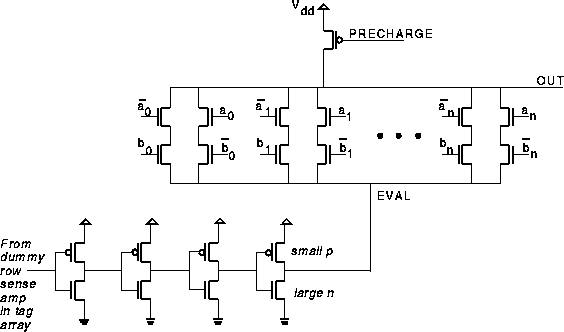
Figure 5: Comparator
Although Wada's model gives access times for set-associative caches, it only models the data portion of a set-associative memory. However, the tag portion of a set-associative memory is often the critical path. Our model assumes the tag memory array circuits are similar to those on the data side with the addition of comparators to choose between different sets.
The comparator that was modeled is shown in Figure 5. The
outputs from the sense amplifiers are connected to the inputs labeled
![]() and
and ![]() -bar. The
-bar. The ![]() and
and
![]() -bar inputs are driven by tag bits in the address. Initially,
the output of the comparator is precharged high; a mismatch in any bit will
close one pull-down path and discharge the output. In order to ensure that
the output is not discharged before the
-bar inputs are driven by tag bits in the address. Initially,
the output of the comparator is precharged high; a mismatch in any bit will
close one pull-down path and discharge the output. In order to ensure that
the output is not discharged before the ![]() bits become stable,
node EVAL is held high until roughly three inverter delays after the
generation of the
bits become stable,
node EVAL is held high until roughly three inverter delays after the
generation of the ![]() -bar signals. This is accomplished
by using a timing chain driven by a sense amp on a dummy row in the tag array.
The output of the timing chain is used as a ``virtual ground''
for the pull-down paths of the comparator.
When the large NMOS transistor in the final inverter in the timing chain
begins to conduct, the virtual ground (and hence the comparator output
if there is a mismatch) begins to discharge.
-bar signals. This is accomplished
by using a timing chain driven by a sense amp on a dummy row in the tag array.
The output of the timing chain is used as a ``virtual ground''
for the pull-down paths of the comparator.
When the large NMOS transistor in the final inverter in the timing chain
begins to conduct, the virtual ground (and hence the comparator output
if there is a mismatch) begins to discharge.