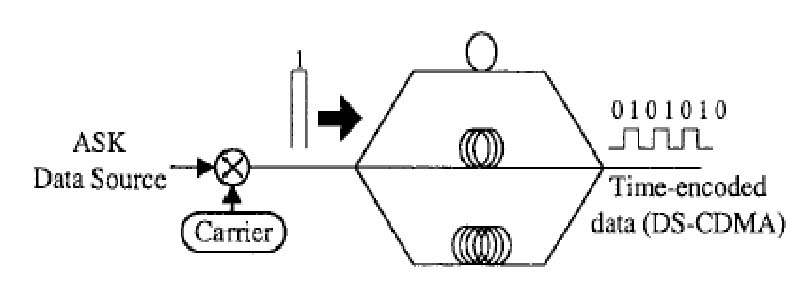
Current Research ProjectCode Division Multiple Access (CDMA) is a technique used to multiplex data streams that are using the same time and frequency spaces. The multiplexing happens by encoding each data stream using a unique codeword called Psudo Random Number (PN) and then at the receiver decode each stream again independently. The ability to separate the different encoded streams at the receiver depends on some properties of the PN codes that allows them to be uniquely decoded at the receiver side. CDMA technique has been mainly applied and considered in wireless communication systems, because of its security and reliability advantages in that medium.
The use of CDMA techniques in optical networks has been in the literature for more than a decade under the name Optical Code Division Multiple Access (OCDMA) or some other variations of the name such as Optical Code Division Multiplexing (OCDM). The main reason that OCDMA has grabbed the attention of researchers in the area of optical transmission is that both encoding and decoding of the transmitted signal can be implemented easily in the optical domain with no need for optical to electrical conversion. Compared to Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) and Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), OCDMA supersedes WDM because of its more flexible granularity, while it has the advantage over TDM because it can be all optically implemented. Our research will aim at further studying the applications of CDMA techniques in the optical network domain to enhance the reliability of the medium and increase its capacity and ability to meet QoS requirements. |