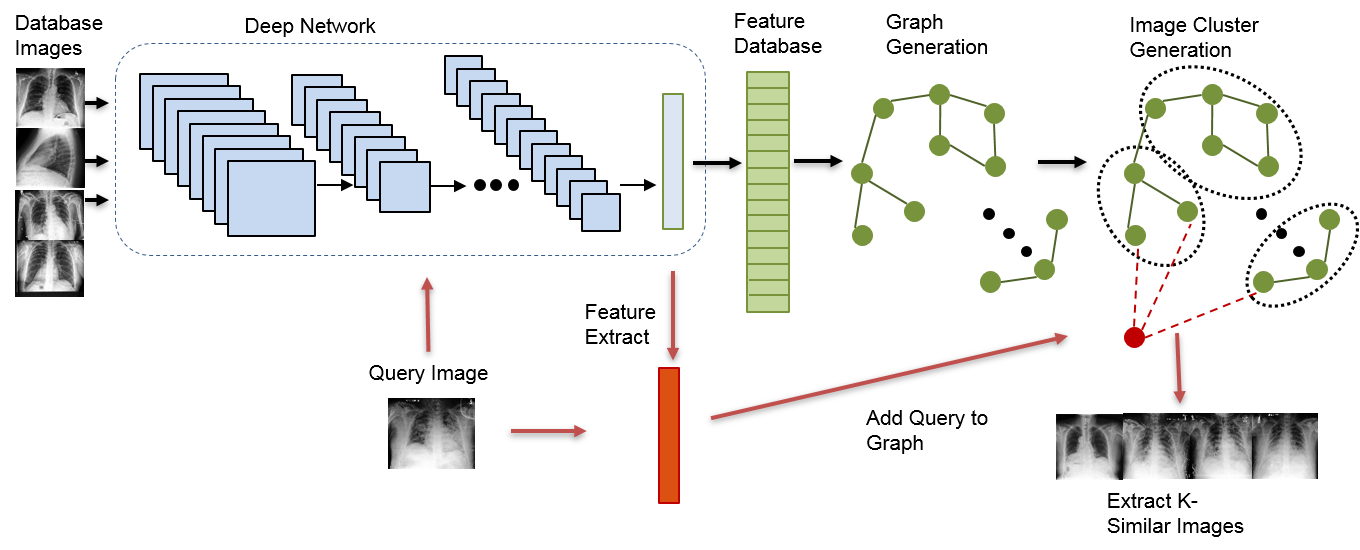
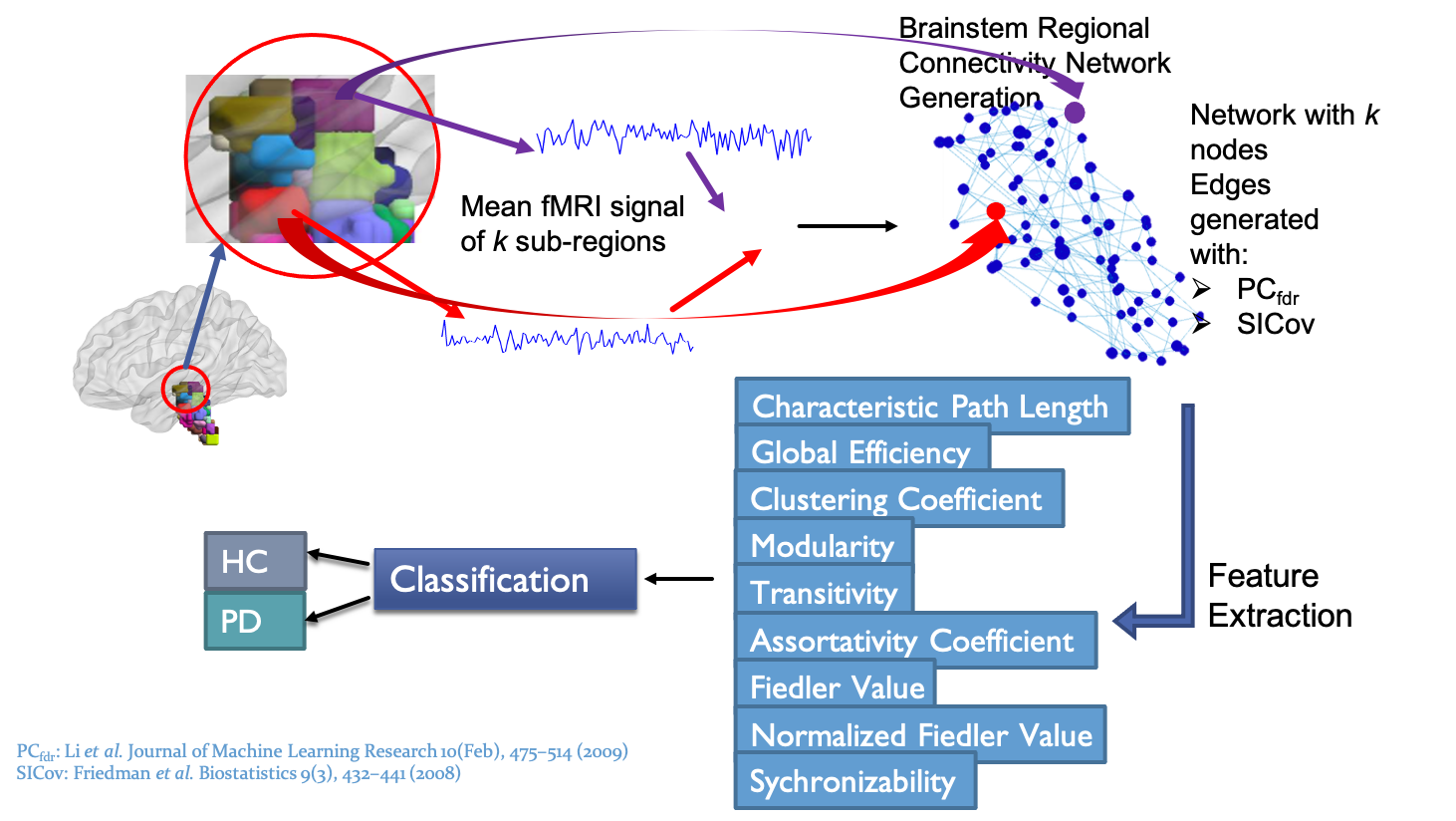
We propose a framework for parcellating a single brain region-of-interest (ROI) into spatially contiguous functional sub-regions (subROIs) based on fMRI connectivity patterns between subROIs and other brain ROIs. First, a functional connectivity network between the voxels in the primary ROI is generated by taking into account the connectivity pattern within the primary ROI and all other ROIs, with a spatial constraint to ensure the spatial continuity of the final subROIs. An unsupervised network clustering algorithm is then applied to the associated adjacency matrix of the connectivity network to parcellate it into functional subROIs. As an illustrative example, the framework was applied to resting state fMRI data from nine healthy subjects to parcellate the putaminal region into two functional subROIs. Training on odd and even time points resulted in more than 98% concurrence of voxels assigned to the same cluster. The relative fraction of voxels assigned to each subROIs was also robust across subjects. As a general tool, the proposed framework has the potential to be integrated into studies investigating subROI alterations in neurological disorders.
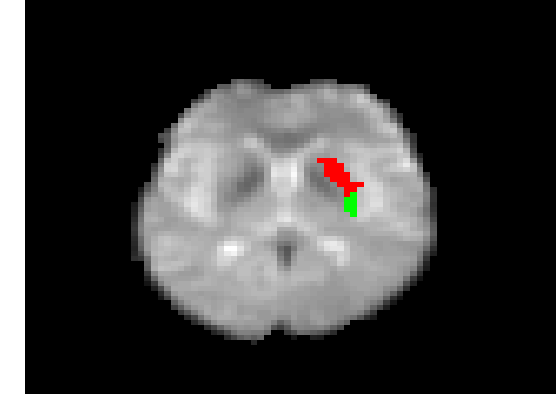
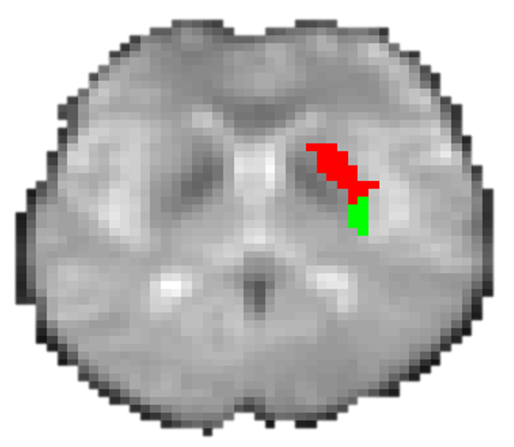
The putamen with a background axial fMRI image for one subject. The putament was divided into two sub-regions with our proposed unsupervised clustering approach. The red region represent the dorsomedial striatum (DMS) subROI and the green region represent the dorsolateral striatum (DLS).