SRC/net_delay.c File Reference
#include <stdio.h>#include "util.h"#include "vpr_types.h"#include "globals.h"#include "net_delay.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | s_linked_rc_edge |
| struct | s_rc_node |
| struct | s_linked_rc_ptr |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct s_linked_rc_edge | t_linked_rc_edge |
| typedef struct s_rc_node | t_rc_node |
| typedef struct s_linked_rc_ptr | t_linked_rc_ptr |
Functions | |
| static t_rc_node * | alloc_and_load_rc_tree (int inet, t_rc_node **rc_node_free_list_ptr, t_linked_rc_edge **rc_edge_free_list_ptr, t_linked_rc_ptr *rr_node_to_rc_node) |
| static void | add_to_rc_tree (t_rc_node *parent_rc, t_rc_node *child_rc, short iswitch, int inode, t_linked_rc_edge **rc_edge_free_list_ptr) |
| static t_rc_node * | alloc_rc_node (t_rc_node **rc_node_free_list_ptr) |
| static void | free_rc_node (t_rc_node *rc_node, t_rc_node **rc_node_free_list_ptr) |
| static t_linked_rc_edge * | alloc_linked_rc_edge (t_linked_rc_edge **rc_edge_free_list_ptr) |
| static void | free_linked_rc_edge (t_linked_rc_edge *rc_edge, t_linked_rc_edge **rc_edge_free_list_ptr) |
| static float | load_rc_tree_C (t_rc_node *rc_node) |
| static void | load_rc_tree_T (t_rc_node *rc_node, float T_arrival) |
| static void | load_one_net_delay (float **net_delay, int inet, t_linked_rc_ptr *rr_node_to_rc_node) |
| static void | load_one_constant_net_delay (float **net_delay, int inet, float delay_value) |
| static void | free_rc_tree (t_rc_node *rc_root, t_rc_node **rc_node_free_list_ptr, t_linked_rc_edge **rc_edge_free_list_ptr) |
| static void | reset_rr_node_to_rc_node (t_linked_rc_ptr *rr_node_to_rc_node, int inet) |
| static void | free_rc_node_free_list (t_rc_node *rc_node_free_list) |
| static void | free_rc_edge_free_list (t_linked_rc_edge *rc_edge_free_list) |
| float ** | alloc_net_delay (struct s_linked_vptr **chunk_list_head_ptr) |
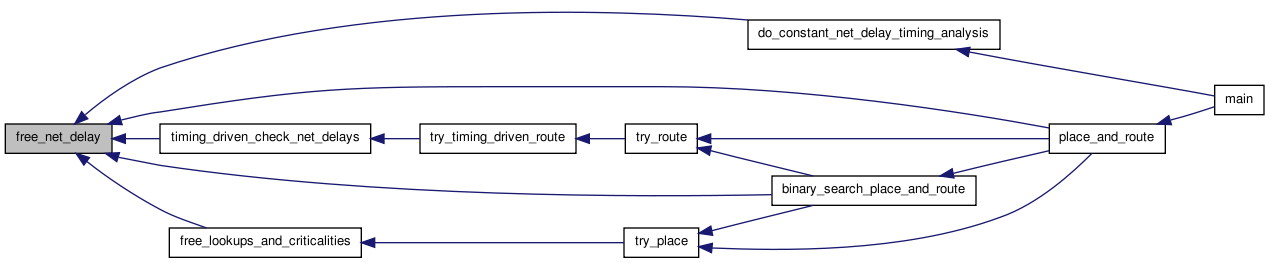
| void | free_net_delay (float **net_delay, struct s_linked_vptr **chunk_list_head_ptr) |
| void | load_net_delay_from_routing (float **net_delay) |
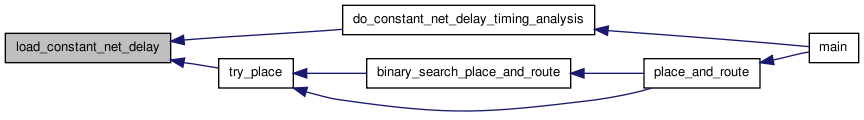
| void | load_constant_net_delay (float **net_delay, float delay_value) |
| void | print_net_delay (float **net_delay, char *fname) |
Typedef Documentation
| typedef struct s_linked_rc_edge t_linked_rc_edge |
Definition at line 17 of file net_delay.c.
| typedef struct s_linked_rc_ptr t_linked_rc_ptr |
Definition at line 61 of file net_delay.c.
Definition at line 40 of file net_delay.c.
Function Documentation
| static void add_to_rc_tree | ( | t_rc_node * | parent_rc, | |
| t_rc_node * | child_rc, | |||
| short | iswitch, | |||
| int | inode, | |||
| t_linked_rc_edge ** | rc_edge_free_list_ptr | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 346 of file net_delay.c.
00351 { 00352 00353 /* Adds child_rc to the child list of parent_rc, and sets the switch between * 00354 * them to iswitch. This routine also intitializes the child_rc properly * 00355 * and sets its node value to inode. */ 00356 00357 t_linked_rc_edge *linked_rc_edge; 00358 00359 linked_rc_edge = alloc_linked_rc_edge(rc_edge_free_list_ptr); 00360 00361 linked_rc_edge->next = parent_rc->u.child_list; 00362 parent_rc->u.child_list = linked_rc_edge; 00363 00364 linked_rc_edge->child = child_rc; 00365 linked_rc_edge->iswitch = iswitch; 00366 00367 child_rc->u.child_list = NULL; 00368 child_rc->inode = inode; 00369 }


| static t_rc_node * alloc_and_load_rc_tree | ( | int | inet, | |
| t_rc_node ** | rc_node_free_list_ptr, | |||
| t_linked_rc_edge ** | rc_edge_free_list_ptr, | |||
| t_linked_rc_ptr * | rr_node_to_rc_node | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 247 of file net_delay.c.
00251 { 00252 00253 /* Builds a tree describing the routing of net inet. Allocates all the data * 00254 * and inserts all the connections in the tree. */ 00255 00256 t_rc_node *curr_rc, *prev_rc, *root_rc; 00257 struct s_trace *tptr; 00258 int inode, prev_node; 00259 short iswitch; 00260 t_linked_rc_ptr *linked_rc_ptr; 00261 00262 root_rc = alloc_rc_node(rc_node_free_list_ptr); 00263 tptr = trace_head[inet]; 00264 00265 if(tptr == NULL) 00266 { 00267 printf 00268 ("Error in alloc_and_load_rc_tree: Traceback for net %d doesn't " 00269 "exist.\n", inet); 00270 exit(1); 00271 } 00272 00273 inode = tptr->index; 00274 iswitch = tptr->iswitch; 00275 root_rc->inode = inode; 00276 root_rc->u.child_list = NULL; 00277 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node = root_rc; 00278 00279 prev_rc = root_rc; 00280 tptr = tptr->next; 00281 00282 while(tptr != NULL) 00283 { 00284 inode = tptr->index; 00285 00286 /* Is this node a "stitch-in" point to part of the existing routing or a * 00287 * new piece of routing along the current routing "arm?" */ 00288 00289 if(rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node == NULL) 00290 { /* Part of current "arm" */ 00291 curr_rc = alloc_rc_node(rc_node_free_list_ptr); 00292 add_to_rc_tree(prev_rc, curr_rc, iswitch, inode, 00293 rc_edge_free_list_ptr); 00294 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node = curr_rc; 00295 prev_rc = curr_rc; 00296 } 00297 00298 else if(rr_node[inode].type != SINK) 00299 { /* Connection to old stuff. */ 00300 00301 #ifdef DEBUG 00302 prev_node = prev_rc->inode; 00303 if(rr_node[prev_node].type != SINK) 00304 { 00305 printf 00306 ("Error in alloc_and_load_rc_tree: Routing of net %d is " 00307 "not a tree.\n", inet); 00308 exit(1); 00309 } 00310 #endif 00311 00312 prev_rc = rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node; 00313 } 00314 00315 else 00316 { /* SINK that this net has connected to more than once. */ 00317 00318 /* I can connect to a SINK node more than once in some weird architectures. * 00319 * That means the routing isn't really a tree -- there is reconvergent * 00320 * fanout from two or more IPINs into one SINK. I convert this structure * 00321 * into a true RC tree on the fly by creating a new rc_node each time I hit * 00322 * the same sink. This means I need to keep a linked list of the rc_nodes * 00323 * associated with the rr_node (inode) associated with that SINK. */ 00324 00325 curr_rc = alloc_rc_node(rc_node_free_list_ptr); 00326 add_to_rc_tree(prev_rc, curr_rc, iswitch, inode, 00327 rc_edge_free_list_ptr); 00328 00329 linked_rc_ptr = (t_linked_rc_ptr *) 00330 my_malloc(sizeof(t_linked_rc_ptr)); 00331 linked_rc_ptr->next = rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].next; 00332 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].next = linked_rc_ptr; 00333 linked_rc_ptr->rc_node = curr_rc; 00334 00335 prev_rc = curr_rc; 00336 } 00337 iswitch = tptr->iswitch; 00338 tptr = tptr->next; 00339 } 00340 00341 return (root_rc); 00342 }

| static t_linked_rc_edge * alloc_linked_rc_edge | ( | t_linked_rc_edge ** | rc_edge_free_list_ptr | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 409 of file net_delay.c.
00410 { 00411 00412 /* Allocates a new linked_rc_edge, from the free list if possible, from the * 00413 * free store otherwise. */ 00414 00415 t_linked_rc_edge *linked_rc_edge; 00416 00417 linked_rc_edge = *rc_edge_free_list_ptr; 00418 00419 if(linked_rc_edge != NULL) 00420 { 00421 *rc_edge_free_list_ptr = linked_rc_edge->next; 00422 } 00423 else 00424 { 00425 linked_rc_edge = (t_linked_rc_edge *) my_malloc(sizeof 00426 (t_linked_rc_edge)); 00427 } 00428 00429 return (linked_rc_edge); 00430 }


| float** alloc_net_delay | ( | struct s_linked_vptr ** | chunk_list_head_ptr | ) |
Definition at line 125 of file net_delay.c.
00126 { 00127 00128 /* Allocates space for the net_delay data structure * 00129 * [0..num_nets-1][1..num_pins-1]. I chunk the data to save space on large * 00130 * problems. */ 00131 00132 float **net_delay; /* [0..num_nets-1][1..num_pins-1] */ 00133 float *tmp_ptr; 00134 int inet; 00135 int chunk_bytes_avail; 00136 char *chunk_next_avail_mem; 00137 00138 *chunk_list_head_ptr = NULL; 00139 chunk_bytes_avail = 0; 00140 chunk_next_avail_mem = NULL; 00141 00142 net_delay = (float **)my_malloc(num_nets * sizeof(float *)); 00143 00144 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00145 { 00146 tmp_ptr = 00147 (float *)my_chunk_malloc(((net[inet].num_sinks + 1) - 1) * 00148 sizeof(float), chunk_list_head_ptr, 00149 &chunk_bytes_avail, 00150 &chunk_next_avail_mem); 00151 00152 net_delay[inet] = tmp_ptr - 1; /* [1..num_pins-1] */ 00153 } 00154 00155 return (net_delay); 00156 }

Definition at line 373 of file net_delay.c.
00374 { 00375 00376 /* Allocates a new rc_node, from the free list if possible, from the free * 00377 * store otherwise. */ 00378 00379 t_rc_node *rc_node; 00380 00381 rc_node = *rc_node_free_list_ptr; 00382 00383 if(rc_node != NULL) 00384 { 00385 *rc_node_free_list_ptr = rc_node->u.next; 00386 } 00387 else 00388 { 00389 rc_node = (t_rc_node *) my_malloc(sizeof(t_rc_node)); 00390 } 00391 00392 return (rc_node); 00393 }

| static void free_linked_rc_edge | ( | t_linked_rc_edge * | rc_edge, | |
| t_linked_rc_edge ** | rc_edge_free_list_ptr | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 434 of file net_delay.c.
00436 { 00437 00438 /* Adds the rc_edge to the rc_edge free list. */ 00439 00440 rc_edge->next = *rc_edge_free_list_ptr; 00441 *rc_edge_free_list_ptr = rc_edge; 00442 }

| void free_net_delay | ( | float ** | net_delay, | |
| struct s_linked_vptr ** | chunk_list_head_ptr | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 160 of file net_delay.c.
00162 { 00163 00164 /* Frees the net_delay structure. Assumes it was chunk allocated. */ 00165 00166 free(net_delay); 00167 free_chunk_memory(*chunk_list_head_ptr); 00168 *chunk_list_head_ptr = NULL; 00169 }

| static void free_rc_edge_free_list | ( | t_linked_rc_edge * | rc_edge_free_list | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 685 of file net_delay.c.
00686 { 00687 00688 /* Really frees (i.e. calls free()) all the rc_edges on the free list. */ 00689 00690 t_linked_rc_edge *rc_edge, *next_edge; 00691 00692 rc_edge = rc_edge_free_list; 00693 00694 while(rc_edge != NULL) 00695 { 00696 next_edge = rc_edge->next; 00697 free(rc_edge); 00698 rc_edge = next_edge; 00699 } 00700 }

Definition at line 397 of file net_delay.c.
00399 { 00400 00401 /* Adds rc_node to the proper free list. */ 00402 00403 rc_node->u.next = *rc_node_free_list_ptr; 00404 *rc_node_free_list_ptr = rc_node; 00405 }

| static void free_rc_node_free_list | ( | t_rc_node * | rc_node_free_list | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 665 of file net_delay.c.
00666 { 00667 00668 /* Really frees (i.e. calls free()) all the rc_nodes on the free list. */ 00669 00670 t_rc_node *rc_node, *next_node; 00671 00672 rc_node = rc_node_free_list; 00673 00674 while(rc_node != NULL) 00675 { 00676 next_node = rc_node->u.next; 00677 free(rc_node); 00678 rc_node = next_node; 00679 } 00680 }

| static void free_rc_tree | ( | t_rc_node * | rc_root, | |
| t_rc_node ** | rc_node_free_list_ptr, | |||
| t_linked_rc_edge ** | rc_edge_free_list_ptr | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 612 of file net_delay.c.
00615 { 00616 00617 /* Puts the rc tree pointed to by rc_root back on the free list. Depth- * 00618 * first post-order traversal via recursion. */ 00619 00620 t_rc_node *rc_node, *child_node; 00621 t_linked_rc_edge *rc_edge, *next_edge; 00622 00623 rc_node = rc_root; 00624 rc_edge = rc_node->u.child_list; 00625 00626 while(rc_edge != NULL) 00627 { /* For all children */ 00628 child_node = rc_edge->child; 00629 free_rc_tree(child_node, rc_node_free_list_ptr, 00630 rc_edge_free_list_ptr); 00631 next_edge = rc_edge->next; 00632 free_linked_rc_edge(rc_edge, rc_edge_free_list_ptr); 00633 rc_edge = next_edge; 00634 } 00635 00636 free_rc_node(rc_node, rc_node_free_list_ptr); 00637 }


| void load_constant_net_delay | ( | float ** | net_delay, | |
| float | delay_value | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 221 of file net_delay.c.
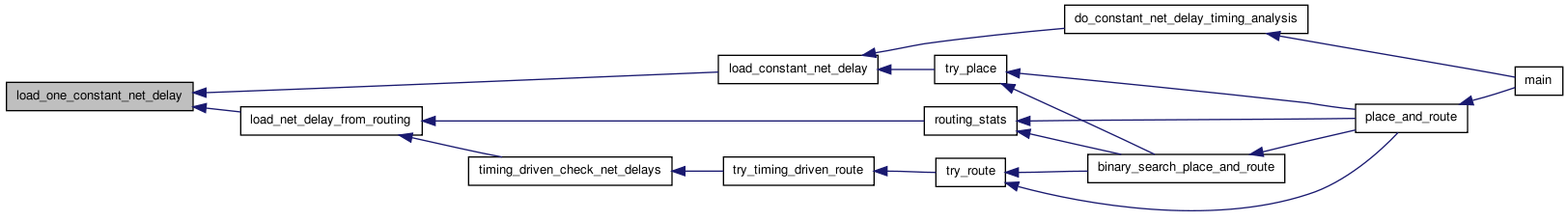
00223 { 00224 00225 /* Loads the net_delay array with delay_value for every source - sink * 00226 * connection that is not on a global resource, and with 0. for every source * 00227 * - sink connection on a global net. (This can be used to allow timing * 00228 * analysis before routing is done with a constant net delay model). */ 00229 00230 int inet; 00231 00232 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00233 { 00234 if(net[inet].is_global) 00235 { 00236 load_one_constant_net_delay(net_delay, inet, 0.); 00237 } 00238 else 00239 { 00240 load_one_constant_net_delay(net_delay, inet, delay_value); 00241 } 00242 } 00243 }

| void load_net_delay_from_routing | ( | float ** | net_delay | ) |
Definition at line 173 of file net_delay.c.
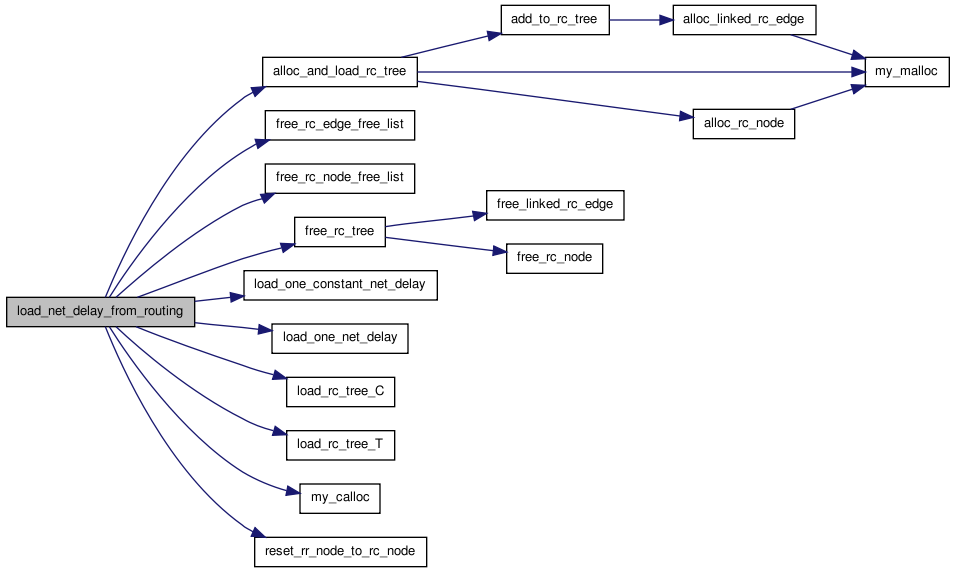
00174 { 00175 00176 /* This routine loads net_delay[0..num_nets-1][1..num_pins-1]. Each entry * 00177 * is the Elmore delay from the net source to the appropriate sink. Both * 00178 * the rr_graph and the routing traceback must be completely constructed * 00179 * before this routine is called, and the net_delay array must have been * 00180 * allocated. */ 00181 00182 t_rc_node *rc_node_free_list, *rc_root; 00183 t_linked_rc_edge *rc_edge_free_list; 00184 int inet; 00185 t_linked_rc_ptr *rr_node_to_rc_node; /* [0..num_rr_nodes-1] */ 00186 00187 rr_node_to_rc_node = (t_linked_rc_ptr *) my_calloc(num_rr_nodes, 00188 sizeof 00189 (t_linked_rc_ptr)); 00190 00191 rc_node_free_list = NULL; 00192 rc_edge_free_list = NULL; 00193 00194 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00195 { 00196 if(net[inet].is_global) 00197 { 00198 load_one_constant_net_delay(net_delay, inet, 0.); 00199 } 00200 else 00201 { 00202 rc_root = alloc_and_load_rc_tree(inet, &rc_node_free_list, 00203 &rc_edge_free_list, 00204 rr_node_to_rc_node); 00205 load_rc_tree_C(rc_root); 00206 load_rc_tree_T(rc_root, 0.); 00207 load_one_net_delay(net_delay, inet, rr_node_to_rc_node); 00208 free_rc_tree(rc_root, &rc_node_free_list, 00209 &rc_edge_free_list); 00210 reset_rr_node_to_rc_node(rr_node_to_rc_node, inet); 00211 } 00212 } 00213 00214 free_rc_node_free_list(rc_node_free_list); 00215 free_rc_edge_free_list(rc_edge_free_list); 00216 free(rr_node_to_rc_node); 00217 }

| static void load_one_constant_net_delay | ( | float ** | net_delay, | |
| int | inet, | |||
| float | delay_value | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 597 of file net_delay.c.
00600 { 00601 00602 /* Sets each entry of the net_delay array for net inet to delay_value. */ 00603 00604 int ipin; 00605 00606 for(ipin = 1; ipin < (net[inet].num_sinks + 1); ipin++) 00607 net_delay[inet][ipin] = delay_value; 00608 }
| static void load_one_net_delay | ( | float ** | net_delay, | |
| int | inet, | |||
| t_linked_rc_ptr * | rr_node_to_rc_node | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 534 of file net_delay.c.
00537 { 00538 00539 /* Loads the net delay array for net inet. The rc tree for that net must * 00540 * have already been completely built and loaded. */ 00541 00542 int ipin, inode; 00543 float Tmax; 00544 t_rc_node *rc_node; 00545 t_linked_rc_ptr *linked_rc_ptr, *next_ptr; 00546 00547 for(ipin = 1; ipin < (net[inet].num_sinks + 1); ipin++) 00548 { 00549 00550 inode = net_rr_terminals[inet][ipin]; 00551 00552 00553 linked_rc_ptr = rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].next; 00554 rc_node = rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node; 00555 Tmax = rc_node->Tdel; 00556 00557 /* If below only executes when one net connects several times to the * 00558 * same SINK. In this case, I can't tell which net pin each connection * 00559 * to this SINK corresponds to (I can just choose arbitrarily). To make * 00560 * sure the timing behaviour converges, I pessimistically set the delay * 00561 * for all of the connections to this SINK by this net to be the max. of * 00562 * the delays from this net to this SINK. NB: This code only occurs * 00563 * when a net connect more than once to the same pin class on the same * 00564 * logic block. Only a weird architecture would allow this. */ 00565 00566 if(linked_rc_ptr != NULL) 00567 { 00568 00569 /* The first time I hit a multiply-used SINK, I choose the largest delay * 00570 * from this net to this SINK and use it for every connection to this * 00571 * SINK by this net. */ 00572 00573 do 00574 { 00575 rc_node = linked_rc_ptr->rc_node; 00576 if(rc_node->Tdel > Tmax) 00577 { 00578 Tmax = rc_node->Tdel; 00579 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node = 00580 rc_node; 00581 } 00582 next_ptr = linked_rc_ptr->next; 00583 free(linked_rc_ptr); 00584 linked_rc_ptr = next_ptr; 00585 } 00586 while(linked_rc_ptr != NULL); /* End do while */ 00587 00588 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].next = NULL; 00589 } 00590 /* End of if multiply-used SINK */ 00591 net_delay[inet][ipin] = Tmax; 00592 } 00593 }

| static float load_rc_tree_C | ( | t_rc_node * | rc_node | ) | [static] |
Definition at line 446 of file net_delay.c.
00447 { 00448 00449 /* Does a post-order traversal of the rc tree to load each node's * 00450 * C_downstream with the proper sum of all the downstream capacitances. * 00451 * This routine calls itself recursively to perform the traversal. */ 00452 00453 t_linked_rc_edge *linked_rc_edge; 00454 t_rc_node *child_node; 00455 int inode; 00456 short iswitch; 00457 float C, C_downstream; 00458 00459 linked_rc_edge = rc_node->u.child_list; 00460 inode = rc_node->inode; 00461 C = rr_node[inode].C; 00462 00463 while(linked_rc_edge != NULL) 00464 { /* For all children */ 00465 iswitch = linked_rc_edge->iswitch; 00466 child_node = linked_rc_edge->child; 00467 C_downstream = load_rc_tree_C(child_node); 00468 00469 if(switch_inf[iswitch].buffered == FALSE) 00470 C += C_downstream; 00471 00472 linked_rc_edge = linked_rc_edge->next; 00473 } 00474 00475 rc_node->C_downstream = C; 00476 return (C); 00477 }

| static void load_rc_tree_T | ( | t_rc_node * | rc_node, | |
| float | T_arrival | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 481 of file net_delay.c.
00483 { 00484 00485 /* This routine does a pre-order depth-first traversal of the rc tree to * 00486 * compute the Tdel to each node in the rc tree. The T_arrival is the time * 00487 * at which the signal hits the input to this node. This routine calls * 00488 * itself recursively to perform the traversal. */ 00489 00490 float Tdel, Rmetal, Tchild; 00491 t_linked_rc_edge *linked_rc_edge; 00492 t_rc_node *child_node; 00493 short iswitch; 00494 int inode; 00495 00496 Tdel = T_arrival; 00497 inode = rc_node->inode; 00498 Rmetal = rr_node[inode].R; 00499 00500 /* NB: rr_node[inode].C gives the capacitance of this node, while * 00501 * rc_node->C_downstream gives the unbuffered downstream capacitance rooted * 00502 * at this node, including the C of the node itself. I want to multiply * 00503 * the C of this node by 0.5 Rmetal, since it's a distributed RC line. * 00504 * Hence 0.5 Rmetal * Cnode is a pessimistic estimate of delay (i.e. end to * 00505 * end). For the downstream capacitance rooted at this node (not including * 00506 * the capacitance of the node itself), I assume it is, on average, * 00507 * connected halfway along the line, so I also multiply by 0.5 Rmetal. To * 00508 * be totally pessimistic I would multiply the downstream part of the * 00509 * capacitance by Rmetal. Play with this equation if you like. */ 00510 00511 /* Rmetal is distributed so x0.5 */ 00512 Tdel += 0.5 * rc_node->C_downstream * Rmetal; 00513 rc_node->Tdel = Tdel; 00514 00515 /* Now expand the children of this node to load their Tdel values. */ 00516 00517 linked_rc_edge = rc_node->u.child_list; 00518 00519 while(linked_rc_edge != NULL) 00520 { /* For all children */ 00521 iswitch = linked_rc_edge->iswitch; 00522 child_node = linked_rc_edge->child; 00523 00524 Tchild = Tdel + switch_inf[iswitch].R * child_node->C_downstream; 00525 Tchild += switch_inf[iswitch].Tdel; /* Intrinsic switch delay. */ 00526 load_rc_tree_T(child_node, Tchild); 00527 00528 linked_rc_edge = linked_rc_edge->next; 00529 } 00530 }

| void print_net_delay | ( | float ** | net_delay, | |
| char * | fname | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 704 of file net_delay.c.
00706 { 00707 00708 /* Dumps the net delays into file fname. */ 00709 00710 FILE *fp; 00711 int inet, ipin; 00712 00713 fp = my_fopen(fname, "w"); 00714 00715 for(inet = 0; inet < num_nets; inet++) 00716 { 00717 fprintf(fp, "Net: %d.\n", inet); 00718 fprintf(fp, "Delays:"); 00719 00720 for(ipin = 1; ipin < (net[inet].num_sinks + 1); ipin++) 00721 fprintf(fp, " %g", net_delay[inet][ipin]); 00722 00723 fprintf(fp, "\n\n"); 00724 } 00725 00726 fclose(fp); 00727 }

| static void reset_rr_node_to_rc_node | ( | t_linked_rc_ptr * | rr_node_to_rc_node, | |
| int | inet | |||
| ) | [static] |
Definition at line 641 of file net_delay.c.
00643 { 00644 00645 /* Resets the rr_node_to_rc_node mapping entries that were set during * 00646 * construction of the RC tree for net inet. Any extra linked list entries * 00647 * added to deal with a SINK being connected to multiple times have already * 00648 * been freed by load_one_net_delay. */ 00649 00650 struct s_trace *tptr; 00651 int inode; 00652 00653 tptr = trace_head[inet]; 00654 00655 while(tptr != NULL) 00656 { 00657 inode = tptr->index; 00658 rr_node_to_rc_node[inode].rc_node = NULL; 00659 tptr = tptr->next; 00660 } 00661 }

 1.6.1
1.6.1