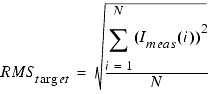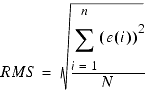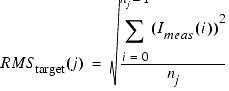Print version of this Book (PDF file)
RMS Error Definition
The error ej(i) can be absolute or relative (see Relative/Absolute Error Formulation). In both cases, the error is either zero or a positive value.
When multiple inputs are defined in the input table, the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm uses one single array of points. When choosing absolute error formulation, the error terms e(i) are normalized using the RMS of all the target points:
The absolute error term used by the Levenberg -Marquardt optimizer becomes:
In optimizers other that the Levenberg-Marquardt, when selecting absolute error, the error term uses different normalizing factors, called RMStarget (j), for each input column on the Inputs page.
These normalizing factors are calculated using the target data sets related to each input column on the Inputs page. The RMS error is calculated as shown:
- where
- j is the target index (or column on the Inputs page)
- nj is the number of points of the j-th input.
- j is the target index (or column on the Inputs page)
For a definition of the RMSerror function, see Chapter 8, "IC-CAP Functions" in the Reference manual.