Model Parameters
Model parameter extractions are based on the concept that, under steady-state conditions, specific sets of parameters uniquely simulate device performance. This allows extractions to be performed over isolated regions of the device's electrical response.
Forward and reverse DC bias extractions and junction capacitance characteristics are virtually independent of each other. Series resistance and small-signal high-frequency extractions depend on DC and capacitance parameters.
Model parameter extractions produce parameters that are referenced to a temperature of 27°C. To perform extractions at other temperatures, change the system variable TEMP to the correct value.
The following table provides definitions and SPICE default values of the bipolar model parameters, which fall into four primary categories: DC, capacitance, AC, and temperature effects. DC parameters are divided into three categories: DC forward, DC reverse, and series resistance. The parameter values are displayed in the Model Parameters folder.
Table 82 lists setup attributes.
Table 81 UCB Bipolar Transistor Parameters
|
|
|
DC Large Signal Forward Bias
|
BF
|
Ideal Maximum Forward Beta. Basic parameter for Ebers-Moll and Gummel-Poon models.
|
100
|
IKF
|
Knee Current for Forward Beta High Current Roll-off. Models variation in forward Beta at high collector currents. Use if device is to be used with high collector currents.
|
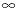 Amp Amp
|
IS
|
Transport Saturation Current. Basic parameter for Ebers-Moll and Gummel-Poon models.
|
1×10-16 Amp
|
ISE
|
Base Emitter Leakage Saturation Current. Models variation in forward Beta at low base currents. Use if device is to be used with low base emitter voltage.
|
0 Amp
|
NE
|
Base Emitter Leakage Emission Coefficient. Models variation in forward Beta at low base currents. Use if device is to be used with low base emitter voltage.
|
1.5
|
NF
|
Forward Current Emission Coefficient. Used to model deviation of emitter base diode from ideal (usually approximately 1).
|
1.0
|
VAF
|
Forward Early Voltage. Models base collector bias effects. Used to model base collector bias on forward Beta and IS.
|
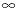 volt volt
|
DC Large Signal Reverse Bias
|
BR
|
Ideal Maximum Reverse Beta. The basic parameter for both Ebers-Moll and Gummel-Poon models. Use when the transistor is saturated or operating in reverse mode.
|
1.0
|
IKR
|
Knee Current for Reverse Beta High Current Roll-off. Specifies variation in reverse Beta at high emitter currents. Needed only if transistor is operated in reverse mode.
|
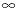 Amp Amp
|
ISC
|
Base Collector Leakage Saturation Current. Specifies variation in reverse Beta at low base currents. Models base current at low base collector voltage. Use only if transistor is operated in reverse mode.
|
0 Amp
|
NC
|
Base Collector Leakage Emission Coefficient. Specifies variation in reverse Beta at low currents. Models base current at low base collector voltage. Use only if transistor is operated in reverse mode.
|
2.0
|
NR
|
Reverse Current Emission Coefficient. Used to model deviation of base collector diode from the ideal (usually about 1).
|
1.0
|
VAR
|
Reverse Early Voltage. Models emitter base bias effects. Use to model emitter base bias on reverse Beta and IS.
|
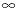 Volt Volt
|
Series Resistance
|
IRB
|
Base Resistance Roll-off Current. Models the base current at which the base resistance is halfway between minimum and maximum.
|
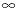 Amp Amp
|
RB
|
Zero Bias Base Resistance. Maximum value of parasitic resistance in base.
|
0 Ohm
|
RBM
|
Minimum Base Resistance. The minimum value of base resistance at high current levels. Models the way base resistance varies as base current varies.
|
RB Ohm
|
RC
|
Collector Resistance. Parasitic resistance in the collector. Important in high current and high frequency applications.
|
0 Ohm
|
RE
|
Emitter Resistance. Parasitic resistance in the emitter. Important in small signal applications.
|
0 Ohm
|
Capacitance
|
CJC
|
Base Collector Zero Bias Capacitance. Helps model switching time and high frequency effects.
|
0 Farad
|
CJE
|
Base Emitter Zero Bias Capacitance. Helps model switching time and high frequency effects.
|
0 Farad
|
CJS
|
Zero Bias Substrate Capacitance. Helps model switching time and high frequency effects.
|
0 Farad
|
MJC
|
Base Collector Junction Grading Coefficient. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.33
|
MJE
|
Base Emitter Junction Grading Coefficient. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.33
|
MJS
|
Substrate Junction Grading Coefficient. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.33
|
VJC
|
Base Collector Built-in Potential. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.75 Volt
|
VJE
|
Base Emitter Built-in Potential. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.75 Volt
|
VJS
|
Substrate Junction Built-in Potential. Models the way junction capacitance varies with bias.
|
0.75 Volt
|
XCJC
|
Fraction of Base Collector. Capacitance that connects to the internal base node. Important in high frequency applications.
|
1.0
|
FC
|
Coefficient for Forward Bias Capacitance Formula. Provides continuity between capacitance equations for forward and reverse bias.
|
0.5
|
AC Small-Signal
|
ITF
|
High Current Parameter for Effect on TF. Models decline of TF with high collector current.
|
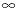 Amp Amp
|
PTF
|
Excess Phase at FT. Models excess phase at FT.
|
0 Degree
|
TF
|
Ideal Forward Transit Time. Models finite bandwidth of device in forward mode.
|
0 Sec
|
TR
|
Ideal Reverse Transit Time. Models finite bandwidth of device in reverse mode.
|
0 Sec
|
VTF
|
Voltage Describing TF Dependence on Base-Collector Voltage. Models base-collector voltage bias effects on TF.
|
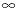 Volt Volt
|
XTF
|
Coefficient for Bias Dependence on TF. Models minimum value of TF at low collector-emitter voltage and high collector current.
|
0
|
Temperature Effects
|
EG
|
Energy Gap for Modeling Temperature. Effect on IS, ISE, and ISC. Used to calculate the temperature variation of saturation currents in the collector, and base-emitter and collector base diodes.
|
1.11EV
|
XTB
|
Forward and Reverse Beta Temperature Exponent. Models the way Beta varies with temperature.
|
0
|
XTI
|
Temperature Exponent for Modeling. Temperature Variation of IS. Models the way saturation current varies with temperature.
|
3.0
|
TNOM
|
This global variable can be assigned temperature values in degrees C, for use by extractions and simulations.
|
27°C
|
Table 82 UCB Bipolar Model Setup Attributes
|
|
|
|
|
|
dc/
fearly
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ic
|
none
|
none
|
VAF (from rearly setup)
|
dc/
rearly
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ie
|
evextract
|
BJTDC_vaf_var
|
VAF, VAR
|
dc/
fgummel
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ib, ic
|
beta
|
equation: ic/ib
|
none
|
isextract
|
BJTDC_is_nf
|
IS, NF
|
fgextract
|
BJTDC_fwd_gummel
|
BF, IKF, ISE, NE
|
optim1
|
Optimize
|
IS, NF
|
optim2
|
Optimize
|
BF, IKF, ISE, NE
|
dc/
rgummel
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ib, ie
|
beta
|
equation: ie/ib
|
none
|
nrextract
|
BJTDC_nr
|
NR
|
rgextract
|
BJTDC_rev_gummel
|
BR, IKR, ISC, NC
|
optimize
|
Optimize
|
BR, IKR, ISC, NC
|
cbe/
cj
|
vbe
|
cbe
|
extract
|
Optimize
|
CJE, VJE, MJE
|
cjfunc
|
PNCAPsimu
|
none: simulates c vs v
|
set_CJ
|
Program
|
initial zero bias CJE
|
cbc/
cj
|
vbc
|
cbc
|
extract
|
Optimize
|
CJC, VJC, MJC
|
cjfunc
|
PNCAPsimu
|
none: simulates c vs v
|
set_CJ
|
Program
|
initial zero bias CJC
|
ccs/
cj
|
vcs
|
ccs
|
extract
|
Optimize
|
CJS, VJS, MJS
|
cjfunc
|
PNCAPsimu
|
none: simulates c vs v
|
set_CJ
|
Program
|
initial zero bias CJS
|
prdc/
reflyback
|
ib, ic, ve, is
|
vc
|
extract
|
BJTDC_re
|
RE
|
prdc/
rcsat
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ic
|
extract
|
BJTDC_rc
|
RC (saturation)
|
prdc/
rcactive
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ib,ic
|
RC_active
|
Program
|
RC (active)
|
prdc/
rbbib
|
vb, vc, ve, vs
|
ib
|
rbb
|
RBBcalc
|
none: calc rb vs ib
|
ac/
rbbac
|
vb, vc, ve, vs, freq
|
h
|
extract
|
BJTAC_rb_rbm_irb
|
RB, RBM, IRB
|
h11corr
|
H11corr
|
corrects H11 for Zout
|
htos
|
TwoPort
|
none: h-par to s-par
|
ac/
h21vsvbe
|
vb, vc, ve, vs, freq
|
h
|
acextract
|
BJTAC_high_freq
|
TF, ITF, XTF, VTF, PTF
|
scale_params
|
Program
|
none: scales AC parameters
|
ac/
h21vsvbc
|
vb, vc, ve, vs, freq
|
h
|
extract_TR
|
Optimize
|
TR
|
|
 Amp
Amp