vpr/SRC/util/hash.h File Reference
 This graph shows which files directly or indirectly include this file:
This graph shows which files directly or indirectly include this file:Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | s_hash |
| struct | s_hash_iterator |
Functions | |
| struct s_hash ** | alloc_hash_table (void) |
| void | free_hash_table (struct s_hash **hash_table) |
| struct s_hash_iterator | start_hash_table_iterator (void) |
| struct s_hash * | get_next_hash (struct s_hash **hash_table, struct s_hash_iterator *hash_iterator) |
| struct s_hash * | insert_in_hash_table (struct s_hash **hash_table, char *name, int next_free_index) |
| struct s_hash * | get_hash_entry (struct s_hash **hash_table, char *name) |
Function Documentation
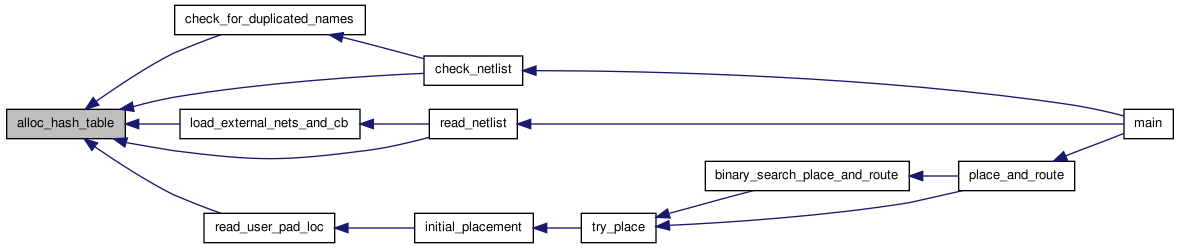
| struct s_hash** alloc_hash_table | ( | void | ) | [read] |
Creates a hash table with HASHSIZE different locations (hash values).
Definition at line 14 of file hash.c.
{
struct s_hash **hash_table;
hash_table = (struct s_hash **)my_calloc(sizeof(struct s_hash *),
HASHSIZE);
return (hash_table);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
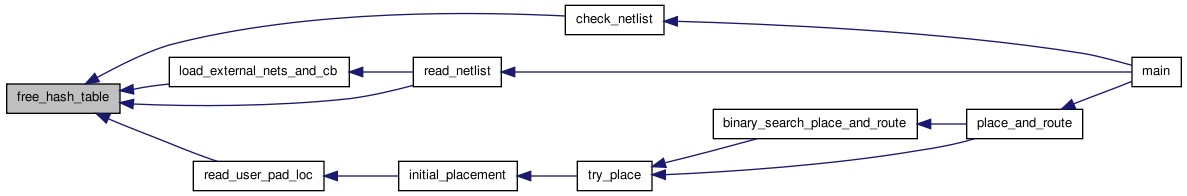
Here is the caller graph for this function:| void free_hash_table | ( | struct s_hash ** | hash_table | ) |
Frees all the storage associated with a hash table.
Definition at line 26 of file hash.c.
{
int i;
struct s_hash *h_ptr, *temp_ptr;
for(i = 0; i < HASHSIZE; i++)
{
h_ptr = hash_table[i];
while(h_ptr != NULL)
{
free(h_ptr->name);
temp_ptr = h_ptr->next;
free(h_ptr);
h_ptr = temp_ptr;
}
}
free(hash_table);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:Returns the hash entry with this name, or NULL if there is no corresponding entry.
Definition at line 142 of file hash.c.
{
int i;
struct s_hash *h_ptr;
i = hash_value(name);
h_ptr = hash_table[i];
while(h_ptr != NULL)
{
if(strcmp(h_ptr->name, name) == 0)
return (h_ptr);
h_ptr = h_ptr->next;
}
return (NULL);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| struct s_hash* get_next_hash | ( | struct s_hash ** | hash_table, |
| struct s_hash_iterator * | hash_iterator | ||
| ) | [read] |
Returns the next occupied hash entry, and moves the iterator structure forward so the next call gets the next entry.
Definition at line 64 of file hash.c.
{
int i;
struct s_hash *h_ptr;
i = hash_iterator->i;
h_ptr = hash_iterator->h_ptr;
while(h_ptr == NULL)
{
i++;
if(i >= HASHSIZE)
return (NULL); /* End of table */
h_ptr = hash_table[i];
}
hash_iterator->h_ptr = h_ptr->next;
hash_iterator->i = i;
return (h_ptr);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
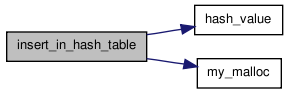
Here is the caller graph for this function:| struct s_hash* insert_in_hash_table | ( | struct s_hash ** | hash_table, |
| char * | name, | ||
| int | next_free_index | ||
| ) | [read] |
Adds the string pointed to by name to the hash table, and returns the hash structure created or updated. If name is already in the hash table the count member of that hash element is incremented. Otherwise a new hash entry with a count of zero and an index of next_free_index is created.
Definition at line 95 of file hash.c.
{
int i;
struct s_hash *h_ptr, *prev_ptr;
i = hash_value(name);
prev_ptr = NULL;
h_ptr = hash_table[i];
while(h_ptr != NULL)
{
if(strcmp(h_ptr->name, name) == 0)
{
h_ptr->count++;
return (h_ptr);
}
prev_ptr = h_ptr;
h_ptr = h_ptr->next;
}
/* Name string wasn't in the hash table. Add it. */
h_ptr = (struct s_hash *)my_malloc(sizeof(struct s_hash));
if(prev_ptr == NULL)
{
hash_table[i] = h_ptr;
}
else
{
prev_ptr->next = h_ptr;
}
h_ptr->next = NULL;
h_ptr->index = next_free_index;
h_ptr->count = 1;
h_ptr->name = (char *)my_malloc((strlen(name) + 1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(h_ptr->name, name);
return (h_ptr);
}
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:| struct s_hash_iterator start_hash_table_iterator | ( | void | ) | [read] |
Call this routine before you start going through all the elements in a hash table. It sets the internal indices to the start of the table.
Definition at line 51 of file hash.c.
{
struct s_hash_iterator hash_iterator;
hash_iterator.i = -1;
hash_iterator.h_ptr = NULL;
return (hash_iterator);
}
 Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function: