node); 00544 next_edge = rt_edge->next; 00545 free_linked_rt_edge(rt_edge); 00546 rt_edge = next_edge; 00547 } 00548 00549 free_rt_node(rt_node); 00550 }
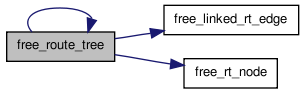
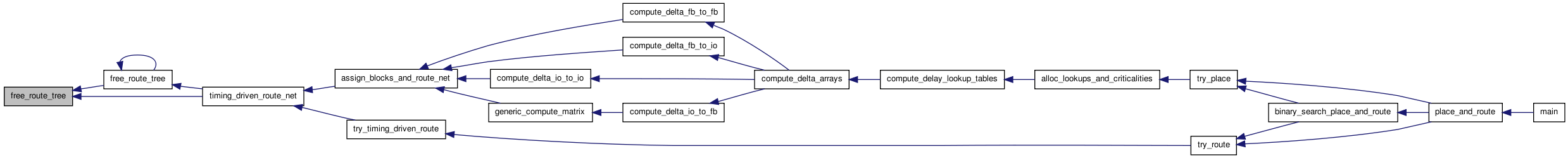
| void free_route_tree_timing_structs | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 80 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00081 { 00082 00083 /* Frees the structures needed to build routing trees, and really frees * 00084 * (i.e. calls free) all the data on the free lists. */ 00085 00086 t_rt_node *rt_node, *next_node; 00087 t_linked_rt_edge *rt_edge, *next_edge; 00088 00089 free(rr_node_to_rt_node); 00090 rr_node_to_rt_node = NULL; 00091 00092 rt_node = rt_node_free_list; 00093 00094 while(rt_node != NULL) 00095 { 00096 next_node = rt_node->u.next; 00097 free(rt_node); 00098 rt_node = next_node; 00099 } 00100 00101 rt_node_free_list = NULL; 00102 00103 rt_edge = rt_edge_free_list; 00104 00105 while(rt_edge != NULL) 00106 { 00107 next_edge = rt_edge->next; 00108 free(rt_edge); 00109 rt_edge = next_edge; 00110 } 00111 00112 rt_edge_free_list = NULL; 00113 }

| static void free_rt_node | ( | t_rt_node * | rt_node | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 141 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00142 { 00143 00144 /* Adds rt_node to the proper free list. */ 00145 00146 rt_node->u.next = rt_node_free_list; 00147 rt_node_free_list = rt_node; 00148 }
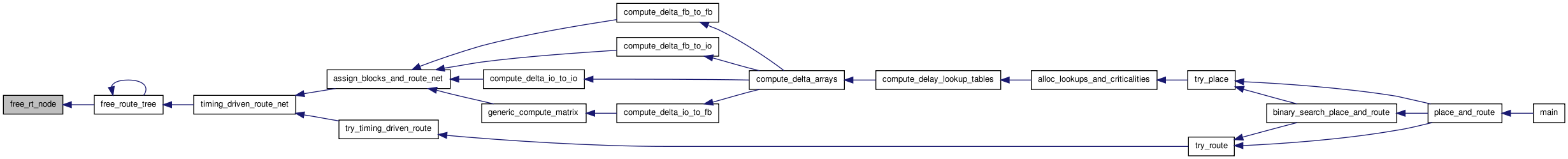
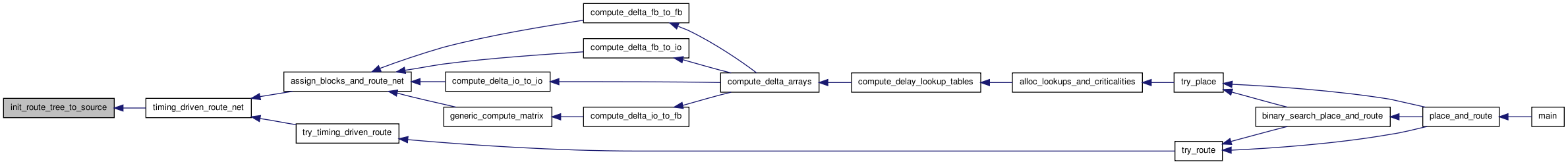
| t_rt_node* init_route_tree_to_source | ( | int | inet | ) |
Definition at line 188 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00189 { 00190 00191 /* Initializes the routing tree to just the net source, and returns the root * 00192 * node of the rt_tree (which is just the net source). */ 00193 00194 t_rt_node *rt_root; 00195 int inode; 00196 00197 rt_root = alloc_rt_node(); 00198 rt_root->u.child_list = NULL; 00199 rt_root->parent_node = NULL; 00200 rt_root->parent_switch = OPEN; 00201 rt_root->re_expand = TRUE; 00202 00203 inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][0]; /* Net source */ 00204 00205 rt_root->inode = inode; 00206 rt_root->C_downstream = rr_node[inode].C; 00207 rt_root->R_upstream = rr_node[inode].R; 00208 rt_root->Tdel = 0.5 * rr_node[inode].R * rr_node[inode].C; 00209 rr_node_to_rt_node[inode] = rt_root; 00210 00211 return (rt_root); 00212 }

| static void load_new_path_R_upstream | ( | t_rt_node * | start_of_new_path_rt_node | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 395 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00396 { 00397 00398 /* Sets the R_upstream values of all the nodes in the new path to the * 00399 * correct value. */ 00400 00401 float R_upstream; 00402 int inode; 00403 short iswitch; 00404 t_rt_node *rt_node, *parent_rt_node; 00405 t_linked_rt_edge *linked_rt_edge; 00406 00407 rt_node = start_of_new_path_rt_node; 00408 iswitch = rt_node->parent_switch; 00409 inode = rt_node->inode; 00410 parent_rt_node = rt_node->parent_node; 00411 00412 R_upstream = switch_inf[iswitch].R + rr_node[inode].R; 00413 00414 if(switch_inf[iswitch].buffered == FALSE) 00415 R_upstream += parent_rt_node->R_upstream; 00416 00417 rt_node->R_upstream = R_upstream; 00418 00419 /* Note: the traversal below makes use of the fact that this new path * 00420 * really is a path (not a tree with branches) to do a traversal without * 00421 * recursion, etc. */ 00422 00423 linked_rt_edge = rt_node->u.child_list; 00424 00425 while(linked_rt_edge != NULL) 00426 { /* While SINK not reached. */ 00427 00428 #ifdef DEBUG 00429 if(linked_rt_edge->next != NULL) 00430 { 00431 printf 00432 ("Error in load_new_path_R_upstream: new routing addition is\n" 00433 "a tree (not a path).\n"); 00434 exit(1); 00435 } 00436 #endif 00437 00438 rt_node = linked_rt_edge->child; 00439 iswitch = linked_rt_edge->iswitch; 00440 inode = rt_node->inode; 00441 00442 if(switch_inf[iswitch].buffered) 00443 R_upstream = switch_inf[iswitch].R + rr_node[inode].R; 00444 else 00445 R_upstream += switch_inf[iswitch].R + rr_node[inode].R; 00446 00447 rt_node->R_upstream = R_upstream; 00448 linked_rt_edge = rt_node->u.child_list; 00449 } 00450 }

| static void load_rt_subtree_Tdel | ( | t_rt_node * | subtree_rt_root, | |
| float | Tarrival | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 485 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00487 { 00488 00489 /* Updates the Tdel values of the subtree rooted at subtree_rt_root by * 00490 * by calling itself recursively. The C_downstream values of all the nodes * 00491 * must be correct before this routine is called. Tarrival is the time at * 00492 * at which the signal arrives at this node's *input*. */ 00493 00494 int inode; 00495 short iswitch; 00496 t_rt_node *child_node; 00497 t_linked_rt_edge *linked_rt_edge; 00498 float Tdel, Tchild; 00499 00500 inode = subtree_rt_root->inode; 00501 00502 /* Assuming the downstream connections are, on average, connected halfway * 00503 * along a wire segment's length. See discussion in net_delay.c if you want * 00504 * to change this. */ 00505 00506 Tdel = Tarrival + 0.5 * subtree_rt_root->C_downstream * rr_node[inode].R; 00507 subtree_rt_root->Tdel = Tdel; 00508 00509 /* Now expand the children of this node to load their Tdel values (depth- * 00510 * first pre-order traversal). */ 00511 00512 linked_rt_edge = subtree_rt_root->u.child_list; 00513 00514 while(linked_rt_edge != NULL) 00515 { 00516 iswitch = linked_rt_edge->iswitch; 00517 child_node = linked_rt_edge->child; 00518 00519 Tchild = Tdel + switch_inf[iswitch].R * child_node->C_downstream; 00520 Tchild += switch_inf[iswitch].Tdel; /* Intrinsic switch delay. */ 00521 load_rt_subtree_Tdel(child_node, Tchild); 00522 00523 linked_rt_edge = linked_rt_edge->next; 00524 } 00525 }

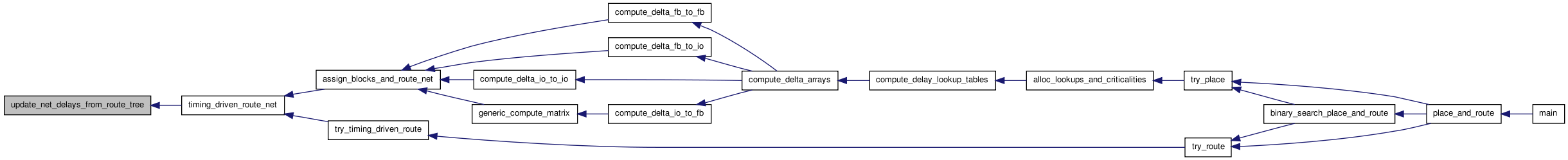
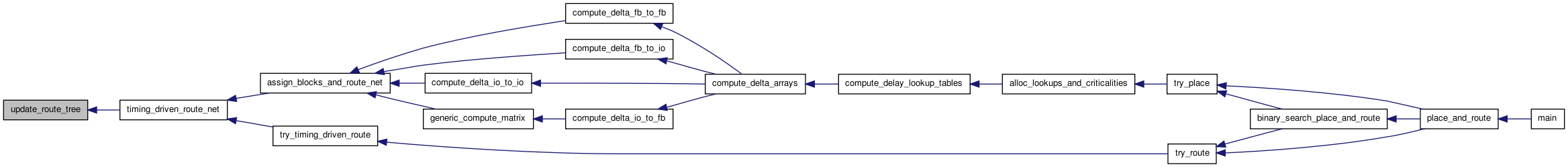
| void update_net_delays_from_route_tree | ( | float * | net_delay, | |
| t_rt_node ** | rt_node_of_sink, | |||
| int | inet | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 554 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00557 { 00558 00559 /* Goes through all the sinks of this net and copies their delay values from * 00560 * the route_tree to the net_delay array. */ 00561 00562 int isink; 00563 t_rt_node *sink_rt_node; 00564 00565 for(isink = 1; isink <= net[inet].num_sinks; isink++) 00566 { 00567 sink_rt_node = rt_node_of_sink[isink]; 00568 net_delay[isink] = sink_rt_node->Tdel; 00569 } 00570 }
Definition at line 216 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00217 { 00218 00219 /* Adds the most recently finished wire segment to the routing tree, and * 00220 * updates the Tdel, etc. numbers for the rest of the routing tree. hptr * 00221 * is the heap pointer of the SINK that was reached. This routine returns * 00222 * a pointer to the rt_node of the SINK that it adds to the routing. */ 00223 00224 t_rt_node *start_of_new_path_rt_node, *sink_rt_node; 00225 t_rt_node *unbuffered_subtree_rt_root, *subtree_parent_rt_node; 00226 float Tdel_start; 00227 short iswitch; 00228 00229 start_of_new_path_rt_node = add_path_to_route_tree(hptr, &sink_rt_node); 00230 load_new_path_R_upstream(start_of_new_path_rt_node); 00231 unbuffered_subtree_rt_root = 00232 update_unbuffered_ancestors_C_downstream(start_of_new_path_rt_node); 00233 00234 subtree_parent_rt_node = unbuffered_subtree_rt_root->parent_node; 00235 00236 if(subtree_parent_rt_node != NULL) 00237 { /* Parent exists. */ 00238 Tdel_start = subtree_parent_rt_node->Tdel; 00239 iswitch = unbuffered_subtree_rt_root->parent_switch; 00240 Tdel_start += switch_inf[iswitch].R * 00241 unbuffered_subtree_rt_root->C_downstream; 00242 Tdel_start += switch_inf[iswitch].Tdel; 00243 } 00244 else 00245 { /* Subtree starts at SOURCE */ 00246 Tdel_start = 0.; 00247 } 00248 00249 load_rt_subtree_Tdel(unbuffered_subtree_rt_root, Tdel_start); 00250 00251 return (sink_rt_node); 00252 }
| static t_rt_node * update_unbuffered_ancestors_C_downstream | ( | t_rt_node * | start_of_new_path_rt_node | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 454 of file route_tree_timing.c.
00456 { 00457 00458 /* Updates the C_downstream values for the ancestors of the new path. Once * 00459 * a buffered switch is found amongst the ancestors, no more ancestors are * 00460 * affected. Returns the root of the "unbuffered subtree" whose Tdel * 00461 * values are affected by the new path's addition. */ 00462 00463 t_rt_node *rt_node, *parent_rt_node; 00464 short iswitch; 00465 float C_downstream_addition; 00466 00467 rt_node = start_of_new_path_rt_node; 00468 C_downstream_addition = rt_node->C_downstream; 00469 parent_rt_node = rt_node->parent_node; 00470 iswitch = rt_node->parent_switch; 00471 00472 while(parent_rt_node != NULL && switch_inf[iswitch].buffered == FALSE) 00473 { 00474 rt_node = parent_rt_node; 00475 rt_node->C_downstream += C_downstream_addition; 00476 parent_rt_node = rt_node->parent_node; 00477 iswitch = rt_node->parent_switch; 00478 } 00479 00480 return (rt_node); 00481 }

Variable Documentation
t_rt_node** rr_node_to_rt_node = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 25 of file route_tree_timing.c.
t_linked_rt_edge* rt_edge_free_list = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 30 of file route_tree_timing.c.
t_rt_node* rt_node_free_list = NULL [static] |
Definition at line 29 of file route_tree_timing.c.
 1.6.1
1.6.1