vpr/SRC/pack/cluster.c File Reference
#include <stdio.h>#include <assert.h>#include <string.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "globals.h"#include "cluster.h"#include "heapsort.h"#include "output_clustering.h"#include "output_blif.h"#include "SetupGrid.h"#include "read_xml_arch_file.h"#include "cluster_legality.h"#include "path_delay2.h"#include "path_delay.h" Include dependency graph for cluster.c:
Include dependency graph for cluster.c:Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | s_ilink |
Defines | |
| #define | AAPACK_MAX_FEASIBLE_BLOCK_ARRAY_SIZE 30 |
| #define | SCALE_NUM_PATHS 1e-2 |
| #define | SCALE_DISTANCE_VAL 1e-4 |
| #define | MARKED_FRAC 2 |
Enumerations | |
| enum | e_gain_update { GAIN, NO_GAIN } |
| enum | e_feasibility { FEASIBLE, INFEASIBLE } |
| enum | e_gain_type { HILL_CLIMBING, NOT_HILL_CLIMBING } |
| enum | e_removal_policy { REMOVE_CLUSTERED, LEAVE_CLUSTERED } |
| enum | e_net_relation_to_clustered_block { INPUT, OUTPUT } |
Functions | |
| static int | num_ext_inputs (int iblk) |
| static void | check_clocks (boolean *is_clock) |
| static int | get_max_cluster_size (t_pb_type *pb_type) |
| static int | get_max_primitive_inputs (t_pb_type *pb_type) |
| static int | get_max_pb_depth (t_pb_type *pb_type) |
| static boolean | is_logical_blk_in_pb (int iblk, t_pb *pb) |
| static void | add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates (int iblk, float *gain, t_pb *pb) |
| static void | alloc_and_init_clustering (boolean global_clocks, float alpha, float beta, int max_cluster_size, int max_primitive_inputs, int max_pb_depth, int max_models) |
| static void | free_pb_stats_recursive (t_pb *pb, int max_models) |
| static boolean | outputs_clocks_and_models_feasible (enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, int iblk, boolean *is_clock, t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static boolean | models_feasible (enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, int iblk, const t_pb_type *cur_pb_type, t_pb *cur_pb, int mode) |
| static boolean | primitive_feasible (int iblk, t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static boolean | primitive_type_feasible (int iblk, const t_pb_type *cur_pb_type, t_pb *memory_class_pb, int sibling_memory_blk) |
| static int | get_logical_block_by_num_ext_inputs (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb, INP int ext_inps, INP enum e_removal_policy remove_flag) |
| static int | get_free_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs_for_cluster (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static int | get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs (int max_primitive_inputs) |
| static void | alloc_and_load_pb_stats (t_pb *pb, int max_models, int max_cluster_size, int max_primitive_inputs) |
| static enum e_block_pack_status | alloc_and_load_pb (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INP t_pb_graph_node *pb_graph_node, INP int iblock, INOUTP t_pb *pb, INP int max_models, INP int max_cluster_size, INP int max_primitive_inputs) |
| static void | update_connection_gain_values (int inet, int clustered_block, t_pb *cur_pb, enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block net_relation_to_clustered_block) |
| static void | update_length_gain_values (int inet, int clustered_block, t_pb *cur_pb, enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block net_relation_to_clustered_block) |
| static void | mark_and_update_partial_gain (int inet, enum e_gain_update gain_flag, int clustered_block, int port_on_clustered_block, int pin_on_clustered_block, boolean timing_driven, boolean connection_driven, enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block net_relation_to_clustered_block) |
| static void | update_total_gain (float alpha, float beta, boolean timing_driven, boolean connection_driven, boolean global_clocks, t_pb *pb) |
| static void | update_cluster_stats (INP int new_blk, INP int clb_index, INP boolean *is_clock, INP boolean global_clocks, INP float alpha, INP float beta, INP boolean timing_driven, INP boolean connection_driven) |
| static void | start_new_cluster (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INP const t_arch *arch, INOUTP t_block *new_cluster, INP int clb_index, INP int istart, INP float aspect, INOUTP int *num_used_instances_type, INOUTP int *num_instances_type, INP int num_models, INP int max_cluster_size, INP int max_primitive_inputs) |
| static boolean | inputs_outputs_models_and_clocks_feasible (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, int iblk, boolean *is_clock, t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static int | get_highest_gain_logical_block (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb, INP boolean *is_clock, INP boolean(*is_feasible)(enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, int iblk, boolean *is_clock, t_pb *cur_pb), INP enum e_gain_type gain_mode) |
| static int | get_logical_block_for_cluster (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INP t_pb *cur_pb, INP boolean *is_clock, INP boolean allow_unrelated_clustering) |
| static int | get_free_logical_block_with_fewest_ext_inputs (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static int | get_most_feasible_logical_block (INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb) |
| static void | alloc_and_load_cluster_info (INP int num_clb, INOUTP t_block *clb) |
| static void | check_clustering (int num_clb, t_block *clb, boolean *is_clock) |
| static void | check_cluster_logical_blocks (t_pb *pb, boolean *blocks_checked) |
| static int | get_most_critical_unclustered_block (void) |
| static void | free_cb (t_pb *pb, int max_models) |
| static void | free_pb_stats (t_pb_stats pb_stats, int max_models) |
| static void | free_pb (t_pb *pb, int max_models) |
| void | do_clustering (const t_arch *arch, int num_models, boolean global_clocks, boolean *is_clock, boolean hill_climbing_flag, char *out_fname, boolean timing_driven, enum e_cluster_seed cluster_seed_type, float alpha, float beta, int recompute_timing_after, float block_delay, float intra_cluster_net_delay, float inter_cluster_net_delay, float aspect, boolean allow_unrelated_clustering, boolean allow_early_exit, boolean connection_driven, enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, boolean hack_no_legal_frac_lut, boolean hack_safe_latch) |
| static enum e_block_pack_status | alloc_and_load_pb (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INP t_pb_graph_node *pb_graph_node, INP int iblock, INOUTP t_pb *pb, INP int max_models, int max_cluster_size, int max_primitive_inputs) |
| static int | get_logical_block_for_cluster (INP enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, INOUTP t_pb *cur_pb, INP boolean *is_clock, INP boolean allow_unrelated_clustering) |
Variables | |
| static struct s_ilink * | unclustered_list_head |
| int | unclustered_list_head_size |
| static struct s_ilink * | memory_pool |
| static int * | net_output_feeds_driving_block_input |
| static int | hack_frac_lut_no_legality |
| static int | hack_force_safe_latch |
| static int | indexofcrit |
| static float ** | net_pin_backward_criticality = NULL |
| static float ** | net_pin_forward_criticality = NULL |
| static float * | criticality = NULL |
| static int * | critindexarray = NULL |
Detailed Description
Main clustering algorithm Author(s): Vaughn Betz (first revision - VPack), Alexander Marquardt (second revision - T-VPack), Jason Luu (third revision - AAPack) June 8, 2011
Definition in file cluster.c.
Define Documentation
| #define AAPACK_MAX_FEASIBLE_BLOCK_ARRAY_SIZE 30 |
| #define MARKED_FRAC 2 |
1/MARKED_FRAC is the fraction of nets or blocks that must be marked in order for the brute force (go through the whole data structure linearly) gain update etc. code to be used. This is done for speed only; make MARKED_FRAC whatever number speeds the code up most.
| #define SCALE_DISTANCE_VAL 1e-4 |
| #define SCALE_NUM_PATHS 1e-2 |
this value is used as a multiplier to assign a slightly higher criticality value to nets that affect a large number of critical paths versus nets that do not have such a broad effect. Note that this multiplier is intentionally very small compared to the total criticality because we want to make sure that vpack_net criticality is primarily determined by slacks, with this acting only as a tie-breaker between otherwise equal nets
Enumeration Type Documentation
| enum e_feasibility |
| enum e_gain_type |
| enum e_gain_update |
| enum e_removal_policy |
Function Documentation
| static void add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates | ( | int | iblk, |
| float * | gain, | ||
| t_pb * | pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
Add blk to list of feasible blocks sorted according to gain
Definition at line 743 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
i = 0;
if(i == pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models) {
/* Corresponding model not found, add it */
pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models++;
pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] = 1;
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][0] = iblk;
} else {
/* found matching model, bubble sort */
if(pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] >= AAPACK_MAX_FEASIBLE_BLOCK_ARRAY_SIZE - 1) {
/* maximum size for array, remove smallest gain element and sort */
if(gain[iblk] > gain[pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][0]]) {
/* single loop insertion sort */
for(j = 0; j < pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] - 1; j++) {
if(gain[iblk] <= gain[pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j + 1]]) {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j] = iblk;
break;
} else {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j] = pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j + 1];
}
}
if(j == pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] - 1) {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j] = iblk;
}
}
} else {
/* Expand array and single loop insertion sort */
for(j = pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if(gain[pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j]] > gain[iblk]) {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j + 1] = pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j];
} else {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][j + 1] = iblk;
break;
}
}
if(j < 0) {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][0] = iblk;
}
pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i]++;
}
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void alloc_and_init_clustering | ( | boolean | global_clocks, |
| float | alpha, | ||
| float | beta, | ||
| int | max_cluster_size, | ||
| int | max_primitive_inputs, | ||
| int | max_pb_depth, | ||
| int | max_models | ||
| ) | [static] |
Allocates the main data structures used for clustering and properly initializes them.
Definition at line 793 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, ext_inps, ipin, driving_blk, inet;
struct s_ilink *next_ptr;
alloc_and_load_cluster_legality_checker();
for (i=0;i<num_logical_blocks;i++) {
logical_block[i].clb_index = NO_CLUSTER;
}
unclustered_list_head = (struct s_ilink *) my_calloc(max_primitive_inputs + 1, sizeof(struct s_ilink));
unclustered_list_head_size = max_primitive_inputs + 1;
for (i = 0; i <= max_primitive_inputs; i++) {
unclustered_list_head[i].next = NULL;
}
memory_pool = (struct s_ilink *) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (struct s_ilink));
next_ptr = memory_pool;
for (i=0;i<num_logical_blocks;i++) {
ext_inps = num_ext_inputs(i);
next_ptr->next = unclustered_list_head[ext_inps].next;
unclustered_list_head[ext_inps].next = next_ptr;
next_ptr->iblk = i;
next_ptr++;
}
net_output_feeds_driving_block_input = (int *) my_malloc (
num_logical_nets * sizeof (int));
for (inet=0;inet<num_logical_nets;inet++) {
net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] = 0;
driving_blk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[0];
for (ipin=1;ipin<=vpack_net[inet].num_sinks;ipin++) {
if (vpack_net[inet].node_block[ipin] == driving_blk) {
net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet]++;
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void alloc_and_load_cluster_info | ( | INP int | num_clb, |
| INOUTP t_block * | clb | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 2149 of file cluster.c.
{
/* Loads all missing clustering info necessary to complete clustering. */
int i, j, i_clb, node_index, ipin, iclass;
int inport, outport, clockport;
const t_pb_type * pb_type;
t_pb *pb;
for(i_clb = 0; i_clb < num_clb; i_clb++) {
rr_node = clb[i_clb].pb->rr_graph;
pb_type = clb[i_clb].pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
pb = clb[i_clb].pb;
clb[i_clb].nets = my_malloc(clb[i_clb].type->num_pins * sizeof(int));
for(i = 0; i < clb[i_clb].type->num_pins; i++) {
clb[i_clb].nets[i] = OPEN;
}
inport = outport = clockport = 0;
ipin = 0;
/* Assume top-level pb and clb share a one-to-one connection */
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_ports; i++) {
if(!pb_type->ports[i].is_clock && pb_type->ports[i].type == IN_PORT) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->ports[i].num_pins; j++) {
iclass = clb[i_clb].type->pin_class[ipin];
assert(clb[i_clb].type->class_inf[iclass].type == RECEIVER);
assert(!clb[i_clb].type->is_global_pin[ipin]);
node_index = pb->pb_graph_node->input_pins[inport][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
clb[i_clb].nets[ipin] = rr_node[node_index].net_num;
ipin++;
}
inport++;
} else if(pb_type->ports[i].type == OUT_PORT) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->ports[i].num_pins; j++) {
iclass = clb[i_clb].type->pin_class[ipin];
assert(clb[i_clb].type->class_inf[iclass].type == DRIVER);
node_index = pb->pb_graph_node->output_pins[outport][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
clb[i_clb].nets[ipin] = rr_node[node_index].net_num;
ipin++;
}
outport++;
} else {
assert(pb_type->ports[i].is_clock && pb_type->ports[i].type == IN_PORT);
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->ports[i].num_pins; j++) {
iclass = clb[i_clb].type->pin_class[ipin];
assert(clb[i_clb].type->class_inf[iclass].type == RECEIVER);
assert(clb[i_clb].type->is_global_pin[ipin]);
node_index = pb->pb_graph_node->clock_pins[clockport][j].pin_count_in_cluster;
clb[i_clb].nets[ipin] = rr_node[node_index].net_num;
ipin++;
}
clockport++;
}
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static enum e_block_pack_status alloc_and_load_pb | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INP t_pb_graph_node * | pb_graph_node, | ||
| INP int | iblock, | ||
| INOUTP t_pb * | pb, | ||
| INP int | max_models, | ||
| INP int | max_cluster_size, | ||
| INP int | max_primitive_inputs | ||
| ) | [static] |
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static enum e_block_pack_status alloc_and_load_pb | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INP t_pb_graph_node * | pb_graph_node, | ||
| INP int | iblock, | ||
| INOUTP t_pb * | pb, | ||
| INP int | max_models, | ||
| int | max_cluster_size, | ||
| int | max_primitive_inputs | ||
| ) | [static] |
Allocate space within pb and load data for it given the current logical block. Note: pb space and parent info must be loaded before calling this function
TODO: add-in some heuristic for determing which pb to select if there are multiple choices
Definition at line 1336 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j, k;
const t_pb_type *pb_type;
boolean is_primitive;
enum e_block_pack_status block_pack_status;
pb->pb_graph_node = pb_graph_node;
pb->logical_block = NO_CLUSTER;
block_pack_status = BLK_STATUS_UNDEFINED;
if(iblock == NO_CLUSTER) {
return BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE;
}
pb_type = pb_graph_node->pb_type;
is_primitive = (pb_type->num_modes == 0);
/* TODO: It would be good to save and prune away nodes of types that I know won't fit, that way, I don't have to traverse the tree
for types that don't work, this runtime optimization can be done later */
if(is_primitive) {
if(!primitive_feasible(iblock, pb)) {
return BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE;
}
assert(pb->logical_block == OPEN);
/* check if I can add and route this block, if they yes, then success, if not, fail */
if(hack_frac_lut_no_legality) {
block_pack_status = BLK_PASSED;
pb->logical_block = iblock;
logical_block[iblock].pb = pb;
} else {
block_pack_status = try_add_block_to_current_cluster_and_primitive(iblock, pb);
}
if(block_pack_status == BLK_PASSED) {
pb->name = my_strdup(logical_block[iblock].name);
}
} else {
if(pb->child_pbs == NULL) {
/* first time here so must allocate space and determine mode of operation */
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_modes && block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED; i++) {
pb->mode = i;
if(!models_feasible(packer_algorithm, iblock, pb_type, pb, pb->mode)) {
continue;
}
set_pb_mode(pb, 0, 0); /* default mode is to use mode 1 */
set_pb_mode(pb, i, 1);
pb->child_pbs = my_calloc(pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children, sizeof(t_pb *));
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
/* allocate space for children if first time allocating space */
pb->child_pbs[j] = my_calloc(pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb, sizeof(t_pb));
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb; k++) {
pb->child_pbs[j][k].parent_pb = pb;
alloc_and_load_pb_stats(&pb->child_pbs[j][k], max_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
}
}
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children && block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb && block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED; k++) {
block_pack_status = alloc_and_load_pb(packer_algorithm, &pb_graph_node->child_pb_graph_nodes[i][j][k], iblock, &pb->child_pbs[j][k], max_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
if(block_pack_status == BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE) {
/* sibling blocks differ only in interconnect,
if feasibility fails then it is failing on something other than interconnect
therefore, no point trying the same thing for siblings */
break;
}
}
}
if(block_pack_status == BLK_PASSED) {
pb->name = my_strdup(logical_block[iblock].name);
} else {
set_pb_mode(pb, i, 0); /* default mode is to use mode 1 */
set_pb_mode(pb, 0, 1);
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
if(pb->child_pbs[j] != NULL) {
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb; k++) {
free_pb_stats(pb->child_pbs[j][k].pb_stats, max_models);
}
free(pb->child_pbs[j]);
}
}
free(pb->child_pbs);
pb->child_pbs = NULL;
}
}
} else {
/*
* Another block has been allocated inside so must select placement carefully
*/
i = pb->mode;
if(!models_feasible(packer_algorithm, iblock, pb_type, pb, pb->mode)) {
block_pack_status = BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE;
} else {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children && block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb && block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED; k++) {
/* Simple heuristic: assume that any packed cluster is well-packed, try to pack into new child only */
/* Brute force heuristic: traverse whole tree always */
if(pb->child_pbs[j][k].name == NULL) {
block_pack_status = alloc_and_load_pb(packer_algorithm, &pb_graph_node->child_pb_graph_nodes[i][j][k], iblock, &pb->child_pbs[j][k], max_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
} else if (packer_algorithm == PACK_BRUTE_FORCE && pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_modes != 0) {
block_pack_status = alloc_and_load_pb(packer_algorithm, &pb_graph_node->child_pb_graph_nodes[i][j][k], iblock, &pb->child_pbs[j][k], max_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
}
if(block_pack_status == BLK_FAILED_FEASIBLE && packer_algorithm != PACK_BRUTE_FORCE) {
/* Children blocks differ only in routing, don't continue if feasibility fails
Brute force algorithm may have just ran into a node that was full, therefore it should not break out
*/
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return block_pack_status;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:| static void alloc_and_load_pb_stats | ( | t_pb * | pb, |
| int | max_models, | ||
| int | max_cluster_size, | ||
| int | max_primitive_inputs | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 1277 of file cluster.c.
{
int j;
/* If statement below is for speed. If nets are reasonably low-fanout, *
* only a relatively small number of blocks will be marked, and updating *
* only those logical_block structures will be fastest. If almost all blocks *
* have been touched it should be faster to just run through them all *
* in order (less addressing and better cache locality). */
pb->pb_stats.gain = (float *) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (float));
pb->pb_stats.lengthgain=(float*) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (float));
pb->pb_stats.sharinggain=(float*) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (float));
pb->pb_stats.hillgain =(float*) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (float));
pb->pb_stats.connectiongain = (float*) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof (float));
pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail = NOT_VALID;
pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail = NOT_VALID;
pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail = NOT_VALID;
pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models = 0;
pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model = NOT_VALID;
pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks = my_calloc(max_models, sizeof(int));
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks = my_malloc(max_models * sizeof(int*));
for (j=0;j<max_models;j++) {
pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[j] = (int*) my_malloc (AAPACK_MAX_FEASIBLE_BLOCK_ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof (int));
}
for (j=0;j<num_logical_blocks;j++) {
pb->pb_stats.gain[j] = 0.0;
pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[j]= 0.0;
pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[j] = 0;
pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[j]=NOT_VALID;
pb->pb_stats.hillgain[j]=NOT_VALID;
}
pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb = (int *) my_malloc (num_logical_nets * sizeof(int));
pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb = (boolean *) my_malloc (num_logical_nets * sizeof(boolean));
for (j=0;j<num_logical_nets;j++) {
pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[j] = 0;
pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[j] = FALSE;
}
pb->pb_stats.marked_nets = (int *) my_malloc ((max_primitive_inputs + 2) * max_cluster_size * sizeof(int));
pb->pb_stats.marked_blocks = (int *) my_malloc (num_logical_blocks * sizeof(int));
pb->pb_stats.num_marked_nets = 0;
pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks = 0;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void check_clocks | ( | boolean * | is_clock | ) | [static] |
Checks that nets used as clock inputs to latches are never also used as VPACK_LUT inputs. It's electrically questionable, and more importantly would break the clustering code.
Definition at line 642 of file cluster.c.
{
int inet, iblk, ipin;
t_model_ports *port;
for (iblk=0;iblk<num_logical_blocks;iblk++) {
if (logical_block[iblk].type != VPACK_OUTPAD) {
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
while(port) {
for (ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
inet = logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][ipin];
if (inet != OPEN) {
if (is_clock[inet]) {
printf("Error in check_clocks. Net %d (%s) is a clock, but "
"also\n"
"\tconnects to a logic block input on logical_block %d (%s).\n", inet,
vpack_net[inet].name, iblk, logical_block[iblk].name);
printf("This would break the current clustering "
"implementation and is electrically\n"
"\tquestionable, so clustering has been aborted.\n");
exit (1);
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
}
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Definition at line 2254 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
const t_pb_type *pb_type;
boolean has_child;
has_child = FALSE;
pb_type = pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
if(pb_type->num_modes == 0) {
/* primitive */
if(pb->logical_block != OPEN) {
if(blocks_checked[pb->logical_block] != FALSE) {
printf(ERRTAG "pb %s contains logical block %s #%d but logical block is already contained in another pb\n",
pb->name, logical_block[pb->logical_block].name, pb->logical_block);
exit(1);
}
blocks_checked[pb->logical_block] = TRUE;
if(pb != logical_block[pb->logical_block].pb) {
printf(ERRTAG "pb %s contains logical block %s #%d but logical block does not link to pb\n",
pb->name, logical_block[pb->logical_block].name, pb->logical_block);
exit(1);
}
}
} else {
/* this is a container pb, all container pbs must contain children */
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->modes[pb->mode].num_pb_type_children; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[pb->mode].pb_type_children[i].num_pb; j++) {
if(pb->child_pbs[i] != NULL) {
if(pb->child_pbs[i][j].name != NULL) {
has_child = TRUE;
check_cluster_logical_blocks(&pb->child_pbs[i][j], blocks_checked);
}
}
}
}
assert(has_child);
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Definition at line 2209 of file cluster.c.
{
int i;
t_pb * cur_pb;
boolean *blocks_checked;
blocks_checked = my_calloc(num_logical_blocks, sizeof(boolean));
/*
* Check that each logical block connects to one primitive and that the primitive links up to the parent clb
*/
for(i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++) {
if(logical_block[i].pb->logical_block != i) {
printf(ERRTAG "pb %s does not contain logical block %s but logical block %s #%d links to pb\n",
logical_block[i].pb->name, logical_block[i].name, logical_block[i].name, i);
exit(1);
}
cur_pb = logical_block[i].pb;
assert(strcmp(cur_pb->name, logical_block[i].name) == 0);
while(cur_pb->parent_pb) {
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
assert(cur_pb->name);
}
if(cur_pb != clb[num_clb].pb) {
printf(ERRTAG "CLB %s does not match CLB contained by pb %s\n",
cur_pb->name, logical_block[i].pb->name);
exit(1);
}
}
/* Check that I do not have spurious links in children pbs */
for(i = 0; i < num_clb; i++) {
check_cluster_logical_blocks(clb[i].pb, blocks_checked);
}
for(i = 0; i < num_logical_blocks; i++) {
if(blocks_checked[i] == FALSE) {
printf(ERRTAG "Logical block %s #%d not found in any cluster\n", logical_block[i].name, i);
exit(1);
}
}
free(blocks_checked);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
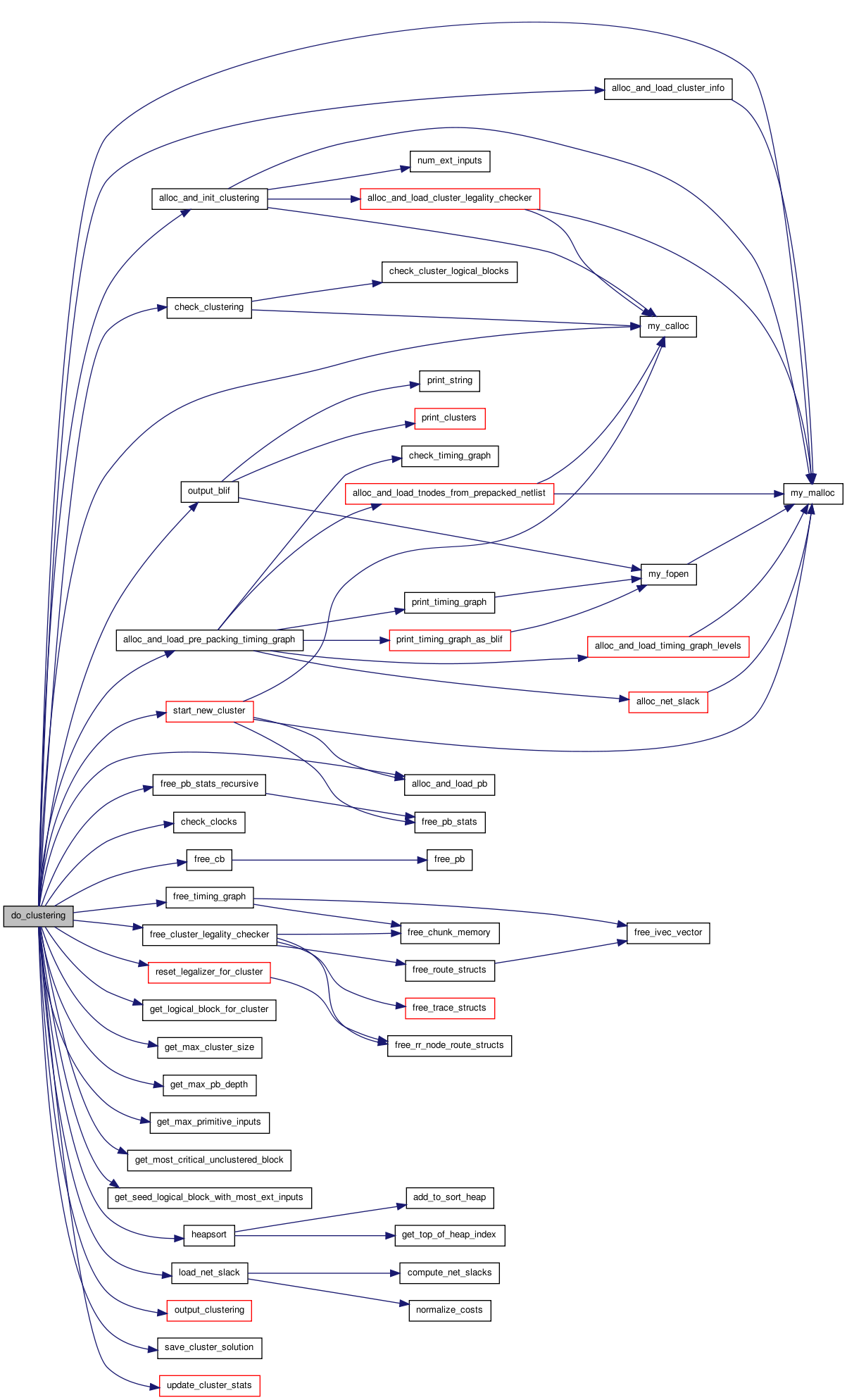
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void do_clustering | ( | const t_arch * | arch, |
| int | num_models, | ||
| boolean | global_clocks, | ||
| boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| boolean | hill_climbing_flag, | ||
| char * | out_fname, | ||
| boolean | timing_driven, | ||
| enum e_cluster_seed | cluster_seed_type, | ||
| float | alpha, | ||
| float | beta, | ||
| int | recompute_timing_after, | ||
| float | block_delay, | ||
| float | intra_cluster_net_delay, | ||
| float | inter_cluster_net_delay, | ||
| float | aspect, | ||
| boolean | allow_unrelated_clustering, | ||
| boolean | allow_early_exit, | ||
| boolean | connection_driven, | ||
| enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, | ||
| boolean | hack_no_legal_frac_lut, | ||
| boolean | hack_safe_latch | ||
| ) |
Does the actual work of clustering multiple VPACK_LUT+FF logic blocks into clusters.
note: I allow timing_driven and connection_driven to be simultaneously true in this case, connection_driven is responsible for all clustering decisions but timing analysis is still enabled (useful for viewing the constant delay results) Algorithm employed: 1. Find type that can legally hold block and create cluster with pb info 2. Populate started cluster 3. Repeat 1 until no more blocks need to be clustered
Definition at line 223 of file cluster.c.
{
int istart, i, j, k, m, iblk;
int blocks_since_last_analysis;
int next_blk, prev_blk;
int num_blocks_hill_added;
int num_logical_blocks_clustered;
int max_cluster_size, cur_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs, cur_primitive_inputs, max_pb_depth, cur_pb_depth;
int *hill_climbing_inputs_avail;
t_block *clb;
t_pb *cur_pb;
int num_clb;
boolean critical_path_minimized;
boolean early_exit;
enum e_block_pack_status block_pack_status;
int *num_used_instances_type, *num_instances_type; /* [0..num_types] Holds array for total number of each cluster_type available */
float **net_slack = NULL;
float num_paths_scaling, distance_scaling;
float crit;
hack_frac_lut_no_legality = hack_no_legal_frac_lut;
hack_force_safe_latch = hack_safe_latch;
/* TODO: This is memory inefficient, fix if causes problems */
clb = my_calloc(num_logical_blocks,sizeof(t_block));
num_clb = 0;
istart = NO_CLUSTER;
/* determine bound on cluster size and primitive input size */
max_cluster_size = 0;
max_primitive_inputs = 0;
max_pb_depth = 0;
indexofcrit = 0;
for(i = 0; i < num_types; i++) {
if(EMPTY_TYPE == &type_descriptors[i])
continue;
cur_cluster_size = get_max_cluster_size(type_descriptors[i].pb_type);
cur_primitive_inputs = get_max_primitive_inputs(type_descriptors[i].pb_type);
cur_pb_depth = get_max_pb_depth(type_descriptors[i].pb_type);
if(cur_cluster_size > max_cluster_size) {
max_cluster_size = cur_cluster_size;
}
if(cur_primitive_inputs > max_primitive_inputs) {
max_primitive_inputs = cur_primitive_inputs;
}
if(cur_pb_depth > max_pb_depth) {
max_pb_depth = cur_pb_depth;
}
}
if(hill_climbing_flag) {
hill_climbing_inputs_avail = (int *) my_calloc (max_cluster_size + 1, sizeof(int));
} else {
hill_climbing_inputs_avail = NULL; /* if used, die hard */
}
/* TODO: make better estimate for nx and ny */
nx = ny = 1;
check_clocks (is_clock);
#if 0
check_for_duplicate_inputs ();
#endif
alloc_and_init_clustering (global_clocks, alpha, beta, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs, max_pb_depth, num_models);
blocks_since_last_analysis = 0;
critical_path_minimized = FALSE;
early_exit = FALSE;
num_logical_blocks_clustered = 0;
num_blocks_hill_added = 0;
num_used_instances_type = (int*)my_calloc (num_types, sizeof (int));
num_instances_type = (int*)my_calloc (num_types, sizeof (int));
assert(max_cluster_size < MAX_SHORT); /* Limit maximum number of elements for each cluster */
if (timing_driven){
net_slack = alloc_and_load_pre_packing_timing_graph(block_delay, inter_cluster_net_delay, arch->models);
load_net_slack(net_slack, 0);
criticality=(float*)my_calloc(num_logical_blocks,sizeof(float));
critindexarray=(int*)my_malloc(num_logical_blocks*sizeof(int));
for(i = 0; i < num_logical_blocks; i++) {
critindexarray[i] = i;
}
/* Calculate criticality based on slacks and tie breakers (# paths, distance from source) */
for(i = 0; i < num_tnodes; i++) {
iblk = tnode[i].block;
num_paths_scaling = SCALE_NUM_PATHS * (float)tnode[i].normalized_total_critical_paths;
distance_scaling = SCALE_DISTANCE_VAL * (float)tnode[i].normalized_T_arr;
crit = (1 - tnode[i].normalized_slack) + num_paths_scaling + distance_scaling;
if(criticality[iblk] < crit) {
criticality[iblk] = crit;
}
}
net_pin_backward_criticality = (float**)my_calloc(num_logical_nets, sizeof(float*));
net_pin_forward_criticality = (float**)my_calloc(num_logical_nets, sizeof(float*));
for(i = 0; i < num_logical_nets; i++) {
net_pin_backward_criticality[i] = (float *)my_calloc(vpack_net[i].num_sinks + 1, sizeof(float));
net_pin_forward_criticality[i] = (float *)my_calloc(vpack_net[i].num_sinks + 1, sizeof(float));
for(j = 0; j <= vpack_net[i].num_sinks; j++) {
net_pin_backward_criticality[i][j] = criticality[vpack_net[i].node_block[j]];
net_pin_forward_criticality[i][j] = criticality[vpack_net[i].node_block[0]];
}
}
heapsort(critindexarray, criticality, num_logical_blocks, 1);
/*print_critical_path("clustering_critical_path.echo");*/
if (cluster_seed_type == VPACK_TIMING){
istart=get_most_critical_unclustered_block();
}
else {/*max input seed*/
printf("get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs\n");
istart = get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs(max_primitive_inputs);
}
}
else /*cluster seed is max input (since there is no timing information)*/{
istart = get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs(max_primitive_inputs);
}
while (istart != NO_CLUSTER) {
reset_legalizer_for_cluster(&clb[num_clb]);
/* start a new cluster and reset all stats */
start_new_cluster(packer_algorithm, arch, &clb[num_clb], num_clb, istart, aspect, num_used_instances_type, num_instances_type, num_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
if(logical_block[istart].type != VPACK_INPAD && logical_block[istart].type != VPACK_OUTPAD)
{
printf("Complex Block %d: %s type %s\n", num_clb, clb[num_clb].name, clb[num_clb].type->name);
fflush(stdout);
}
update_cluster_stats (istart, num_clb, is_clock, global_clocks, alpha, beta, timing_driven, connection_driven);
num_clb++;
num_logical_blocks_clustered ++;
if (timing_driven && !early_exit) {
blocks_since_last_analysis++;
/*it doesn't make sense to do a timing analysis here since there*
*is only one logical_block clustered it would not change anything */
}
/* First try to pack primitive into cluster, select next block based on closest open sibling if available */
cur_pb = logical_block[istart].pb->parent_pb;
prev_blk = NO_CLUSTER;
while (cur_pb) {
if(packer_algorithm == PACK_BRUTE_FORCE) { /* if using brute force approach, look at all possible free blocks in cluster */
cur_pb = clb[num_clb - 1].pb;
}
next_blk = get_logical_block_for_cluster(packer_algorithm,
cur_pb,
is_clock,
allow_unrelated_clustering);
block_pack_status = alloc_and_load_pb(packer_algorithm, cur_pb->pb_graph_node, next_blk, cur_pb, num_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
if(block_pack_status != BLK_PASSED) {
if(next_blk != NO_CLUSTER && prev_blk != next_blk) {
if(block_pack_status == BLK_FAILED_ROUTE) {
#ifdef DEBUG_FAILED_PACKING_CANDIDATES
printf("NO_ROUTE:%s#%d|%s ", logical_block[next_blk].name, next_blk, logical_block[next_blk].model->name);
#else
printf(".");
#endif
} else {
#ifdef DEBUG_FAILED_PACKING_CANDIDATES
printf("FAILED_CHECK:%s#%d|%s check %d", logical_block[next_blk].name, next_blk, logical_block[next_blk].model->name, block_pack_status);
#else
printf(".");
#endif
}
prev_blk = next_blk;
} else {
prev_blk = NO_CLUSTER;
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
continue;
} else {
/* Continue packing by filling smallest cluster */
if(hack_frac_lut_no_legality) {
logical_block[next_blk].clb_index = num_clb - 1;
}
cur_pb = logical_block[next_blk].pb->parent_pb;
prev_blk = NO_CLUSTER;
#ifdef DEBUG_FAILED_PACKING_CANDIDATES
printf("PASSED:%s#%d ", logical_block[next_blk].name, next_blk);
#else
printf(".");
#endif
}
update_cluster_stats (next_blk, num_clb - 1, is_clock, global_clocks,
alpha, beta, timing_driven, connection_driven);
num_logical_blocks_clustered ++;
if (timing_driven && !early_exit) {
blocks_since_last_analysis++; /* historically, timing slacks were recomputed after X number of blocks were packed, but this doesn't significantly alter results so I (jluu) did not port the code */
}
}
if(logical_block[istart].type != VPACK_INPAD && logical_block[istart].type != VPACK_OUTPAD)
{
printf("\n");
}
save_cluster_solution();
if(hack_frac_lut_no_legality) {
k = 0;
for(i = 0; i < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_input_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_input_pins[i]; j++) {
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
if(!clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && !vpack_net[k].is_global && clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] != 0)
{
rr_node[clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->input_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster].net_num = k;
k++;
break;
}
k++;
}
}
}
/* check if nets are overused */
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
if(!clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && !vpack_net[k].is_global && clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] != 0)
{
printf(ERRTAG "Too many input nets used in cluster %s\n", clb[num_clb-1].name);
assert(0);
}
k++;
}
k = 0;
for(i = 0; i < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_output_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_output_pins[i]; j++) {
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
for(m = 0; m <= vpack_net[k].num_sinks; m++) {
if(logical_block[vpack_net[k].node_block[m]].clb_index != num_clb - 1) {
break;
}
}
if(clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && (clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] < vpack_net[k].num_sinks + 1))
{
rr_node[clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->output_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster].net_num = k;
k++;
break;
}
k++;
}
}
}
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
if(clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && (clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] < vpack_net[k].num_sinks + 1))
{
printf(ERRTAG "Too many output nets used in cluster %s\n", clb[num_clb-1].name);
assert(0);
}
k++;
}
k = 0;
for(i = 0; i < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_clock_ports; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->num_clock_pins[i]; j++) {
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
if(!clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && vpack_net[k].is_global && clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] != 0)
{
rr_node[clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_graph_node->clock_pins[i][j].pin_count_in_cluster].net_num = k;
k++;
break;
}
k++;
}
}
}
while(k < num_logical_nets) {
if(!clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[k] && vpack_net[k].is_global && clb[num_clb-1].pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[k] != 0)
{
printf(ERRTAG "Too many clock nets used in cluster %s\n", clb[num_clb-1].name);
assert(0);
}
k++;
}
}
if (timing_driven){
if (num_blocks_hill_added > 0 && !early_exit) {
blocks_since_last_analysis += num_blocks_hill_added;
}
if (cluster_seed_type == VPACK_TIMING){
istart=get_most_critical_unclustered_block();
}
else { /*max input seed*/
istart = get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs(max_primitive_inputs);
}
}
else /*cluster seed is max input (since there is no timing information)*/
istart=get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs(max_primitive_inputs);
free_pb_stats_recursive (clb[num_clb-1].pb, num_models);
}
if (timing_driven){
free_timing_graph(net_slack);
}
free_cluster_legality_checker();
alloc_and_load_cluster_info (num_clb, clb);
check_clustering (num_clb, clb, is_clock);
output_clustering( clb, num_clb, global_clocks, is_clock, out_fname, FALSE);
#ifdef DUMP_BLIF_ECHO
if(!hack_frac_lut_no_legality) /* must have routing graph before dumping blif */
output_blif( clb, num_clb, global_clocks, is_clock, "post_packing_blif.echo", FALSE);
#endif
if(hill_climbing_flag)
{
free (hill_climbing_inputs_avail);
}
for(i = 0; i < num_clb; i++) {
free_cb(clb[i].pb, num_models);
free(clb[i].name);
free(clb[i].nets);
free(clb[i].pb);
}
free(clb);
free (num_used_instances_type);
free (num_instances_type);
free (unclustered_list_head);
free (memory_pool);
free (net_output_feeds_driving_block_input);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void free_cb | ( | t_pb * | pb, |
| int | max_models | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 2313 of file cluster.c.
{
const t_pb_type * pb_type;
int i, total_nodes;
pb_type = pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
total_nodes = pb->pb_graph_node->total_pb_pins + pb_type->num_input_pins + pb_type->num_output_pins + pb_type->num_clock_pins;
for(i = 0; i < total_nodes; i++) {
if(pb->rr_graph[i].edges != NULL) {
free(pb->rr_graph[i].edges);
}
if(pb->rr_graph[i].switches != NULL) {
free(pb->rr_graph[i].switches);
}
}
free(pb->rr_graph);
free_pb(pb, max_models);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void free_pb | ( | t_pb * | pb, |
| int | max_models | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 2334 of file cluster.c.
{
const t_pb_type * pb_type;
int i, j, mode;
pb_type = pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
if(pb_type->blif_model == NULL) {
mode = pb->mode;
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->modes[mode].num_pb_type_children && pb->child_pbs != NULL; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i].num_pb && pb->child_pbs[i] != NULL; j++) {
if(pb->child_pbs[i][j].name != NULL) {
free_pb(&pb->child_pbs[i][j], max_models);
}
}
if(pb->child_pbs[i])
free(pb->child_pbs[i]);
}
if(pb->child_pbs);
free(pb->child_pbs);
free(pb->name);
} else {
/* Primitive */
if(pb->name)
free(pb->name);
pb->name = NULL;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void free_pb_stats | ( | t_pb_stats | pb_stats, |
| int | max_models | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 2362 of file cluster.c.
{
int i;
if(pb_stats.gain != NULL) {
free(pb_stats.gain);
free(pb_stats.lengthgain);
free(pb_stats.sharinggain);
free(pb_stats.hillgain);
free(pb_stats.connectiongain);
free(pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks);
for(i = 0; i < max_models; i ++) {
free(pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i]);
}
free(pb_stats.feasible_blocks);
free(pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb);
free(pb_stats.net_output_in_pb);
free(pb_stats.marked_nets);
free(pb_stats.marked_blocks);
pb_stats.gain = NULL;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void free_pb_stats_recursive | ( | t_pb * | pb, |
| int | max_models | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 845 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
/* Releases all the memory used by clustering data structures. */
if(pb) {
if(pb->pb_graph_node != NULL) {
if(pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_modes != 0) {
for(i = 0; i < pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->modes[pb->mode].num_pb_type_children; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->modes[pb->mode].pb_type_children[i].num_pb; j++) {
if(pb->child_pbs && pb->child_pbs[i]) {
free_pb_stats_recursive (&pb->child_pbs[i][j], max_models);
}
}
}
}
}
free_pb_stats(pb->pb_stats, max_models);
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_free_logical_block_with_fewest_ext_inputs | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
| static int get_free_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs_for_cluster | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
This routine is used to find new blocks for clustering when there are no feasible blocks with any attraction to the current cluster (i.e. it finds blocks which are unconnected from the current cluster). It returns the logical_block with the largest number of used inputs that satisfies the clocking and number of inputs constraints. If no suitable logical_block is found, the routine returns NO_CLUSTER.
Definition at line 1207 of file cluster.c.
{
int ext_inps;
int best_block;
int inputs_avail;
inputs_avail = cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail;
if(inputs_avail == NOT_VALID) {
inputs_avail = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_input_pins;
}
best_block = NO_CLUSTER;
if(inputs_avail >= unclustered_list_head_size) {
inputs_avail = unclustered_list_head_size - 1;
}
for (ext_inps = inputs_avail; ext_inps >= 0; ext_inps--) {
best_block = get_logical_block_by_num_ext_inputs (packer_algorithm, cur_pb, ext_inps, REMOVE_CLUSTERED);
if (best_block != NO_CLUSTER) {
break;
}
}
return best_block;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_highest_gain_logical_block | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| INP boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| INP boolean(*)(enum e_packer_algorithm packer_algorithm, int iblk, boolean *is_clock, t_pb *cur_pb) | is_feasible, | ||
| INP enum e_gain_type | gain_mode | ||
| ) | [static] |
This routine populates a list of feasible blocks outside the cluster then returns the best one for the list not currently in a cluster and satisfies the feasibility function passed in as is_feasible. If there are no feasible blocks it returns NO_CLUSTER.
Definition at line 2011 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j, iblk, index;
int best_hillgain;
float best_gain;
int best_block;
best_gain = (float)NOT_VALID + 1.0;
best_hillgain=NOT_VALID+1;
best_block = NO_CLUSTER;
if(cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model == NOT_VALID) {
/* Divide into two cases for speed only. */
/* Typical case: not too many blocks have been marked. */
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks < num_logical_blocks / MARKED_FRAC) {
for (i=0;i<cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks;i++) {
iblk = cur_pb->pb_stats.marked_blocks[i];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
if (gain_mode != HILL_CLIMBING){
if (is_feasible (packer_algorithm, iblk, is_clock, cur_pb)) {
add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates(iblk, cur_pb->pb_stats.gain, cur_pb);
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] > best_gain) {
best_gain = cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk];
best_block = iblk;
}
}
}
else{ /*hill climbing*/
if (is_feasible (packer_algorithm, iblk, is_clock, cur_pb)) {
add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates(iblk, cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain, cur_pb);
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk] > best_hillgain) {
best_hillgain = cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk];
best_block = iblk;
}
}
}
}
}
}
else { /* Some high fanout nets marked lots of blocks. */
for (iblk=0;iblk<num_logical_blocks;iblk++) {
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
if (gain_mode != HILL_CLIMBING){
if (is_feasible (packer_algorithm, iblk, is_clock, cur_pb)) {
add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates(iblk, cur_pb->pb_stats.gain, cur_pb);
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] > best_gain) {
best_gain = cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk];
best_block = iblk;
}
}
}
else{ /*hill climbing*/
if (is_feasible (packer_algorithm, iblk, is_clock, cur_pb)) {
add_blk_to_pb_stats_candidates(iblk, cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain, cur_pb);
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk] > best_hillgain) {
best_hillgain = cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk];
best_block = iblk;
}
}
}
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models; i++) {
index = cur_pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[i][cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] - 1];
if (gain_mode != HILL_CLIMBING) {
if(cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[index] == cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[best_block]) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model = i;
break;
}
} else {
if(cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[index] == cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[best_block]) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model = i;
break;
}
}
}
assert(cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models == 0 || i < cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models);
}
if(cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model == NOT_VALID) {
return NO_CLUSTER;
}
for(i = 0; i < cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i]; j++) {
if(cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model] != 0) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model]--;
index = cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model];
iblk = cur_pb->pb_stats.feasible_blocks[cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model][index];
cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model = (cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model + 1) % cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models;
return iblk;
}
}
}
return NO_CLUSTER;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_logical_block_by_num_ext_inputs | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| INP int | ext_inps, | ||
| INP enum e_removal_policy | remove_flag | ||
| ) | [static] |
This routine returns a logical_block which has not been clustered, has no connection to the current cluster, satisfies the cluster clock constraints, is a valid subblock inside the cluster, does not exceed the cluster subblock units available, and has ext_inps external inputs. If there is no such logical_block it returns NO_CLUSTER. Remove_flag controls whether or not blocks that have already been clustered are removed from the unclustered_list data structures. NB: to get a logical_block regardless of clock constraints just set clocks_avail > 0.
Definition at line 1165 of file cluster.c.
{
struct s_ilink *ptr, *prev_ptr;
int ilogical_blk;
prev_ptr = &unclustered_list_head[ext_inps];
ptr = unclustered_list_head[ext_inps].next;
while (ptr != NULL) {
ilogical_blk = ptr->iblk;
/* TODO: Get better candidate logical block in future, eg. return most timing critical or some other smarter metric */
if (logical_block[ilogical_blk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
if (outputs_clocks_and_models_feasible(packer_algorithm, ilogical_blk, NULL, cur_pb)) {
return ilogical_blk;
}
prev_ptr = ptr;
}
else if (remove_flag == REMOVE_CLUSTERED) {
prev_ptr->next = ptr->next;
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return NO_CLUSTER;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_logical_block_for_cluster | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| INP boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| INP boolean | allow_unrelated_clustering | ||
| ) | [static] |
Finds the vpack block with the the greatest gain that satisifies the input, clock and capacity constraints of a cluster that are passed in. If no suitable vpack block is found it returns NO_CLUSTER.
Definition at line 2124 of file cluster.c.
{
int best_block;
/* If cannot pack into primitive, try packing into cluster */
best_block = get_highest_gain_logical_block (packer_algorithm, cur_pb, is_clock, inputs_outputs_models_and_clocks_feasible,
NOT_HILL_CLIMBING);
/* If no blocks have any gain to the current cluster, the code above *
* will not find anything. However, another logical_block with no inputs in *
* common with the cluster may still be inserted into the cluster. */
if (allow_unrelated_clustering)
if (best_block == NO_CLUSTER)
best_block = get_free_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs_for_cluster (packer_algorithm, cur_pb);
return best_block;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:| static int get_logical_block_for_cluster | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INP t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| INP boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| INP boolean | allow_unrelated_clustering | ||
| ) | [static] |
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_max_cluster_size | ( | t_pb_type * | pb_type | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 672 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
int max_size, temp_size;
if (pb_type->modes == 0) {
max_size = pb_type->num_pb;
} else {
max_size = 0;
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_modes; i++) {
temp_size = 0;
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
temp_size += pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j].num_pb *
get_max_cluster_size(&pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j]);
}
if(temp_size > max_size) {
max_size = temp_size;
}
}
}
return max_size;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_max_pb_depth | ( | t_pb_type * | pb_type | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 714 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
int max_depth, temp_depth;
max_depth = pb_type->depth;
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_modes; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
temp_depth = get_max_pb_depth(&pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j]);
if(temp_depth > max_depth) {
max_depth = temp_depth;
}
}
}
return max_depth;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_max_primitive_inputs | ( | t_pb_type * | pb_type | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 694 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
int max_size, temp_size;
if (pb_type->blif_model != NULL) {
max_size = pb_type->num_input_pins;
} else {
max_size = 0;
for(i = 0; i < pb_type->num_modes; i++) {
temp_size = 0;
for(j = 0; j < pb_type->modes[i].num_pb_type_children; j++) {
temp_size = get_max_primitive_inputs(&pb_type->modes[i].pb_type_children[j]);
if(temp_size > max_size) {
max_size = temp_size;
}
}
}
}
return max_size;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_most_critical_unclustered_block | ( | void | ) | [static] |
calculate_timing_information must be called before this, or this function will return garbage
Definition at line 2295 of file cluster.c.
{
/*indexofcrit is a global variable that is reset to 0 each time a *
*timing analysis is done (reset in sort_blocks_by_criticality) */
int critidx, blkidx;
for (critidx=indexofcrit; critidx<num_logical_blocks; critidx++) {
blkidx=critindexarray[critidx];
if (logical_block[blkidx].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
indexofcrit=critidx+1;
return(blkidx);
}
}
/*if it makes it to here , there are no more blocks available*/
return(NO_CLUSTER);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int get_most_feasible_logical_block | ( | INOUTP t_pb * | cur_pb | ) | [static] |
| static int get_seed_logical_block_with_most_ext_inputs | ( | int | max_primitive_inputs | ) | [static] |
This routine is used to find the first seed logical_block for the clustering. It returns the logical_block with the largest number of used inputs that satisfies the clocking and number of inputs constraints. If no suitable logical_block is found, the routine returns NO_CLUSTER.
Definition at line 1240 of file cluster.c.
{
int iblk, ext_inps;
struct s_ilink *ptr, *prev_ptr;
iblk = NO_CLUSTER;
for (ext_inps=max_primitive_inputs;ext_inps>=0;ext_inps--) {
prev_ptr = &unclustered_list_head[ext_inps];
ptr = unclustered_list_head[ext_inps].next;
while (ptr != NULL) {
iblk = ptr->iblk;
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
prev_ptr->next = ptr->next; /* remove blk from list */
break;
} else {
iblk = NO_CLUSTER;
}
prev_ptr = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
if (iblk != NO_CLUSTER)
return (iblk);
}
return (NO_CLUSTER); /* No suitable logical_block found. */
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean inputs_outputs_models_and_clocks_feasible | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| int | iblk, | ||
| boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| t_pb * | cur_pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
Checks if adding iblk to the currently open cluster would violate the cluster input and clock pin limitations. Returns TRUE if iblk can be added to the cluster, FALSE otherwise.
Definition at line 1951 of file cluster.c.
{
int ipin, inet, output_net;
t_model_ports *port;
t_pb* temp_pb;
boolean inputs_feasible = TRUE;
int inputs_avail;
temp_pb = cur_pb;
while(temp_pb && inputs_feasible) {
inputs_avail = temp_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail;
if(inputs_avail == NOT_VALID) {
inputs_avail = temp_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_input_pins;
}
port = logical_block[iblk].model->outputs;
while(port) {
/* Outputs that connect to internal blocks free up an input pin. */
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
output_net = logical_block[iblk].output_nets[port->index][ipin];
if (output_net != OPEN && temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[output_net] != 0 && !is_clock[output_net])
inputs_avail++;
}
port = port->next;
}
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
while(port) {
if(!port->is_clock) {
/* Inputs that do not connect to an output pin of an internal block (including this one) require an input pin. */
for (ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
inet = logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][ipin];
if (inet != OPEN && temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 0) {
if(net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] == 0) {
inputs_avail--;
}
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
inputs_feasible = (inputs_avail >= 0);
temp_pb = temp_pb->parent_pb;
}
if (outputs_clocks_and_models_feasible (packer_algorithm, iblk, is_clock, cur_pb) == FALSE)
return (FALSE);
if (inputs_feasible)
return (TRUE);
else
return (FALSE);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
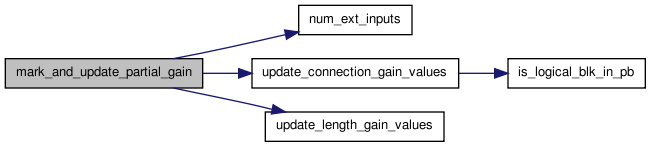
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void mark_and_update_partial_gain | ( | int | inet, |
| enum e_gain_update | gain_flag, | ||
| int | clustered_block, | ||
| int | port_on_clustered_block, | ||
| int | pin_on_clustered_block, | ||
| boolean | timing_driven, | ||
| boolean | connection_driven, | ||
| enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block | net_relation_to_clustered_block | ||
| ) | [static] |
Updates the marked data structures, and if gain_flag is GAIN, the gain when a logic logical_block is added to a cluster. The sharinggain is the number of inputs that a logical_block shares with blocks that are already in the cluster. Hillgain is the reduction in number of pins-required by adding a logical_block to the cluster. The lengthgain is the criticality of the most critical vpack_net between this logical_block and a logical_block in the cluster.
Definition at line 1558 of file cluster.c.
{
int iblk, ipin, ifirst;
t_pb *cur_pb;
cur_pb = logical_block[clustered_block].pb->parent_pb;
while(cur_pb) {
/* Mark vpack_net as being visited, if necessary. */
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 0) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.marked_nets[cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_nets] = inet;
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_nets++;
}
/* Update gains of affected blocks. */
if (gain_flag == GAIN) {
/* Check if this vpack_net lists its driving logical_block twice. If so, avoid *
* double counting this logical_block by skipping the first (driving) pin. */
if (net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] == 0)
ifirst = 0;
else
ifirst = 1;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet]==0) {
for (ipin=ifirst;ipin<=vpack_net[inet].num_sinks;ipin++) {
iblk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[ipin];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk] == NOT_VALID) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.marked_blocks[cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks] = iblk;
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks++;
cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk]=1;
cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk] = 1 - num_ext_inputs (iblk);
}
else {
cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk]++;
cur_pb->pb_stats.hillgain[iblk]++;
}
}
}
}
if (connection_driven) {
update_connection_gain_values(inet, clustered_block, cur_pb, net_relation_to_clustered_block);
}
if (timing_driven) {
update_length_gain_values(inet, clustered_block, cur_pb, net_relation_to_clustered_block);
}
}
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet]++;
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean models_feasible | ( | enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| int | iblk, | ||
| const t_pb_type * | cur_pb_type, | ||
| t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| int | mode | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 961 of file cluster.c.
{
struct s_linked_vptr *cur_model;
int i, j, k, cur_ptr;
struct s_ilink *ptr;
boolean feasible;
const t_pb_type *child_pb_type;
cur_model = cur_pb_type->models_contained;
assert(cur_pb == NULL || cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type == cur_pb_type);
assert(cur_pb == NULL || cur_pb->mode == mode);
feasible = FALSE;
while(cur_model) {
if(cur_model->data_vptr == logical_block[iblk].model) {
feasible = TRUE;
break;
}
cur_model = cur_model->next;
}
if(!feasible) {
return FALSE;
}
if(packer_algorithm == PACK_BRUTE_FORCE) {
/* let the brute force packer determine if an empty slot exists */
return TRUE;
}
feasible = FALSE;
if(cur_pb_type->num_modes == 0) {
if(hack_force_safe_latch) {
/* TODO: Either remove hack or actually make it a feature properly
hack to make the LUT get packed before the LATCH gets packed for cases that the LATCH can be absorbed
for fracturable LUT architectures
*/
if(strcmp(logical_block[iblk].model->name, "latch") == 0) {
i = logical_block[iblk].input_nets[0][0];
j = vpack_net[i].node_block[0];
if(logical_block[j].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER && vpack_net[i].num_sinks == 1 &&
strcmp(logical_block[j].model->name, "names") == 0) {
cur_ptr = logical_block[j].model->inputs[0].size;
ptr = unclustered_list_head[cur_ptr].next;
while(ptr == NULL && cur_ptr > 0) {
cur_ptr--;
ptr = unclustered_list_head[cur_ptr].next;
}
if (cur_ptr > 2)
return FALSE;
}
}
}
return primitive_type_feasible(iblk, cur_pb_type, NULL, OPEN);
}
for(i = 0; i < cur_pb_type->modes[mode].num_pb_type_children; i++) {
child_pb_type = &cur_pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i];
if(cur_pb) {
for(k = 0; k < child_pb_type->num_pb && cur_pb->child_pbs && cur_pb->child_pbs[i]; k++) {
if(cur_pb->child_pbs[i][k].name == NULL) {
break;
}
}
if(k == child_pb_type->num_pb) {
/* no free child */
continue;
}
}
if(child_pb_type->num_modes == 0) {
feasible = primitive_type_feasible(iblk, &cur_pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i], NULL, OPEN);
if(feasible) {
return TRUE;
}
} else {
for(j = 0; j < cur_pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i].num_modes; j++) {
feasible = models_feasible(packer_algorithm, iblk, &cur_pb_type->modes[mode].pb_type_children[i], NULL, j);
if(feasible) {
return TRUE;
}
}
}
}
return FALSE;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static int num_ext_inputs | ( | int | iblk | ) | [static] |
Returns the number of input pins on this logical_block that must be hooked up through external interconnect. That is, the number of input pins used - the number which connect (internally) to the outputs.
Definition at line 593 of file cluster.c.
{
int ext_inps, output_net, ipin, opin;
t_model_ports *port, *out_port;
/* TODO: process to get ext_inps is slow, should cache in lookup table */
ext_inps = 0;
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
while(port) {
if(port->is_clock == FALSE) {
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
if(logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][ipin] != OPEN) {
ext_inps++;
}
out_port = logical_block[iblk].model->outputs;
while(out_port) {
for(opin = 0; opin < out_port->size; opin++) {
output_net = logical_block[iblk].output_nets[out_port->index][opin];
if(output_net == OPEN)
continue;
/* TODO: I could speed things up a bit by computing the number of inputs *
* and number of external inputs for each logic logical_block at the start of *
* clustering and storing them in arrays. Look into if speed is a *
* problem. */
if (logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][ipin] == output_net) {
ext_inps--;
break;
}
}
out_port = out_port->next;
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
assert(ext_inps >= 0);
return (ext_inps);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
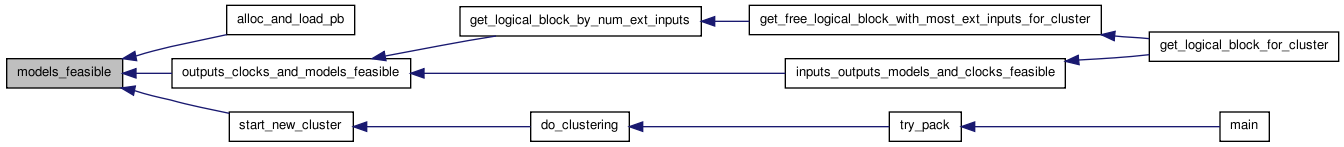
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean outputs_clocks_and_models_feasible | ( | enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| int | iblk, | ||
| boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| t_pb * | cur_pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
Checks if logical_block iblk could be adding to the open cluster without violating clocking constraints. Returns TRUE if it's OK. Some parameters are unused since this function needs the same inter- face as the other feasibility checkers.
Definition at line 872 of file cluster.c.
{
int inet, depth, clocks_avail;
t_model_ports *port;
int ipin, output_net, outputs_avail;
boolean clocks_feasible, outputs_feasible;
t_pb * temp_pb;
/* Assumptions: 1. Clock network unique, can only connect to clock network */
/* 2. Logic block output can't internally connect to clocks. */
clocks_feasible = outputs_feasible = TRUE;
temp_pb = cur_pb;
while(temp_pb && clocks_feasible && outputs_feasible) {
depth = temp_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->depth;
clocks_avail = cur_pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail;
if(clocks_avail == NOT_VALID) {
clocks_avail = temp_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_clock_pins;
}
inet = logical_block[iblk].clock_net;
if (inet != OPEN) {
if (temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 0) {
clocks_avail--;
}
else if (temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 1 &&
temp_pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[inet]) {
clocks_avail--;
}
}
outputs_avail = temp_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail;
port = logical_block[iblk].model->outputs;
while(port) {
/* Outputs that connect to internal blocks free up an input pin. */
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
output_net = logical_block[iblk].output_nets[port->index][ipin];
if (output_net != OPEN) {
if(temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[output_net] >= vpack_net[output_net].num_sinks - net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[output_net]) {
if((temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[output_net] != vpack_net[output_net].num_sinks - net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[output_net])) {
printf("[INTERNAL ERROR] net %d %s %d != %d\n", output_net, vpack_net[output_net].name,
temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[output_net], vpack_net[output_net].num_sinks - net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[output_net]);
}
assert(temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[output_net] == vpack_net[output_net].num_sinks - net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[output_net]);
} else {
outputs_avail--;
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
while(port) {
if(port->is_clock == TRUE) {
port = port->next;
continue;
}
for (ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
inet = logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][ipin];
if(inet != OPEN) {
if(temp_pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[inet] &&
temp_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] + net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] == vpack_net[inet].num_sinks) {
outputs_avail++;
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
clocks_feasible = (clocks_avail >= 0);
outputs_feasible = (outputs_avail >= 0);
temp_pb = temp_pb->parent_pb;
}
if(models_feasible(packer_algorithm, iblk, cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type, cur_pb, cur_pb->mode)) {
if (clocks_feasible && outputs_feasible)
return (TRUE);
else
return (FALSE);
} else {
return FALSE;
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Definition at line 1051 of file cluster.c.
{
const t_pb_type *cur_pb_type;
int i;
t_pb *memory_class_pb; /* Used for memory class only, for memories, open pins must be the same among siblings */
int sibling_memory_blk;
cur_pb_type = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type;
memory_class_pb = NULL;
sibling_memory_blk = OPEN;
assert(cur_pb_type->num_modes == 0); /* primitive */
if(cur_pb->logical_block != OPEN) {
/* This pb already has a logical block */
return FALSE;
}
if(cur_pb_type->class_type == MEMORY_CLASS) {
/* memory class is special, all siblings must share all nets, including open nets, with the exception of data nets */
/* find sibling if one exists */
memory_class_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
for(i = 0; i < cur_pb_type->parent_mode->num_pb_type_children; i++) {
if(memory_class_pb->child_pbs[cur_pb->mode][i].name != NULL && memory_class_pb->child_pbs[cur_pb->mode][i].logical_block != OPEN) {
sibling_memory_blk = memory_class_pb->child_pbs[cur_pb->mode][i].logical_block;
}
}
if(sibling_memory_blk == OPEN) {
memory_class_pb = NULL;
}
}
return primitive_type_feasible(iblk, cur_pb_type, memory_class_pb, sibling_memory_blk);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static boolean primitive_type_feasible | ( | int | iblk, |
| const t_pb_type * | cur_pb_type, | ||
| t_pb * | memory_class_pb, | ||
| int | sibling_memory_blk | ||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 1084 of file cluster.c.
{
t_model_ports *port;
int i, j;
boolean second_pass;
/* check if ports are big enough */
/* for memories, also check that pins are the same with existing siblings */
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
second_pass = FALSE;
while(port || !second_pass) {
/* TODO: This is slow if the number of ports are large, fix if becomes a problem */
if(!port) {
second_pass = TRUE;
port = logical_block[iblk].model->outputs;
}
for(i = 0; i < cur_pb_type->num_ports; i++) {
if(cur_pb_type->ports[i].model_port == port) {
/* TODO: This is slow, I only need to check from 0 if it is a memory block, other blocks I can check from port->size onwards */
for(j = 0; j < port->size; j++) {
if(port->dir == IN_PORT && !port->is_clock) {
if(memory_class_pb) {
if(strstr(cur_pb_type->ports[i].port_class, "data") != cur_pb_type->ports[i].port_class) {
if(logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][j] != logical_block[sibling_memory_blk].input_nets[port->index][j]) {
return FALSE;
}
}
}
if(logical_block[iblk].input_nets[port->index][j] != OPEN && j >= cur_pb_type->ports[i].num_pins) {
return FALSE;
}
} else if(port->dir == OUT_PORT) {
if(memory_class_pb) {
if(strstr(cur_pb_type->ports[i].port_class, "data") != cur_pb_type->ports[i].port_class) {
if(logical_block[iblk].output_nets[port->index][j] != logical_block[sibling_memory_blk].output_nets[port->index][j]) {
return FALSE;
}
}
}
if(logical_block[iblk].output_nets[port->index][j] != OPEN && j >= cur_pb_type->ports[i].num_pins) {
return FALSE;
}
} else {
assert(port->dir == IN_PORT && port->is_clock);
assert(j == 0);
if(memory_class_pb) {
if(logical_block[iblk].clock_net != logical_block[sibling_memory_blk].clock_net) {
return FALSE;
}
}
if(logical_block[iblk].clock_net != OPEN && j >= cur_pb_type->ports[i].num_pins) {
return FALSE;
}
}
}
break;
}
}
if(i == cur_pb_type->num_ports) {
if((logical_block[iblk].model->inputs != NULL && !second_pass) ||
logical_block[iblk].model->outputs != NULL && second_pass) {
/* physical port not found */
return FALSE;
}
}
if(port) {
port = port->next;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void start_new_cluster | ( | INP enum e_packer_algorithm | packer_algorithm, |
| INP const t_arch * | arch, | ||
| INOUTP t_block * | new_cluster, | ||
| INP int | clb_index, | ||
| INP int | istart, | ||
| INP float | aspect, | ||
| INOUTP int * | num_used_instances_type, | ||
| INOUTP int * | num_instances_type, | ||
| INP int | num_models, | ||
| INP int | max_cluster_size, | ||
| INP int | max_primitive_inputs | ||
| ) | [static] |
Given a starting seed block, start_new_cluster determines the next cluster type to use. It expands the FPGA if it cannot find a legal cluster for the logical block
Definition at line 1859 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, j;
boolean success;
assert(new_cluster->name == NULL); /* Check if this cluster is really empty */
/* Allocate a dummy initial cluster and load a logical block as a seed and check if it is legal */
new_cluster->name = my_malloc(strlen(logical_block[istart].name) + 4);
sprintf(new_cluster->name, "cb.%s", logical_block[istart].name);
new_cluster->nets = NULL;
new_cluster->type = NULL;
new_cluster->pb = NULL;
new_cluster->x = UNDEFINED;
new_cluster->y = UNDEFINED;
new_cluster->z = UNDEFINED;
success = FALSE;
while(!success) {
for(i = 0; i < num_types; i++) {
if(num_used_instances_type[i] < num_instances_type[i]) {
new_cluster->type = &type_descriptors[i];
if(new_cluster->type == EMPTY_TYPE) {
continue;
}
new_cluster->pb = my_calloc(1, sizeof(t_pb));
alloc_and_load_pb_stats(new_cluster->pb, num_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs);
new_cluster->pb->parent_pb = NULL;
new_cluster->pb->pb_graph_node = new_cluster->type->pb_graph_head;
alloc_and_load_legalizer_for_cluster(new_cluster, clb_index, arch);
for(j = 0; j < new_cluster->type->pb_graph_head->pb_type->num_modes && !success; j++) {
new_cluster->pb->mode = j;
if(models_feasible(packer_algorithm, istart, new_cluster->pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type, new_cluster->pb, new_cluster->pb->mode)) {
success = (BLK_PASSED == alloc_and_load_pb(packer_algorithm, new_cluster->type->pb_graph_head, istart, new_cluster->pb, num_models, max_cluster_size, max_primitive_inputs));
}
}
if(success) {
if(hack_frac_lut_no_legality) {
logical_block[istart].clb_index = clb_index;
}
/* TODO: For now, just grab any working cluster, in the future, heuristic needed to grab best complex block based on supply and demand */
break;
} else {
free_legalizer_for_cluster(new_cluster);
free_pb_stats(new_cluster->pb->pb_stats, num_models);
free(new_cluster->pb);
}
}
}
/* Expand FPGA size and recalculate number of available cluster types*/
if (!success) {
if(aspect >= 1.0)
{
ny++;
nx = nint(ny * aspect);
}
else
{
nx++;
ny = nint(nx / aspect);
}
printf("Not enough resources expand FPGA size to x = %d y = %d\n", nx, ny);
if((nx > MAX_SHORT) || (ny > MAX_SHORT)) {
printf("Circuit cannot pack into architecture, architecture size (nx = %d, ny = %d) exceeds packer range.\n", nx, ny);
exit(1);
}
alloc_and_load_grid(num_instances_type);
freeGrid();
}
}
num_used_instances_type[new_cluster->type->index]++;
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void update_cluster_stats | ( | INP int | new_blk, |
| INP int | clb_index, | ||
| INP boolean * | is_clock, | ||
| INP boolean | global_clocks, | ||
| INP float | alpha, | ||
| INP float | beta, | ||
| INP boolean | timing_driven, | ||
| INP boolean | connection_driven | ||
| ) | [static] |
Updates cluster stats such as gain, used pins, and clock structures.
Definition at line 1699 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, ipin, inet, depth;
t_model_ports *port;
t_pb *cur_pb;
/* TODO: what a scary comment from Vaughn, we'll have to watch out for this causing problems */
/* Output can be open so the check is necessary. I don't change *
* the gain for clock outputs when clocks are globally distributed *
* because I assume there is no real need to pack similarly clocked *
* FFs together then. Note that by updating the gain when the *
* clock driver is placed in a cluster implies that the output of *
* LUTs can be connected to clock inputs internally. Probably not *
* true, but it doesn't make much difference, since it will still *
* make local routing of this clock very short, and none of my *
* benchmarks actually generate local clocks (all come from pads). */
logical_block[new_blk].clb_index = clb_index;
cur_pb = logical_block[new_blk].pb->parent_pb;
while(cur_pb) {
depth = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->depth;
/* reset list of feasible blocks */
for (i=0;i<cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models;i++){
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_feasible_blocks[i] = 0;
}
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_models = 0;
cur_pb->pb_stats.cur_marked_model = NOT_VALID;
/* determine valid pins */
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail == NOT_VALID)
cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_input_pins;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail == NOT_VALID)
cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_output_pins;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail == NOT_VALID)
cur_pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->num_clock_pins;
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
port = logical_block[new_blk].model->outputs;
while(port) {
for(ipin = 0; ipin < port->size; ipin++) {
inet = logical_block[new_blk].output_nets[port->index][ipin]; /* Output pin first. */
if (inet != OPEN) {
if (!is_clock[inet] || !global_clocks)
mark_and_update_partial_gain (inet, GAIN, new_blk, port->index, ipin,
timing_driven, connection_driven, OUTPUT);
else
mark_and_update_partial_gain (inet, NO_GAIN, new_blk, port->index, ipin,
timing_driven, connection_driven, OUTPUT);
cur_pb = logical_block[new_blk].pb->parent_pb;
while(cur_pb) {
depth = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->depth;
cur_pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[inet] = TRUE;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] > 1 && !is_clock[inet])
cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail++;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] +
net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] != vpack_net[inet].num_sinks + 1) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail--;
} else if (hack_frac_lut_no_legality) {
if(depth > 1)
cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail--; /* frac lut cannot absorb pins after the top two levels */
}
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
port = logical_block[new_blk].model->inputs;
while(port) {
if(port->is_clock) {
port = port->next;
continue;
}
for (ipin=0; ipin<port->size; ipin++) { /* VPACK_BLOCK input pins. */
inet = logical_block[new_blk].input_nets[port->index][ipin];
if (inet != OPEN) {
mark_and_update_partial_gain (inet, GAIN, new_blk, port->index, ipin, timing_driven, connection_driven, INPUT);
cur_pb = logical_block[new_blk].pb->parent_pb;
while(cur_pb) {
depth = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->depth;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 1)
cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail--;
assert(cur_pb->pb_stats.inputs_avail >= 0);
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[inet] &&
cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == vpack_net[inet].num_sinks + 1) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail++;
if (hack_frac_lut_no_legality && depth > 1)
cur_pb->pb_stats.outputs_avail--; /* frac lut cannot absorb pins after the top two levels */
}
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
}
}
port = port->next;
}
/* Note: The code below ONLY WORKS when nets that go to clock inputs *
* NEVER go to the input of a VPACK_COMB. It doesn't really make electrical *
* sense for that to happen, and I check this in the check_clocks *
* function. Don't disable that sanity check. */
inet = logical_block[new_blk].clock_net; /* Clock input pin. */
if (inet != OPEN) {
if (global_clocks)
mark_and_update_partial_gain (inet, NO_GAIN, new_blk, 0,
0, timing_driven,
connection_driven, INPUT);
else
mark_and_update_partial_gain (inet, GAIN, new_blk, 0,
0, timing_driven,
connection_driven, INPUT);
cur_pb = logical_block[new_blk].pb->parent_pb;
while(cur_pb) {
depth = cur_pb->pb_graph_node->pb_type->depth;
if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 1) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail--;
}
else if (cur_pb->pb_stats.num_pins_of_net_in_pb[inet] == 2 && cur_pb->pb_stats.net_output_in_pb[inet]) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.clocks_avail--;
}
/* Note: unlike inputs, I'm currently assuming there is no internal *
* connection in a cluster from VPACK_LUT outputs to clock inputs. */
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
}
update_total_gain(alpha, beta, timing_driven, connection_driven, global_clocks, logical_block[new_blk].pb->parent_pb);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void update_connection_gain_values | ( | int | inet, |
| int | clustered_block, | ||
| t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block | net_relation_to_clustered_block | ||
| ) | [static] |
This function is called when the connectiongain values on the vpack_net inet require updating.
Definition at line 1457 of file cluster.c.
{
int iblk, ipin;
int clb_index;
int num_internal_connections, num_open_connections, num_stuck_connections;
num_internal_connections = num_open_connections = num_stuck_connections = 0;
clb_index = logical_block[clustered_block].clb_index;
/* may wish to speed things up by ignoring clock nets since they are high fanout */
for (ipin=0;ipin<=vpack_net[inet].num_sinks;ipin++) {
iblk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[ipin];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == clb_index && is_logical_blk_in_pb(iblk, logical_block[clustered_block].pb)) {
num_internal_connections++;
} else if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == OPEN) {
num_open_connections++;
} else {
num_stuck_connections++;
}
}
if (net_relation_to_clustered_block==OUTPUT){
for (ipin=1;ipin<=vpack_net[inet].num_sinks;ipin++) {
iblk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[ipin];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
/* Only works if net has one connection to block, TODO: handle case where net has multi-connection to block */
if(num_internal_connections > 1) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk] -= 1 /(float)(vpack_net[inet].num_sinks - (num_internal_connections - 1) + 1 + 1 * num_stuck_connections);
}
cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk] += 1 /(float)(vpack_net[inet].num_sinks - num_internal_connections + 1 + 1 * num_stuck_connections);
}
}
}
if(net_relation_to_clustered_block==INPUT){
/*Calculate the connectiongain for the logical_block which is driving *
*the vpack_net that is an input to a logical_block in the cluster */
iblk=vpack_net[inet].node_block[0];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
if(num_internal_connections > 1) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk] -= 1 / (float)(vpack_net[inet].num_sinks - (num_internal_connections - 1) + 1 + 1 * num_stuck_connections);
}
cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk] += 1 / (float)(vpack_net[inet].num_sinks - num_internal_connections + 1 + 1 * num_stuck_connections);
}
}
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void update_length_gain_values | ( | int | inet, |
| int | clustered_block, | ||
| t_pb * | cur_pb, | ||
| enum e_net_relation_to_clustered_block | net_relation_to_clustered_block | ||
| ) | [static] |
This function is called when the length_gain values on the vpack_net inet requires updating.
Definition at line 1510 of file cluster.c.
{
float lengain;
int newblk, ifirst;
int iblk, ipin;
/* Check if this vpack_net lists its driving logical_block twice. If so, avoid *
* double counting this logical_block by skipping the first (driving) pin. */
if (net_output_feeds_driving_block_input[inet] == FALSE)
ifirst = 0;
else
ifirst = 1;
if (net_relation_to_clustered_block == OUTPUT && !vpack_net[inet].is_global){
for (ipin=ifirst; ipin <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) {
iblk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[ipin];
if (logical_block[iblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
lengain=net_pin_backward_criticality[inet][ipin];
if (lengain>cur_pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[iblk])
cur_pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[iblk]=lengain;
}
}
}
if(net_relation_to_clustered_block == INPUT && !vpack_net[inet].is_global){
/*Calculate the length gain for the logical_block which is driving *
*the vpack_net that is an input to a logical_block in the cluster */
newblk = vpack_net[inet].node_block[0];
if (logical_block[newblk].clb_index == NO_CLUSTER) {
for (ipin=1; ipin <= vpack_net[inet].num_sinks; ipin++) {
lengain=net_pin_forward_criticality[inet][ipin];
if (lengain>cur_pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[newblk])
cur_pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[newblk]=lengain;
}
}
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| static void update_total_gain | ( | float | alpha, |
| float | beta, | ||
| boolean | timing_driven, | ||
| boolean | connection_driven, | ||
| boolean | global_clocks, | ||
| t_pb * | pb | ||
| ) | [static] |
Updates the total gain array to reflect the desired tradeoff between input sharing (sharinggain) and path_length minimization (lengthgain)
Definition at line 1625 of file cluster.c.
{
int i, iblk, j, k;
t_pb * cur_pb;
int num_input_pins, num_output_pins;
int num_used_input_pins, num_used_output_pins;
t_model_ports *port;
cur_pb = pb;
while(cur_pb) {
for (i=0;i<cur_pb->pb_stats.num_marked_blocks;i++) {
iblk=cur_pb->pb_stats.marked_blocks[i];
/* Todo: This was used to explore different normalization options, can be made more efficient once we decide on which one to use*/
num_input_pins = 0;
port = logical_block[iblk].model->inputs;
j =0;
num_used_input_pins = 0;
while(port) {
num_input_pins += port->size;
if(!port->is_clock) {
for(k = 0; k < port->size; k++) {
if(logical_block[iblk].input_nets[j][k] != OPEN) {
num_used_input_pins++;
}
}
j++;
}
port = port->next;
}
if(num_input_pins == 0) {
num_input_pins = 1;
}
num_used_output_pins = 0;
j = 0;
num_output_pins = 0;
port = logical_block[iblk].model->outputs;
while(port) {
num_output_pins += port->size;
for(k = 0; k < port->size; k++) {
if(logical_block[iblk].output_nets[j][k] != OPEN) {
num_used_output_pins++;
}
}
port = port->next;
j++;
}
/* end todo */
/* Calculate area-only cost function */
if (connection_driven) {
/*try to absorb as many connections as possible*/
/* TODO: change back to used pins when done testing */
cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] = ((1-beta)*(float)cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk] + beta*(float)cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk])/(num_input_pins + num_output_pins);
/* cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] = ((1-beta)*(float)cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk] + beta*(float)cur_pb->pb_stats.connectiongain[iblk])/(num_used_input_pins + num_used_output_pins); */
} else {
/*cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] = ((float)cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk])/(num_used_input_pins + num_used_output_pins); */
cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] = ((float)cur_pb->pb_stats.sharinggain[iblk])/(num_input_pins + num_output_pins);
}
/* Add in timing driven cost into cost function */
if (timing_driven) {
cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk] = alpha*cur_pb->pb_stats.lengthgain[iblk] + (1.0-alpha)*(float)cur_pb->pb_stats.gain[iblk];
}
}
cur_pb = cur_pb->parent_pb;
}
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Variable Documentation
float* criticality = NULL [static] |
int* critindexarray = NULL [static] |
int hack_force_safe_latch [static] |
int hack_frac_lut_no_legality [static] |
int indexofcrit [static] |
struct s_ilink* memory_pool [static] |
int* net_output_feeds_driving_block_input [static] |
Does the logical_block that drives the output of this vpack_net also appear as a receiver (input) pin of the vpack_net? [0..num_logical_nets-1]. If so, then by how much? This is used in the gain routines to avoid double counting the connections from the current cluster to other blocks (hence yielding better clusterings). The only time a logical_block should connect to the same vpack_net twice is when one connection is an output and the other is an input, so this should take care of all multiple connections.
float** net_pin_backward_criticality = NULL [static] |
float** net_pin_forward_criticality = NULL [static] |
struct s_ilink* unclustered_list_head [static] |
Keeps a linked list of the unclustered blocks to speed up looking for unclustered blocks with a certain number of *external* inputs. [0..lut_size]. Unclustered_list_head[i] points to the head of the list of blocks with i inputs to be hooked up via external interconnect.